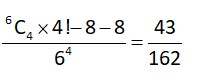Maths
Get insights from 6.5k questions on Maths, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Maths
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
Total time = 182s
2 + 4 + 6 + 8 +……………+ n terms = 182
i.e. n=13
Total distance covered = 2* [12 + 2 2+ 32 +……. …………. + 132]
= 2 * 13 * 14 *
Average speed = 9 * 13 *
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
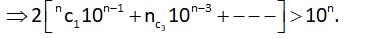
->For the inequality Satisfies.
For n= 4. 2 [4 * 103 + 4 * 10] > 104
->8 * 1010 > 104 which is a contradiction
all values satisfies. Hence possible values of n is 96
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
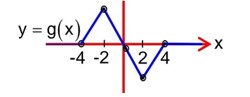
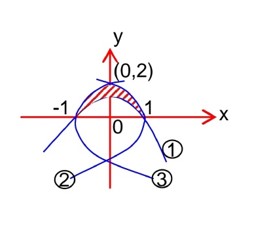
g(x) is continuous every where but not differentiable
at x = -4, -2, 2 and 4
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
f : A -> A is bijective
where A = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
and f (1) + f (2) + f (3) = 3
-> 0 1 2 3! ways
f (0) f (4) f (5) f (6) f (7)
3
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 10
All entries different which can be selected as 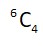
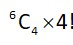
Let be such matrix
|A| = ad – bc
Now | A| = 0 -> ad – bc = 0 cases
1, 6 3, 2 2 * 2 * 2
&nb
New answer posted
3 months agoContributor-Level 9
The bag has 25-paise, 50-paise and 1 -rupee coins in the ratio 8 : 2 : 7. Now this is the ratio of the number of coins while the total value of the coins has been given. So we first need to convert coins into value.
Let the coins be 8x, 2x and 7x respectively.
8x coins of 1/4 rupee each = value is Rs. 2x.
2x coins of 1/2 rupee each = value is Rs. x.
7x coins of 1 rupee each = value is Rs. 7x.
Now
2x + x + 7x = 770
10x = 770 x = 77
Number of 25 paise and 50 coins = 10 x = 770 coins
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers