physics ncert exemplar solutions class 12th chapter two
Get insights from 123 questions on physics ncert exemplar solutions class 12th chapter two, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about physics ncert exemplar solutions class 12th chapter two
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c), (d) Case
A: When key K is kept closed and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle.
The battery maintains the potential difference across connected capacitor in every circumstance. The separation between two plates increases which in turn decreases its capacitance (C=? 0A/d)and potential difference across connected capacitor continue to be the same as capacitor is still connected with battery. So the charge stored decreases as Q = CV.
Case B: When key K is opened and plates of capacitors are moved apart using insulating handle.The charge s
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b) The potential of a body is due to charge of the body and due to the charge of surrounding. If there are no charges anywhere else outside, then the potential of the body will be due to its own charge. If there is a cavity inside a conducting body, then charge can be placed inside the body. Hence there must be charges on its surface or inside itself. Also The charge resides on the outer surface of a closed charged conductor. Hence there cannot be any charge in the body of the conductor.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
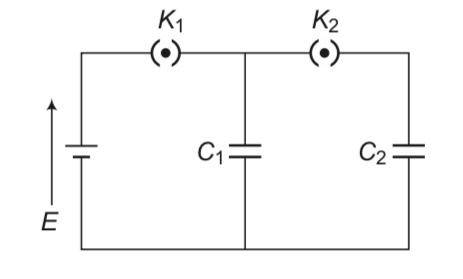
(a), (d) Initially key K1 is closed and key K2 is open, the capacitor C1 is charged by battery and capacitor C2 is still uncharged. Now K1 is opened and K2 is closed, the capacitors C1 and C2 both are connected in parallel. The charge stored by capacitor C1, gets redistributed between C1 and C2 till their potentials become same, i.e., V2 = V1.
By law of conservation of charge, the charge stored in capacitor Cx is equal to sum of charges on capacitors C1 and C2 when K1 is opened and K2 is closed, i.e., Q
New question posted
6 months agoNew answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b), (c) We know, the electric field intensity E and electric potential V are dV related as E =- dV/dr or we can write |E|=ΔV/Δr
The electric field intensity E and electric potential V are related as E = 0 and for V = constant, dV/dr=0 this imply that electric field intensity E = 0.
If some charge is present inside the region then electric field cannot be zero at that region, for this V = constant is not valid.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b), (c) If potential of two point is same then work done is also zero according to relation As W=qdv=q (final potential-initial potential).
Also W=-qdv= -q
For equipotential surface V2-V2=0 and W=0
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (b), (c) Properties of equipotential surfaces
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers