Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Get insights from 2.6k questions on Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Chemistry Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.13 (i) An atom located at the corner of a cubic unit cell is shared by eight adjacent unit cells. Therefore, 1/8th portion of the atom is shared by one unit cell.
(ii) An atom located at the body centre of a cubic unit cell is not shared by its neighbouring unit cell. Therefore, the atom belongs only to the unit cell in which it is present i.e., its contribution to the unit cell is 1
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.12

(ii) Face-centered unit cell: In a face-centered unit cell, the constituent particles are present at the corners
and one at the centre of each face.
End-centered unit cell: An end-centered unit cell contains particles at the corners and one at the centre of
any two opposite faces.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
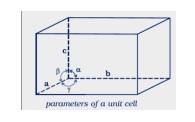
1.11 The six parameters that characterize a unit cell are as follows.
(i) Its dimensions along the three edges, a, b, and c these edges may or may not be equal.
(ii) Angles between the edges these are the angles (between edges b and c), (between edges a and c), and (between edges a and b)
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.10 The significance of a lattice point is that each lattice point represents one constituent particle of a solid which may be an atom, a molecule (group of atom), or an ion.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.9 Metallic solids are electrical conductors, malleable, and ductile.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.8 In solid state, ions are held together by strong electrostatic forces and are not free to move about within the solid. In ionic compounds, electricity is conducted by ions. Hence, in molten state or in solution form, the ions are free to move and can conduct electricity
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.7 The given properties are the resource of a covalent or network solid. Therefore, the given solid is a covalent or network solid. Examples of such solid are quartz (SiO) and diamond (C).
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.6 Potassium sulphate, tin, benzene, urea, ammonia, water, zinc sulphide, graphite, rubidium, argon, silicon carbide. Solids have been classified into different categories based on chemical bonding. The chemical bonding depends on the intermolecular forces of attraction between the atoms.
a) Potassium sulphate →Ionic solid
b) Tin→ Metallic solid
c) Benzene→ Molecular (non-polar) solid
d) Urea→ Polar molecular solid
e) Ammonia→ Solid ammonia is a hydrogen-bonded molecular solid which is also known as polar molecular solid
f) Water→ Hydrogen bonded molecular solid
g) Zinc sulphide→ Ionic solid
h) Graphite→ Covalent or network so
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.5 As isotropic solid has the same value of physical properties when measured along different directions. Therefore, the given solid, having the same value of refractive index along all directions, is isotropic in nature. Hence, the solid is and amorphous solid. When an amorphous solid is cut with a sharp edged tool, it cuts into two pieces with irregular surfaces
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
1.4 Glass is basically an amorphous solid. When glass is made the silica is cooled from its liquid state, and it does not solidifies even when the temperature is dropped below freezing point. Hence, glass is a super cooled liquid. Due to this fluidity property, glass can be considered as a liquid of extremely high viscosity. The evidence of the fact can be seen in the windows getting thicker at bottom over a period of time.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
