- What is the Doppler Effect?
- Derivation of Doppler Effect
- Illustrated Examples
- FAQs on Doppler Effect Derivation
What is the Doppler Effect?
The Doppler Effect is the relationship between the frequency change in a wave and the observer relative to the wave source. This phenomenon was named after the physicist Christian Doppler in 1842. The most common example of the Doppler Effect is the sound of a car horn receding in the distance when it reaches the observer. The received frequency of the wave is comparatively higher than the emitted frequency.
The Doppler Effect depends upon various factors, including the observer’s motion, the wave source’s motion, hindrance in the air, the motion of the medium, etc. These effects of the waves are studied separately to know the phenomenon of the Doppler Effect.
Derivation of Doppler Effect
The derivation can be broken down into two main parts,
- When the source is moving.
- When the observer is moving.
To understand both of these effects, let us study in detail.
(i) When the source is moving
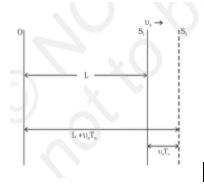
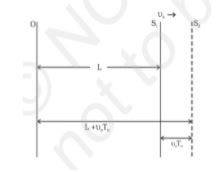
Let us understand the effect when the source is moving, and the observer stays in a stationary motion. We assume that the medium is also at rest. Shown below is the illustration of the Doppler Effect when the source is moving:
The formula can be derived as:
(ii) When the observer is moving
In this case, the observer is in motion, and the source remains at rest, now the derivation happens in the opposite manner and records in the observer’s reference frame. Following the same procedure, we can calculate the first- time travel, as follows:
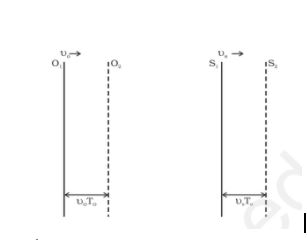
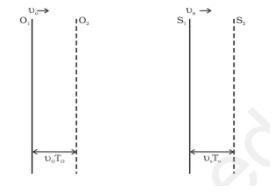
(iii) When both observer and source are moving
There is also a third possibility when both observer and source can be seen moving, the sound wave emits and reaches the observer. The diagrammatic presentation of the same is as follows:
Weightage in Class 11
The chapter ‘Waves’ for class 11 holds a weightage of 5 marks. It consists of 2 short questions of 2 marks and 3 marks each.
Illustrated Examples
1. Provide a diagram example of the Doppler effect when both source and the observer are moving.
Answer:
2. Provide a diagram example showing the Doppler effect when the source is moving.
Answer:
3. State one use of Doppler effect in the medical industry.
Answer: Doppler effect is used to diagnose heart problems.
Image courtesy: NCERT
FAQs on Doppler Effect Derivation
Q: What’s the origin behind the name Doppler Effect?
Q: Explain a basic example of the Doppler Effect.
A: The most common example of the Doppler Effect is the sound of a car horn recedes in the distance when it reaches the observer. The received frequency of the wave is comparatively higher than the emitted frequency.
Q: What factors does the Doppler Effect rely upon?
A: The Doppler Effect depends upon various factors, such as the observer’s motion, the motion of the wave source, hindrance in the air, the motion of the medium, etc.
Q: Explain the two derivative parts of the Doppler Effect?
A:
1) When the source is moving.
2) When the observer is moving.
Q: Name one routine activity during which we can observe the Doppler Effect?
Physics Waves Exam
Student Forum
Other Class 11th Physics Chapters
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Solids
- NCERT Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Notes
- Physics Motion in Plane
- Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Physics Motion in Straight Line
- Physics System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Physics Oscillations
- Physics Waves
- Physics Thermal Properties of Matter
- Physics Motion
- Physics Gravitation
- Physics Thermodynamics
- Physics Work, Energy and Power
- Physics Units and Measurement
- Physics Laws of Motion
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test