Motion in a Straight Line
Get insights from 82 questions on Motion in a Straight Line, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Motion in a Straight Line
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
let speed of two balls be V1and V2
Where v1=2v and v2=v and y1and y2 be the distance covered
So y1= and y2=
So y1-y2= 15
V2=
So clearly we can say v1=20 and v2=10
And y1=20m and y2=5m
If t2 is the time taken by ball 2 through a distance of 5m, y2=v2t-1/2gt2
5=10t2-5t22 so t2 will be 15
Then time covered by ball 1 in 2 sec between two throws = t1-t2= 2-1=1s
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) for maximum velocity dv/dt=0
d/dt (6t-2t2)=0
6-4t=0 t= 6/4=1.5s
(b) v=6t-2t2
ds/dt=6t-2t2
ds=6t-2t2dt
distance in 3s, S= 30
s= 27-18=9m
average velocity = distance /time =9/3 = 3m/s
x= 6t-2t2
3=6t-2t2
After solving we get t= 9/4s approx.
(c) in periodic motion when velocity is zero
0=6t-2t2
0=t (6-2t)
So t=0, 3 sec
(d) distance covered from 0 to 3s=9m
distance covered in 3 to 6s=
S= (18t- )6
S= 108-9 (18)+
S= -4.5m
So total distance covered = 9+ (-4.5)=4.5m
No of cycles covered in that distance =20/4.5=4.44approx
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
speed of car and truck = 72km/h = 72 (5/18) =20m/s
V= u+at
0=20+a (5) so a=-4m/s2
But retarted acceleration will be v=u+at
0=20+a (3)
So a= -20/3m/s2
We also need to consider human response time = 0.5 s
V=u-at (for retarded motion)
V= 20- ….1
Vt=20-4t ….2
From 1 and 2
20-=20-4t
After solving we get t= 5/4s
Distance travelled by truck in time t, S=ut+1/2at2
= 20
To avoid the bump onto the truck car must maintain distance = 23.125-21.875=1.250m
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) velocity attained by a falling rain drop will be =
=
(b) diameter of the rain drop = 2r=4mm
Radius = 2mm= 2
Mass of rain drop = V
Momentum of rain drop= mv= 3.4
(c) time ,t = d/v=
(d) force exerted, F = change in momentum /time=
(e) area =
number of drops striking the the umbrella with separation of 5
so net force =
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
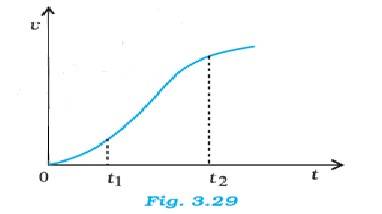
3.28 The graph has a non-uniform slope between the intervals t1 and t2 – the graph is not a straight line. The equations (a), (b), and (e) do not describe the motion of the particle. Only the relations (c), (d) and (f) are correct.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
3.27
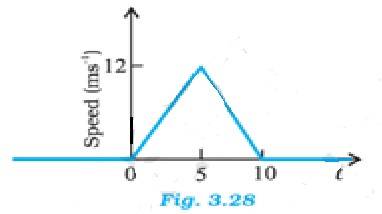
(a) Distance travelled by the particle between t = 0 s and t = 10 s is the area of the triangle = (1/2) x base x height = (1/2) x 10 x 12 = 60 m
The average speed of the particle is 60/10 m/s = 6 m/s
(b) Distance travelled by the particle between t = 2 s and t = 6 s
Let S1 be the distance travelled by the particle in time 2 to 5 s and S2 be the distance travelled between 5 to 6s.
For the motion from 0 to 5 sec, u = 0, t = 5, v = 12 m/s
From the equation v = u + at we get a = (v-u)/t = 12/5 = 2.4 m/s2
Distance covered from 2 to 5 sec, S1 = distance covered in 5 s – distance covered in 2 s
From the equation s = ut + at2 we
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Initial velocity, u1 = 15m/s, acceleration, a = -g = -10 m/s
From the relation s1=s0+u1t+ (1/2)at2 where
s0 = cliff height, s1 = total height of the fall of the first stone, we get
s1 = 200 + 15t – 5t2 ………. (1)
When the stone hit the floor, s1 = 0, so the equation (1) becomes
0 = 200 +15t - 5t2 = t2 -3t – 40 = (t-8) (t+5) = 0
So t = 8s or -5s
Since the stone was thrown at t=0, so t cannot be –ve. Hence t = 8s
For the second stone,
Initial velocity, u1 = 30 m/s, acceleration, a = -g = -10 m/s
From the relation s2=s0+u1t+ (1/2)at2 where
s0 = cliff height, s2= total height of the fall of the s
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
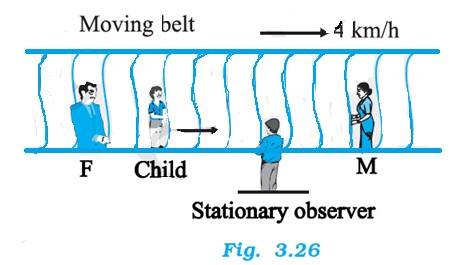
Speed of belt = 4 km/h
(a) When the boy runs in the direction of motion of the belt, then the speed of the child observed by the stationary observer = 9 + 4 = 13 km/h
(b) When the boy runs in the opposite direction of motion of the belt, then the speed of the child observed by the stationary observer = 9-4 = 5 km/h
(c) Distance between the parents = 50 m = 0.05km
Speed of the boy, as observed by both parents = 9 km/h.
Time required by the boy to move to any parent = 0.05 / 9 h = 20s
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
3.24 The initial velocity of the ball, u = 49m/s
First Case: When the ball returns to his hands, total displacement = 0
From the relation s = ut + 0.5at2, we get 0 = 49t + 0.5 (-9.81) t2
4.905 = 49t Hence t = 10s
Second Case:
As the lift started moving up with a speed of 5 m/s, the initial velocity of the ball = 49 + 5 m/s = 54 m/s
If t' is time for the ball to return to his hand, the displacement of the ball will be = 5t'
From the relation s = ut + 0.5 x at2, we get
5t' = 54t' + 0.5 * (-9.8) t'2
49t' = 4.9 t'2
t' = 10 s
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
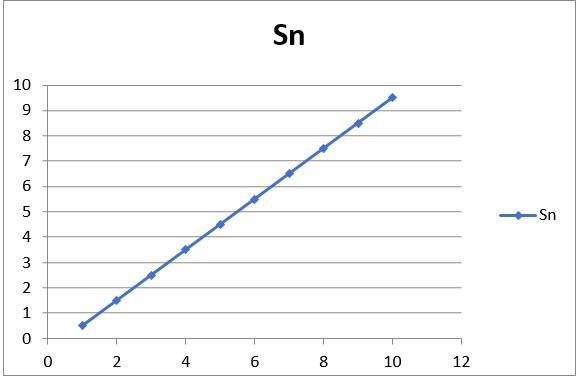
3.23 The distance covered by the 3 wheeler on a straight line in the nth second can be expressed as:
Sn = u + a (2n-1)/2 …… (1),
Where
a = acceleration
u = initial velocity
n = time = 1,2,3, ……., n
Given, u = 0, a = 1m/s2, from equation (1) we get Sn = (2n-1)/2 ……. (2)
With various values of n, we get Sn
n Sn
1 &
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers