Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Thirteen
Get insights from 32 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Thirteen, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Thirteen
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When the gas is compressed adiabatically, the total work done on the gas increases its internal energy which in turn increases the KE of the gas molecule and hence, the collisions between molecules also increases.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
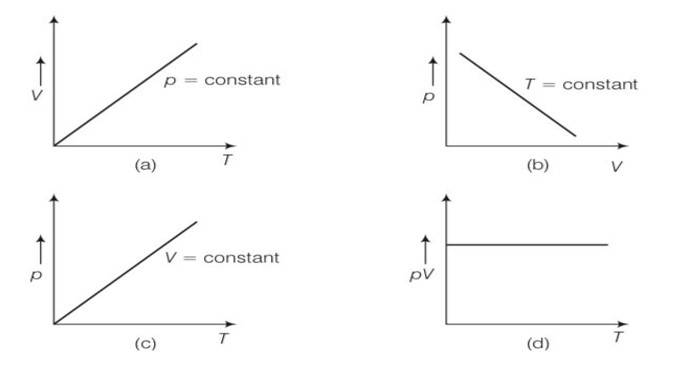
(a), (c) pV=nRT
(a) when pressure p =constant
volume is directly proportional to temperature
(b) when T= constant
from PV =constant
so the graph is rectangular hyperbola
(c) when V =constant
from pressure is directly proportional to temperature.
So the graph is straight the passes through the origin.
PV
PV/T=constant
So the graph hence through origin. So d is correct.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (d) The total energy associated with the molecule is
E=
The number of independent terms in the above expressions is 5. So we can predict velocities of molecule by maxwell's distribution, hence the above expression obeys maxwell 's distribution .
So 2 rotational and 3 translational energies are associated with each molecule
So rotational energy at a given temperature is 2/3 of the translational KE of each molecule.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) According to kinetic theory, we know walls only exert perpendicular forces on molecule. They do not exert parallel force . so there is only change in translational motion.
So pV=2/3E
Where E is representing only translational part of energy.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
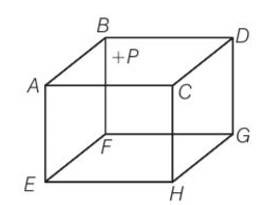
(b), (d) due to the presence of external positive charge on face ABCD. The usual expression for pressure on the basis of kinetic energy will not be valid as ions would also experience electrostatic force. So presence of positive charge the isotropy is also lost.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) pV=nRT
So n= PV/RT
As number moles are fixed
P2=p1V1 (T2/V2T1)
=
= P
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) For a function f (v), the number of molecules n=f (v) which are having speeds between v and v+dv
So f1 (v) and f2 (v) will obey's maxwell distribution law
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) When number of molecules breaks then number of moles would become double.
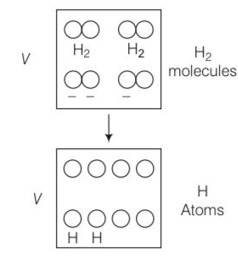
P where n is the number of moles and T is temperature of ideal gas
As gases breaks number of moles becomes twcice of initial so n2 =2n1
= 20
p2=20p1
so 20 times
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
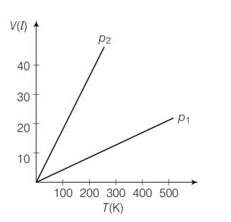
(a) Pressure is inversely proportional to slope
So
So p1 > p2
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
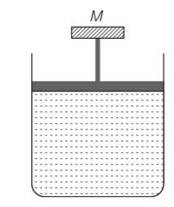
(c) The pressure inside the gas will be
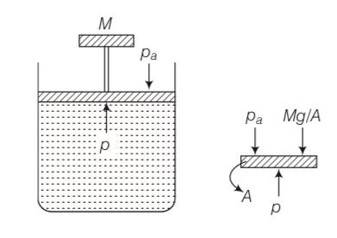
P= pa+Mg/A
A= area of piston
Pa= atmospheric pressure
Mg = weight of piston
When temperature is increases
pV=nRT so volume increases at constant pressure.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 680k Reviews
- 1800k Answers