Gravitation
Get insights from 91 questions on Gravitation, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Gravitation
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Explanation- examples of central force – gravitational force and electrostatic force
Examples of non central force = nuclear force, magnetic force acting between two current carrying loops etc.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-air molecules in the atmosphere are attracted vertically downward by the gravitational force of the earth just like an apple falling from the tree. Air molecules move randomly due to their thermal velocity and hence resultant motion of air molecules move randomly in vertical downward direction. But in case of apple it is heavier than air so it fall downwards only.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- rp= radius of perihelion =2R
Ra = radius of aphelion =6R
So ra=a(1+e)=6R
And rp= a(1-e)=2R
Solving above eqns
We get e = ½
By conservation of angular momentum angular momentum at perigee= angular momentum at apogee
So mvprp=mvara
Va/vp=1/3
Where m is mass of satellite .
By conservation of energy , energy at perigee =energy at apogee
-
So
Vp= =
Vp=6.85km/s , va=2.28km/s
So orbital velocity vc=
R=6R ,vc= 3.23km/s
Hence to transfer to a circular orbit at apogee , we have to boost the velocity by 3.23-2.28=0.95km/s.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation-let m be the mass of the earth vp, va be the velocity of the earth at perigee and apogee respectively. Similarly wp and wa are angular velocities.
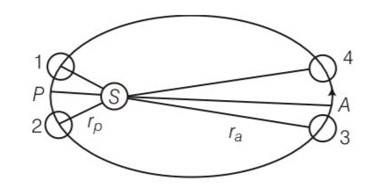
At perigee, at apogee
If a is the semimajor axis of the earth's orbit then rp=a (1-e) and ra=a (1+e)
= 0.00167
Let w be the angular speed which is geometric mean of wp and wa and corresponding to mean solar day.
=1.0691
If w corresponds to 10 per day then wp = 1.0340 per day and wa= 0.9670 per day . since 3610=24, mean solar day we get 361.0340 which corresponds to 24h,8.14' and 360.9670 corresponds to 23h59min52'. So
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Explanation- mass of earth M = 6
Radius of the earth , R = 6400km= 6.4
T=24h= 24
G = 6.67 10-11Nm2/kg2
(a) Time period T =
= 2
= ( )1/3
( )1/3-R
So after solving we get h = 3.59
(b) If satellite is at height h from the earth's surface
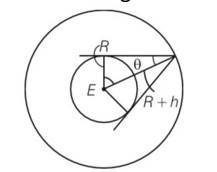
Cos = = cos81018'
= 81018'
=2(81018')= 162036'
If n number of satellite needed to cover entire the earth then
So n = 3600/2 = 2.31
So minimum 3 satellite are required to cover entire earth.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- consider a diagram having vertices A,B,C,D,E and F
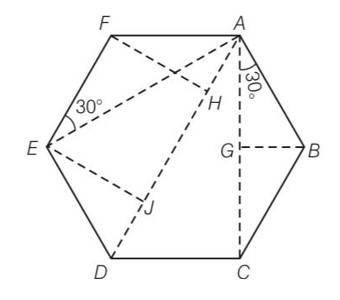
AC= AG+GC=2AG
= 2lcos300= 2l
=
AD=AH+HJ+JD= lsin300+l+lsin300=2l
Force on mass m at A due to mass m at B is f1= along AB
Force on mass m at A due to mass m at C is f2= along AC
Force on mass m at A due to mass m at D is F3= along AD
Force on mass m at A due to mass m at E is F4= = along AE
Force on mass m at A due to mass m at F is F5= along AF
Resultant force due to F1 and F5 is F1=
= along AD
So net force along AD = F1+F2+F3=
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Explanation- when a body og mass m is revolving around a star of mass M.
Linear velocity of the body v= so when r increases then v decreases.
Angular velocity of the body w = 2
According to kepler's law T2 r3
So T= kr3/2
So w= so when r increases, w decreases.
Kinetic energy of the body K= 1/2mv2=1/2m ( ) so when we increase r, KE decreases.
Gravitational potential energy of the body
U=-GMm/r
So when we increase r, PE becomes less negative
Total energy of the body E= KE+PE=
When r increases total energy becomes less negative . i.e increases.
Angular mom
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Initial kinetic energy of the rocket =
Initial potential energy of the rocket =
Total initial energy =
If 20% of initial kinetic energy is lost due to Martian atmosphere resistance, then only 80% of its kinetic energy helps in reaching a height
Total initial energy available = 0.8
Maximum height reached by the rocket = h
At this height, the velocity and hence the kinetic energy of the rocket becomes zero.
Total energy of the rocket at height h =
Applying the law of conservation of energy for the rocket, we can write:
0.4 =
0.4 = GM(
0.4 = GM( )
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mass of the spaceship, = 1000 kg
Mass of the Sun, M = 2 * 1030 kg
Mass of Mars, = 6.4*1023 kg
Orbital radius of Mars, R = 2.28 *108 km = 2.28 *1011 m
Radius of Mars, r = 3395 km = 3.395
Universal Gravitational constant, G = 6.67*10-11 N m2 kg–2
Potential energy of the spaceship due to the gravitational attraction of the Sun =
Potential energy of the spaceship due to the gravitational attraction of Mars=
Since the spaceship is stationed on Mars, its velocity and hence its kinetic energy will be zero
Total energy of the spaceship = = + )
The negative sign indicates that th
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Yes, a body gets stuck to the surface of a star if the inward gravitational force is greater than the outward centrifugal force caused by the rotation of the star.
Gravitational force, = , where M = mass of the star = 2.5 = 5 kg
M = mass of the body, R = radius of the star = 12km = 1.2
= 2.31
Centrifugal force = mr where angular speed = 2 and angular frequency = 1.2 rev/s
mR( = m (1.2 = 6.81
Since , the body will remain stuck to the surface of the star.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers