Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) Both metallic and ionic crystals have strong forces of attraction between their atoms or ions. In metallic crystals there is a strong metallic bond present between electrons and positively charged ions. In ionic crystals there are strong ionic bonds between anions and cations. Both of them conduct electricity,
but metallic crystals conduct electricity in all three states of matter while ionic crystals conduct electricity only in molten state.
(ii) The ionic solids are hard and brittle because they have strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the anions and cations .As a result the anions and cations are tightly hel
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.32 Number of corner atoms per unit cell
= 8 corners atoms *18 atom per unit cell
=8 * 18 = 1 atom
Number of face face centred atoms per unit cell
= 6 face centred atoms * 12 atom per unit cell
= 6 * 12 = 3 atoms
∴ Total number of atoms (lattice point) = 1 + 3 = 4
(ii) As in (i)
No. of lattice points = 4
(iii) In bcc unit cell, number of corner atoms per unit cell
=8 corners*18 per corner atom
=8*18=1 atom
Number of atoms at body centre =1*1 = 1 atom
∴ Total number of atoms (lattice points) = 1 + 1 =
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
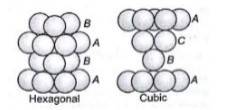
1.31 (i) In hexagonal close packing (hcp), the spheres of the third layer are vertically above the spheres of the first layer. It means tetrahedral voids of the second layer are covered by the spheres of the third layer. The AB. type.In cubic close packing (ccp), the spheres of third layer cover the octahedral voids of second layer. But the spheres of the fourth layers are aligned with those of the first layer. The pattern is ABC. type.
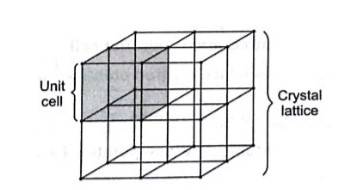
(ii) Crystal lattice is the three dimensional arrangement of identical point in the space which represent how the constituent particles (atoms, ions, molecules) are arranged in a crystal.Unit cell is th
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.30 Stability of a crystal is directly proportional to the magnitude of its melting points. Higher is the magnitude of forces holding the constituent particles together, higher will be the melting point and higher will be the stability. Thus ionic crystals (NaCl, KNO3 etc.) have very high melting points and stable crystal lattices. On other hand, molecular solids (naphthalene, iodine etc.) have low melting points and low stability.
The melting points of solid water, ethyl alcohol, diethyl ether and methane are 273 K, 155.8 K, 156.8 K and 90.5 K respectively.Solid water and ethyl alcohol have higher melting points due to presence of i
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.30 Knowing the density of an unknown metal and the dimension of the unit cell, the atomics mass of the metal can be determined.
Let, Atomic mass of element
(M)=d* a3* NA x Z
Where, d = density
- a3= volume of the unit cell
- NA = Avogadro's number
- Z= number of atoms present in one unit cell.
- Density of the unit cell= Mass of the unit cell / Volume of the unit cell
- d= zm / a3
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.28 Coordination number is the number of the nearest neighbors with which a given atom is in contact. In an
ionic crystal, the coordination number of an ion refers to the number of oppositely charged ions that
surround that ion.
The coordination number of atoms in a
(a) Cubic close-packed structure is 12.
(b) Body-centred cubic structure is 8
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.27 The different solids are classified below:
a) Ionic solids: Ammonium phosphate (NH4)3PO4), LiBr
b) Metallic solid: Brass, Rb
c) Molecular solids: Tetraphosphorous decaoxide (P4O10), Iodine (I2), P4
d) Network (covalent) solids: Graphite, SiC, Si
e) Amorphous solid: Plastics
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.26 Quartzis crystalline solid with long range order and glass is amorphous solid (or pseudo solid or super cooled liquid) with short range order and has a tendency to flow. When quartzis heated, it can be converted into glass.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.25 Amorphous solids have short-range order with irregular shapes of constituent particles. They have isotropic nature and melt over a range of temperatures. They do not have a definite enthalpy of fusion. Examples of amorphous solids are glass, rubber, plastic, etc.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.24 Ferromagnetic substances would make better permanent magnets because when the ferromagnetic substance is placed in a magnetic field, all domains get oriented in the direction of magnetic field and strong a magnetic effect is produced.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers