Motion in a Straight Line
Get insights from 82 questions on Motion in a Straight Line, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Motion in a Straight Line
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
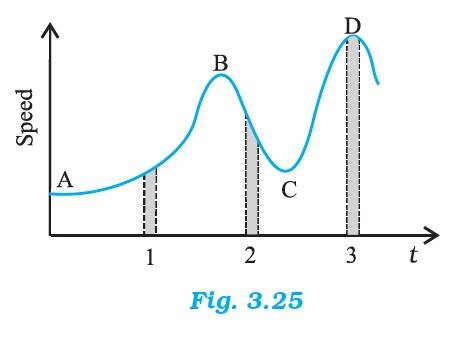
3.22 The change in the speed with time is maximum in interval 2. Therefore, the average acceleration is the greatest in magnitude in interval 2
The average speed is maximum in interval 3
The sign of velocity is positive in intervals 1,2 and 3
Acceleration depends on the slope. The acceleration is positive in interval 1 and 3, as the slope is positive. The acceleration is negative in interval 2, as the slope is negative
Acceleration at A, B, C and D is zero since the slope is parallel to the time axis at these instants
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
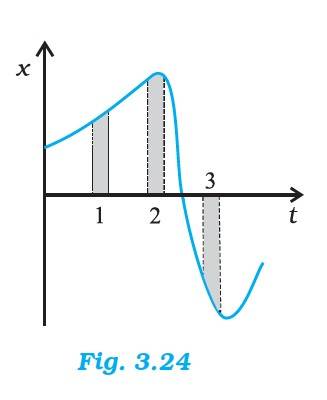
3.21 The average speed in Interval 3 is the greatest and in Interval 2 is the least.
The average velocity is +ve in Interval 1 & 2 and –ve in Interval 3.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
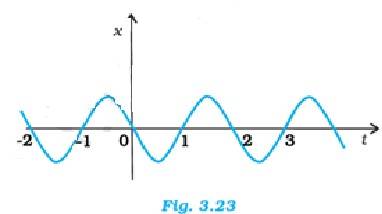
3.20 In simple harmonic motion, the acceleration is expressed as a = - 2x, where is the angular frequency.
(a) At t = 0.3 s, position x is negative, velocity v is negative and acceleration a ( from above equation) will be positive
(b) At t = 1.2 s, position x is positive, velocity is positive, acceleration a will be negative
(c) At t = -1.2 s, position x is negative, velocity is positive and acceleration will be positive.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
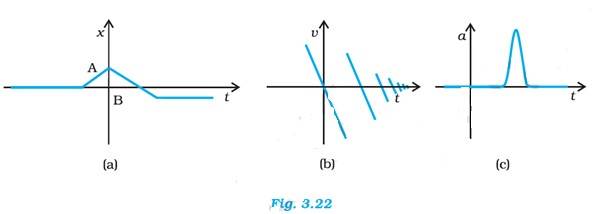
(a) This graph is a Displacement-Time Graph (x- t) that shows the displacement increasing From A to B, and decreasing From B to C. The graph may represent a carom board where the striker hits the edge, rebounds with reduced speed, then moves in the opposite direction, hits the opposite wall and stops.
(b) This graph is a Velocity-Time Graph (v- t) that shows Sudden spikes and drops in velocity. There is a rapid change in velocity. This graph may represent a ball that falls on the ground from a certain height and rebounds with a reduced speed
(c) This graph is an Acceleration -Time Graph (a- t) that shows an instantaneous spike in ac
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
3.18 Speed of the police van = 30 kmph = 8.33 m/s
Speed of the thief's car = 192 kmph = 53.33 m/s
The muzzle speed of the bullet = 150 m/s
Speed of the bullet = speed of the police van + muzzle speed of the bullet = 8.33 + 150m/s = 158.33 m/s
The relative velocity of the bullet = speed of the bullet – speed of the thief's car = 158.33 – 53.33 m/s = 105 m/s
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
3.17 For t<0, we cannot say that the particle moved in a straight line and for t>0 on a parabolic path as the x-t graph does not indicate. Instead, this x-t graph denotes a particle is dropped from a height at t=0
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
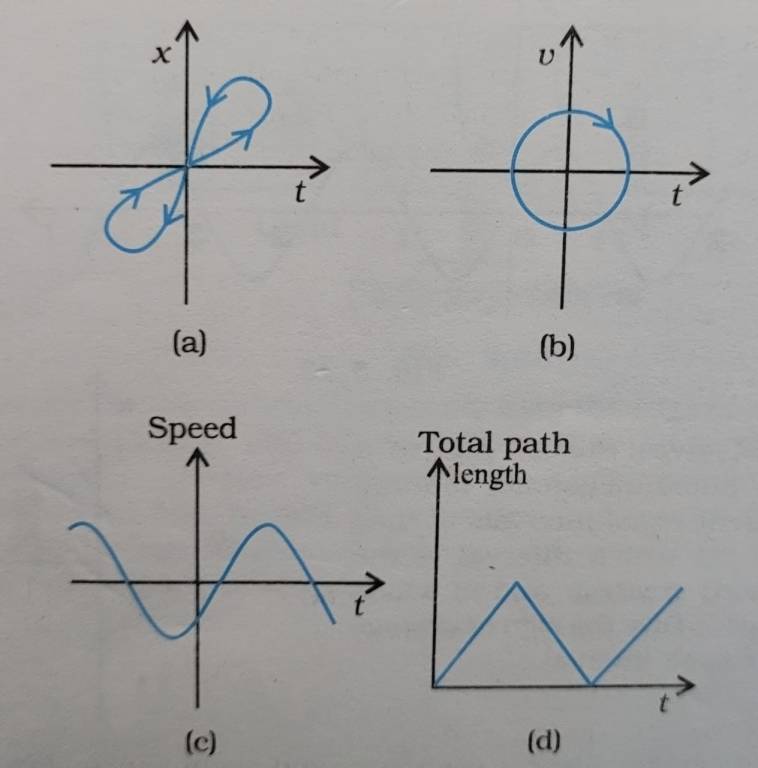
3.16
(a) Figure (a) shows two positions at the same time, which is not possible for a one-dimensional motion
(b) A particle cannot have velocity in two directions at the same time in one-dimensional motion
(c) The graph shows negative speed, which is not possible because speed is always positive
(d) Total path length decreases, which is not possible for a one – dimensional motion
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
3.15 Instantaneous speed and velocity are applicable for a small interval of time because the magnitude of the displacement is effectively equal to the distance travelled by the particle.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
3.14
The distance from home to market = 2.5 km = 2500 m
The speed of the walking while going = 5 kmph = 1.388 m/s
The speed of walking back from market to home = 7.5 kmph = 2.083 m/s
(a) Magnitude of the average velocity = Displacement / time = 0, since the total displacement is zero.
(b)
i. Time taken to reach the market = distance / onward speed = 2500/1.388 = 1801 s = 30 minutes. So the average speed over 0 – 30 min is 5 kmph
ii. Time taken to reach back home = 2500 / 2.083 = 20 minutes. So the average speed = total distance covered / total time taken = (2500 +2500)/ (30 +20) m/min = 100 m/min = 6 kmph
iii. Average speed ove
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
3.13
(a) Let us take the example of football world cup 2022. During Argentina match, Di Mario (A) passed the ball to Messi (B). Messi instantly passed the ball to Di Mario. Now the magnitude of displacement of the ball is 0 as the ball returns to Di Mario at the initial position. But the total length covered by the ball is AB + BA = 2AB. Hence total length covered by the particle (the ball) is more than the magnitude.
(b) If t is the time taken to cover the entire distance, the magnitude of the average velocity of the ball over time interval t = Magnitude of displacement / t = 0 / t = 0
The average speed of the ball = Total lengt
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers