Linear Inequalities
Get insights from 69 questions on Linear Inequalities, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Linear Inequalities
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
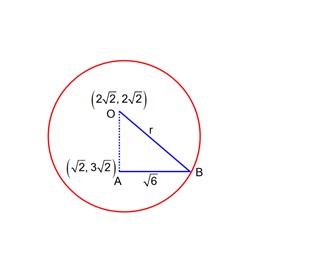
Let y = mx + c is the common tangent
so equation of common tangents will be
which intersects at Q (3, 0)
Major axis and minor axis of ellipse are 12 and 6. So eccentricity
and length of latus rectum
Hence
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Fill in the blanks Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a True or False Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
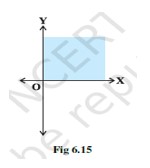
30.
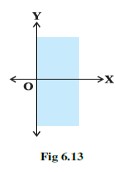
30. For inequality y+8 ≤ 2x, the equation of the line is y+8=2x. We consider the table below to plot of y+8=2x.
The line devides the xy-plane into half planer I and II. We select a point (0,0) and check the correctness of the inequality.
i.e., 0+8 ≤ 2 * 0
0 ≤ 0 which is true.
So, the solution region is I which includes the rigin (0,0). The continuous line also indicates that any points on the line also satisfy the given inequality.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
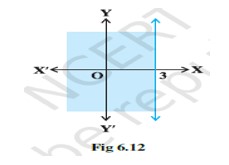
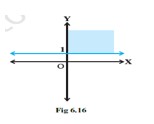
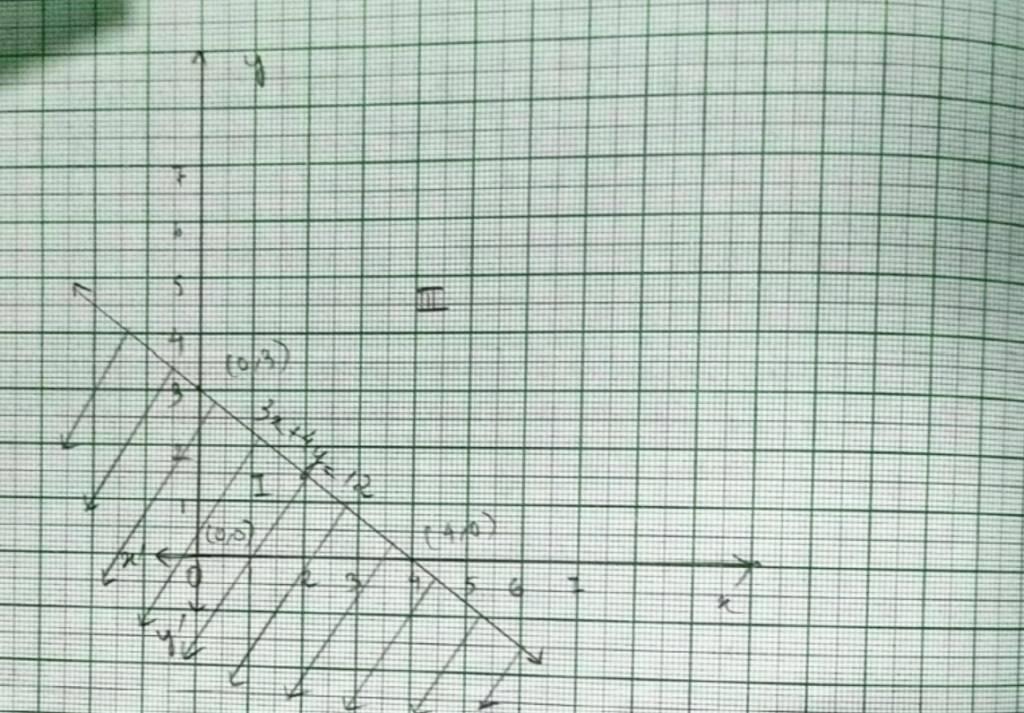
29. For inequality 3x+4y≥ 12 the equation of the line is 3x+4y=12
We consider the table below to plot 3x+4y=12.
This line devides the xy-plane into half planer I and II.
We select point 0 (0,0) and check the correctness of the inequality.
i.e., 3 * 0+4 * 0 ≤ 12.
0+0 ≤ 12
0 ≤12 which is true.
So, the solution region is I which includes the origin (0,0). The continuous line also indicates that any points in the line also satisfy the given inequality.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
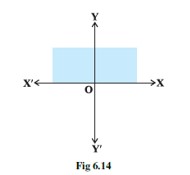
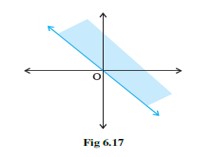
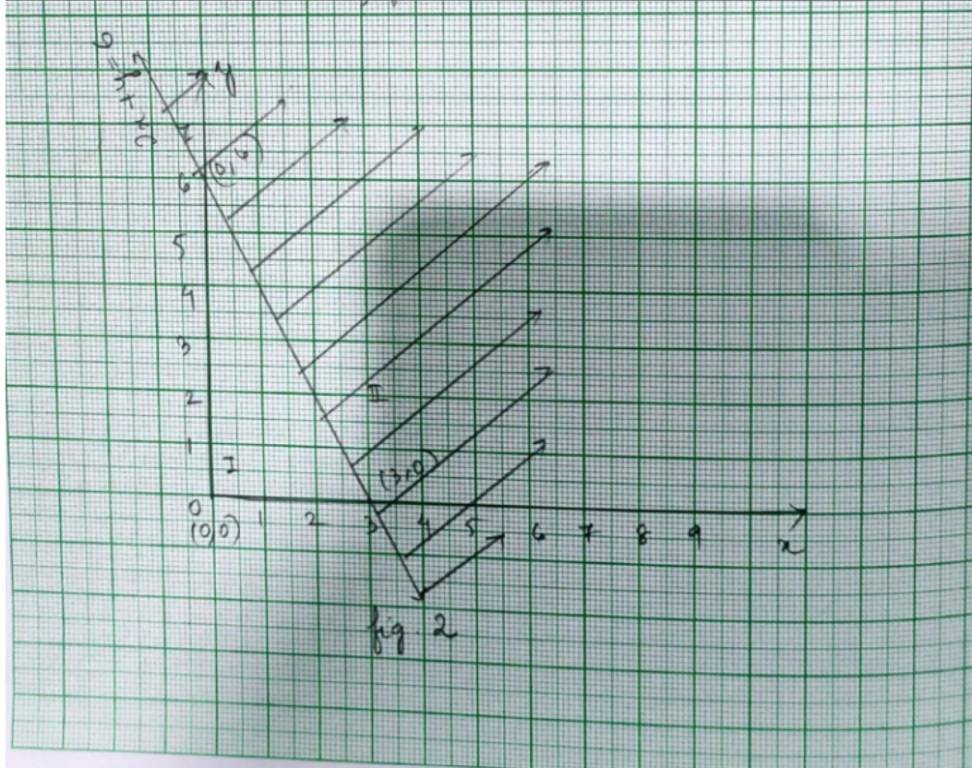
28. For inequality, 2x+y≥ 6, the equation of line is 2x+y=6.
We consider the table below to pot 2x+y=6.
Graph of 2x+y=6 is given as a continuous line in fig 2.
This line divides xy-plane in two half planes I and II.
We select 0 (0,0) and check the correctness of the inequality.
is 2 * 0+0 ≥ 6.
0 ≥ 6 which is false.
So, the solution region is II where origin (0,0) is included.
The continuous line indicates that any point on the line. also satisfy the given inequality.
New question posted
8 months agoNew question posted
8 months agoTaking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers