ncert solutions physics class 11th
Get insights from 152 questions on ncert solutions physics class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about ncert solutions physics class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) Decreases - Acceleration due to gravity at depth h is given by = (1 – )g, where g = acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Earth. From this equation, it is clear that acceleration due to gravity decreases with increase in height
(b) Decreases – Acceleration due to gravity at depth d is given by = (1- )g. So the acceleration due to gravity decreases with increase in depth.
(c) Mass of the body – Acceleration due to gravity of body mass m is given by the relation g = , where G = Universal gravitation constant, M = mass of the Earth and R = radius of the Ear
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
velocity of a freely falling body is v=
And
-1
The wavelength of a photon needed to remove a proton from a nucleus which is bound to the nucleus with 1 MeV energy is nearly
a) 1.2 nm (b) 1.2 x 10-3 nm
(c) 1.2 x 10-6 nm (d). 1.2 x 10 nm
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
(d)
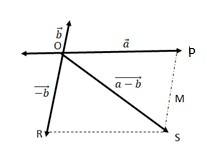
We can write
OS + PS > OP …….(i)
OS > PS – OP …….(ii)
+ ….(iii)
The quantity on the LHS is always positive and that on the RHS can be positive or negative. To make both quantities positive, we take modulus of both sides as:
> ….(iv)
If the two vectors and act along a straight line but in the opposite direction, then we can write = -
Combining (iv) and (v), we get
-
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.30 The decay process of free neutron at rest is given as:
n
From Einstein's mass-energy relation, we have the energy of electron as? where,
? m = Mass defect = Mass of neutron – ( Mass of proton + mass of electron)
c = speed of light
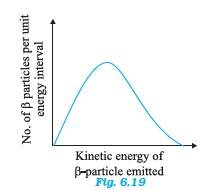
? m and c are constant. Hence, the given two-body decay is unable to explain the continuous energy distribution in the -decay of a neutron or a nucleus. The presence of neutrino von the LHS of the decay correctly explain the continuous energy distribution.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
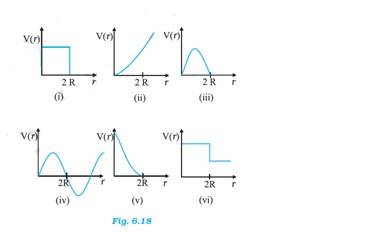
6.29 The potential energy of two masses in a system is inversely proportional to the distance between them. The potential energy of the system of two balls will decrease as they get closer to each other. When the balls touch each other, the potential energy becomes zero, I.e. at r = 2R. The potential energy curve in (i), (ii), (iii), (iv) and (vi) do not satisfy these conditions. So there is no elastic collision.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.28 Mass, m = 200 kg
Speed, v = 36 km/h = 10 m/s
Mass of the boy, M = 20 kg
Initial momentum = (M + m)v = (20 + 200) x 10 kg-m/s = 2200 kg-m/s
If v' is the final velocity of the trolley, then
The final momentum = (M+m) x v' – M x 4= 220v'-80
According to the law of conservation of energy,
Initial momentum = final momentum
2200 = 220v'-80
V' = 10.36 m/s
Time required by the boy to travel 10m = 10/4 = 2.5 s
Distance travel by trolley in 2.5 s = 10.36 x 2.5 m = 25.9 m
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.27 Mass of the bolt, m = 0.3 kg, Height of the elevator, h = 3 m
Since the bolt did not rebound, the entire potential energy got converted into heat.
The potential energy of the bolt = mgh = 0.3 x 9.8 x 3 J = 8.82 J
The heat produced will remain same even if the lift is stationary, since g = constant
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
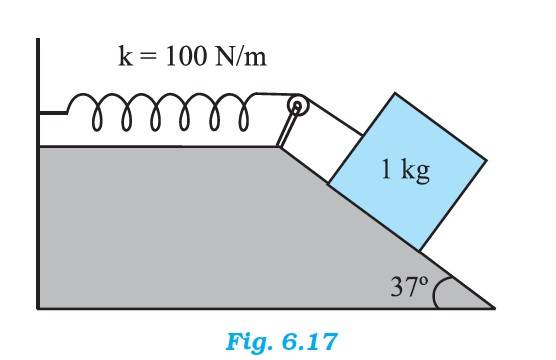
6.26 Mass of the block = 1 kg
Spring constant = 100 N/m
Displacement of the block, x = 10 cm = 0.1 m
At equilibrium, normal reaction, R =
Frictional force, F = =
Net force acting on the block down on the incline = - F
= -
=mg ( )
At equilibrium,
Work done = Potential energy of the stretched string
mg ( ) = (1/2)kx2
1 x 10 x ( ) = (1/2) x 100 x 0.1
10 x (0.602 – = 0.5 x 100 x 0.1
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
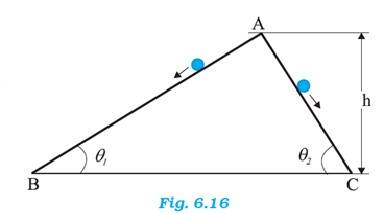
6.25 From the law of conservation of energy,
the potential energy at the top = Kinetic energy at the bottom
mgh = (1/2)m ….(1)
and
mgh = (1/2)m ….(2)
= , Both the stones will reach with the same speed
For stone 1, the force acting on the stone 1 is given by , = m = mg
= g
For stone 2, = g
As , >
From v = u + at, we get t = v/a
Therefore < Stone 2 will reach faster than stone 1
From the law of conservation of energy
mgh = (1/2) mv2
v = = 14 m/s ( Given h = 10 m)
The time taken by two stones given as
&
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.24 Mass of the bullet, = 0.012 kg
Initial speed of the bullet, u = 70 m/s
Mass of the wooden block , = 0.4 kg
Initial speed of the wooden block = 0
Let's assume, final speed of the bullet = v
Applying the law of conservation of momentum
Hence v = ( = 2.04 m/s
Let h be the height by which the block rise. Applying law of conservation of energy
Potential energy of the combined bullet + block = Kinetic energy of the combination
(1/2)
h = /2g = 0.212 m
The heat produced = Initial kinetic energy of the bullet – final kinetic energy of the combination
= (1/2) - (1/2)
= (1/2
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 679k Reviews
- 1800k Answers