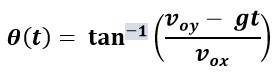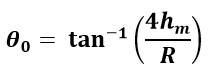ncert solutions physics class 11th
Get insights from 152 questions on ncert solutions physics class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about ncert solutions physics class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.32
(a) Let be the angle at which the projectile is fired w.r.t. the x-axis, since depends on t
Therefore tan since (Vy=Voy -gt and Vx = Vox)
(b) Since = sin2 /2g…….(1)
R = sin2 /g …….(2)
Dividing (1) by (2)
( /R) = [ sin2 /2g]/[ sin2 /g] = / 4
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.31
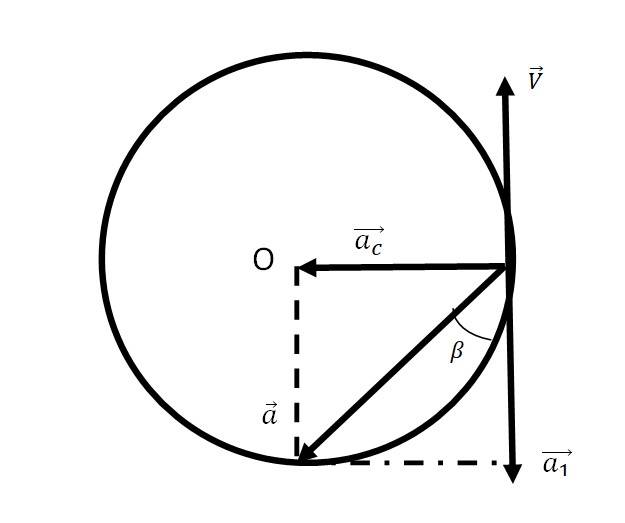
Speed of the cyclist = 27 km/h = 7.5 m/s
Radius of the road = 80m
The net acceleration is due to braking and the centripetal acceleration
Acceleration due to braking = 0.5 m/s2
Centripetal acceleration a = v2r = (7.5)2/80= 0.703 m/s2
The resultant acceleration is given by a = sqrt ( + ) = sqrt ( + ) = 0.86 m/s2
tan = AC / at = 0.7/0.5, = 54.5
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.30
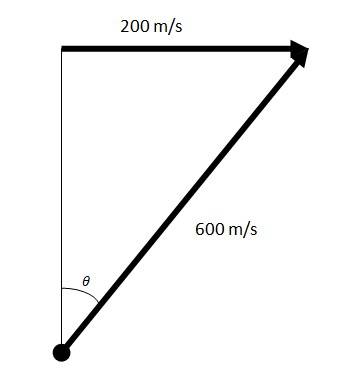
Speed of the fighter plane = 720 km/h = 200 m/s
The altitude of the plane = 1.5 km =1500 m
Velocity of the shell = 600 m/s
= 200/600
Let H be the minimum altitude for the plane to fly, without being hit
Using equation H = sin2 (90-
= (6002cos2 )/2g
= 360000 { ( 1 + cos2 )/2}/2 10
= 16000 m = 16 km
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.29 The angle of projectile = 30
The bullet hits the ground at a distance of 3 km, Range R = 3 km
We know horizontal range for a projectile motion, R = sin2 / g
3 = sin60 / g
= 3/ sin60 = 3.464 …………… (1)
To hit a target at 5 km,
Max Range, = …………. (2)
On comparing equation (1) and (2), we get
= 3.464
Hence, the bullet will not hit the target even by adjusting its angle of projection.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.28
(a) We cannot associate the length of a wire bent into a loop with a vector.
(b) We can associate a plane area with a vector.
(c) We cannot associate the volume of a sphere with a vector.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.27 No in the both the cases.
A physical quantity which is having both direction and magnitude is not necessarily a vector. For instance, in spite of having direction and magnitude, current is a scalar quantity. The basic necessity for a physical quantity to fall in a vector category is that it ought to follow the “law of vector addition”.
As the rotation of a body about an axis does not follow the basic necessity to be a vector i.e. it does not follow the “law of vector addition”.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.26 Yes and No
A vector in space has no distinct location. The reason behind this is that a vector stays unchanged when it displaces in a way that its direction and magnitude do not change.
A vector changes with time. For instance, the velocity vector of a ball moving with a specific speed fluctuates with time.
Two equivalent vectors situated at different locations in space do not generate the same physical effect. For instance, two equivalent forces acting at different points on a body to rotate the body, but the combination will not generate the equivalent turning effect.
New question posted
6 months agoNew answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Initial kinetic energy of the rocket =
Initial potential energy of the rocket =
Total initial energy =
If 20% of initial kinetic energy is lost due to Martian atmosphere resistance, then only 80% of its kinetic energy helps in reaching a height
Total initial energy available = 0.8
Maximum height reached by the rocket = h
At this height, the velocity and hence the kinetic energy of the rocket becomes zero.
Total energy of the rocket at height h =
Applying the law of conservation of energy for the rocket, we can write:
0.4 =
0.4 = GM(
0.4 = GM( )
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mass of the spaceship, = 1000 kg
Mass of the Sun, M = 2 * 1030 kg
Mass of Mars, = 6.4*1023 kg
Orbital radius of Mars, R = 2.28 *108 km = 2.28 *1011 m
Radius of Mars, r = 3395 km = 3.395
Universal Gravitational constant, G = 6.67*10-11 N m2 kg–2
Potential energy of the spaceship due to the gravitational attraction of the Sun =
Potential energy of the spaceship due to the gravitational attraction of Mars=
Since the spaceship is stationed on Mars, its velocity and hence its kinetic energy will be zero
Total energy of the spaceship = = + )
The negative sign indicates that th
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 680k Reviews
- 1800k Answers