ncert solutions physics class 11th
Get insights from 152 questions on ncert solutions physics class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about ncert solutions physics class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.23 Power used by the family = 8 kW = 8000 W
(a) Solar energy received = 200 W/
Percentage conversion of Solar energy to Electrical energy = 20%
If the area required is A then 0.2
A = 200 . The comparable roof size is 14.14 X 14.14 m
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ans.4.21: (a) Velocity , = 10.0 ? m/s Acceleration, = (8.0 ? + 2.0 ?) m s-2 We know = = 8.0 ? + 2.0 ? = (8.0 ? + 2.0 ?)dt Integrating both sides we get (t) = 8.0t ? + 2.0t ? + , Where, velocity vector of the particle at t =0 velocity vector of the particle at time t But = = dt = (8.0t ? + 2.0t ? + )dt Integrating both sides with the condition at t = 0, r =0 and at t =t, r = r t + ½ 8.0 t2 ? + ½ 2.0 t2 ? = t + 4.0 t2 ? + t2 ? Substituting the value of , we get ( 10.0 ?)t + 4.0 t2 ? + t2 ? . This equation can be expressed as x ? + y ? = 4.0 t2 ? + ( 10.0t + t2) ? Since the motion of the particle is confined to the x-y plane, on equating the coefficients of ? and ?, we get x = 4.0 t2 and y = 10.0t + t2 t = (a) When x = 16m, t = 2 s, y = 24m (b) Velocity of the particle (t) = 8.0t ? + 2.0t ? + At t = 2 s, (t) = 8.0 2 ? + 2.0 ? + 10 ? = 16 ? + 14 ? The magnitude of (t) is given by = ( 162 + 142)1/2 = 21.26 m/s |
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.25
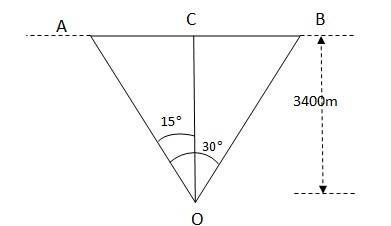
Height of the aircraft from the ground = 3400m
Let A and B be the positions of the aircraft, making an angle of AOB = 30 . The perpendicular OC and OC is the height of the aircraft. Angles AOC = angle BOC = 15
In AOC, AC = OC
= 3400 = 911.03m
AB = AC + CB = 2AC = 1822m
The distance of AB is covered in 10s, so the speed of the aircraft = 1822/10 m/s = 182.2 m/s
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.24
(a) Despite being a scalar quantity, energy is not conserved in elastic collisions. False
(b) Despite being a scalar quantity, the temperature can take negative values. False
(c) The total path length is a scalar quantity. Yet it has the dimension of length. False
(d) A scalar quantity such as gravitational potential can vary from one point to another point in space. False
(e) The value of a scalar does not vary for observers with different orientation of axis. True
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.23
(a) For any arbitrary motion of a particle average velocity cannot be expressed by this equation. False
(b) The arbitrary motion of the particle can be represented by this equation, True
(c) For arbitrary motion of the particle, the acceleration may also be non uniform. False
(d) The motion of the particle is arbitrary, acceleration of the particle may also be non-uniform, so can not represent the motion of the particle in space. False
(e) The arbitrary motion of the particle can be represented by the given equation. True
New answer posted
6 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Significance of de Broglie's Hypothesis in Modern Physics (NCERT-based answer):
De Broglie's hypothesis is a revolutionary idea which changed the understanding of matter and wave as we know it. This hypothesis introduced the concept that particles of matter, like electrons, and Proton, can behave like wave and have wave-like properties, just as light exhibits both wave and particle nature.
According to de Broglie, any moving particle has a wavelength given by:
where is the wavelength, is Planck's constant, is the mass, and is the velocity of the particle.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
2.3
1 Calorie = 4.2 J = 4.2 kgm2s-2
Standard formula for conversion
Given unit / New unit = (M1/M2)x (L1/L2)y (T1/T2)z
Formula for energy = M1L2T-2
Here x = 1, y = 2, z = -2
In this problem
M1 = 1 kg, L1 = 1 m, T1 = 1 s and
M2 =? kg, L2 =? m, T2 =? s
So 1 Calorie = 4.2 (1/? )1 (1/? )2 (1/? )-2
= 4.2? -1? -2? 2
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ans.2.1
(a) The volume of a cube of side 1 is equal to
The volume of the cube = 1 cm * 1 cm * 1 cm = 1 cm3
1 cm3 = 1 * 10-6 m3
(b) The surface area of a solid cylinder of radius 2.0 cm and height 10.0 cm is equal to1.25 * 104 (mm)2
The surface area of a solid cylinder = 2? r (r+)h, where r = 2.0 cm = 20 mm, h = 10 cm = 100 mmSurface area = 2 * 22/7 * 20 * (100 +20) = 1.51 *
(c) A vehicle moving with a speed of 18 km h–1 covers 5 m in 1 s
Vehicle speed = 18 km/h = 18000/3600 m/s = 5 m/s
(d) The relative density of lead is 11.3. Its density is 11.3 g cm–3 or 11.3 * 103.kg m–3.
Relative density or
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.12
Mass of the Sun, = kg, Mass of the Earth, = kg
Orbital radius, r = m
Let the mass of the rocket be, m
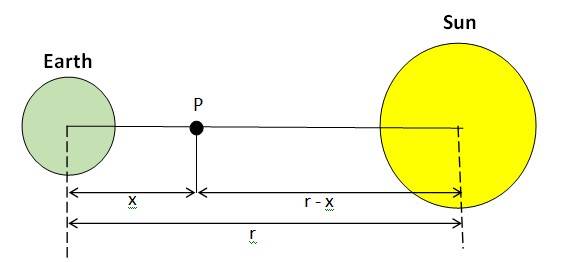
Let x be the distance from the centre of the Earth where the gravitational force acting on satellite P becomes zero.
From Newton's law of gravitation, we can equate gravitational forces acting on the satellite P under the influence of the Sun and the Earth as:
= or(
= ( = ,
= 577.35 , r = 578.35x ,
x = = 2.59 m
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ans.8.1
(a) No. Unlike electrical forces, gravitational force is independent of the status of the objects.
(b) Yes, the size of the space station is large enough and the astronaut will detect the change in Earth's gravity.
(c) Tidal effect depends inversely upon the cube of the distance while gravitational force depends inversely on the square of the distance. Since the distance between the Moon and the Earth is smaller than the distance between the Sun and the Earth, the tidal effect of the Moon's pull is greater than the tidal effect of the Sun's pull.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
