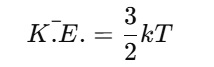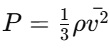ncert solutions physics class 11th
Get insights from 152 questions on ncert solutions physics class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about ncert solutions physics class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
Doppler Effect in class 11 chapter 14 waves refers to the variation in the wavelength or frequency of a wave in relation to an observer moving relative to the wave source. When the wave source moves toward the observer, the frequency increases, and waves are compressed. If the source moves away, the frequency reduces and the waves are stretched. The Doppler Effect can be observed with the sound of a passing train or ambulance. This concept is also used in medical imaging technologies like Doppler ultrasound, radar, and astronomy to find whether galaxies or stars are moving away or towards the Earth.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
The speed of a wave can be found by the medium properties through which it travels. For mechanical waves, the speed of the wave depends on the inertia and elasticity of the medium. For example, the speed of a wave is dependent on the mass of the wave per unit length and the tension in the string.
Also, sound travels in solids at a greater speed than in liquids and gases because, in a solid, the particles are more tightly packed. In the case of electromagnetic waves, the speed of waves is the highest in vacuum and it depends on the magnetic and electric properties of the medium. The type of wave also matters which can be longitudin
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
When two waves of the same amplitude, frequency and speed travel in opposite directions and collide with each other, then a standing wave is formed. It is usually seen in the bounded medium, like a string fixed at both ends. It is different from the travelling waves and does not appear to move along the medium. At fixed locations, it forms specific points called nodes (with zero displacement) and antinodes (with maximum displacement). It is an important concept in understanding musical instruments, resonance and wave behaviour in closed and open pipes. The standing waves help in visualizing how energy can be stored in waveforms.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
According to the principle of superposition, when two or more waves overlap in space, due to each individual wave, at any point the displacement is the vector sum of the displacements. The principle of superposition also explains phenomena like interference where waves combine to amplify or cancel out each other. It can happen in both ways - constructively or destructively. In real life, the superposition can be seen in the noise cancellation technologies, sound beats and the colourful patterns created by overlapping water waves. The principle is the fundamental concept for understanding wave behaviour in acoustics, optics and even qua
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mechanical waves are of two types - transverse waves and longitudinal waves. It requires a medium to travel. The medium particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation in the case of transverse waves. However, the particles oscillate parallel to the wave direction in the longitudinal waves as seen in sound waves. The sound waves propagate by exerting forces by the neighbouring particles. While the wave particles stay close to the original position, the energy is passed on through the interactions among the adjacent particles.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
A disturbance that travels through the space or medium transferring energy without the net movement of particles is called a wave. Rather than moving along with the wave, the particles of the medium only oscillate about their mean position in a wave motion. The wave is fundamentally different as compared to the particle motion where the particles travel from one place to another. In a sound wave, the air molecules do not travel to the sound, they vibrate back and forth. The concept of wave motion is one of the most important concepts in knowing how energy is transmitted in various forms including light, sound and water waves.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The main difference between the real and ideal gases is with respect to the kinetic theory. The ideal gas follows assumptions of the kinetic theory but the real gases do not follow it, especially when the temperature is low and there is high pressure.
The following points are applicable in the case of real gases:
- Real gas molecules do have finite volume.
- In such cases, intermolecular forces such as Van there Waals forces become significant.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
According to the kinetic theory of gases class 11, the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution law describes the gas molecules' distribution of speeds (or velocities). All molecules of gas do not move at the same speed, some move fast, some are slow and most move at an average speed. This law provides a mathematical function that helps in finding at a given temperature, how many molecules have a particular speed. The Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution law helps in defining three important types of speeds:
- Average speed: Arithmetic mean of all speeds.
- Most probable speed: Speed at which the maximum number of molecules travel.
- Root mean square (RMS
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The average kinetic energy of the gas molecules is directly related to the temperature of the gas. The average kinetic energy of one gas molecule, according to the kinetic theory, is given by:
Here T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin, and K is the Boltzmann constant. This equation shows that the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules increases with an increase in temperature. It implies that temperature here is the measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles. The equation also reflects that when gas gets heated why it expands - all molecules move faster and exert more pressure on the container walls.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
According to the NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory, the pressure is exerted due to gas molecules' collisions with the walls of the container. Each gas molecule has a certain mass and velocity. According to Newton's law, when the molecules collide with a wall, it changes momentum and this change in momentum exerts a force on the container wall. By considering the collisions from all molecules over a period in a unit area, the average force per unit area is called pressure. Mathematically, pressure P is:
p is the gas density.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 680k Reviews
- 1800k Answers