Physics
Get insights from 5.6k questions on Physics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Displacement of an elastic wave y =3sinwt+4coswt
3= acos
4=asin
On dividing above equation
tan =4/3
a2cos2 +a2sin2 = 32+42
a2 (cos2 )=25
a2.1=25
a=5
Y= 5cos +5sin
= 5 [cos ]=5sin (wt+ )
Hence amplitude =5cm
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Frequency of tuning fork A
Hz
Probable frequency of tuning fork B
Hz or 507Hz
When B is loaded its frequency reduces .
If it is 517Hz it might reduced to 507Hz given again a beat of 5Hz
If it 507Hz reduction will always increase the beat frequency, hence Hz
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As the organ pipe is open at both ends, hence for first harmonic
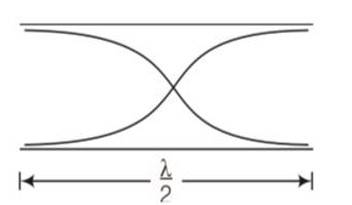
l=
V=c/2l
For pipe closed at one end
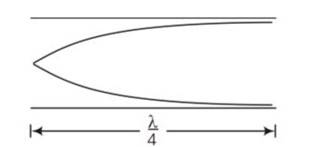
V'=c/4L'
Hence v=v'
c/2L =c/4L'
L'/L=2/4=1/2
L'=L/2
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Wire of twice the length vibrates in its second harmonic . thus, if the tuning fork resonates at L, it will resonate at 2L
So the sonometer frequency is
Now if it vibrates with length L we assume
n=n1
When length is doubled then
Dividing above equations
To Keep the resonance
n2=2n1 so it resonates 2nd harmonic.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Wave functions y= 2cos2 (10t-0.0080x + 3.5)
= 2cos(20 )
Now standard equation of travelling wave can be written as
Y= a cos (wt-kx+ )
So by comparing with above equation
a= 2cm
w=20
k=0.016
path difference =4cm
(a) phase difference path difference
(e) T= /w=2 /20
At x=100cm
t=T
=20
= 20
Again at x=100cm t=5s
=20
=100
From above two equation phase difference
=(100 )-
= 100
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
standard equation of a progressive wave is given by
Y=asin(wt-kx+ )
This is travelling along positive x- direction
Given equation is y=5sin(100 )
Comparing with standard equation
(a) amplitude =5m
(b) k=2 =0.4x
wavelength =2 =
(c) w=10
w=2
frequency v= 100 =50Hz
(d) wave velocity
=100 =1000/4
250m/s
(e) y= 5sin(100 )
dy/dt = particle velocity
dy/dt = 5(100 cos[100 ]
for particle velocity amplitude (dy/dt)max which will be for cos[100 ]max=1
so particle velocity amplitude =(dy/dt)max =5(100 ) =550 m/s
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) The equation y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x ) is representing a travelling wave along x-direction
(b) The equation y = 5 cos (4x ) sin (20t) represents a stationary wave, because it contains sin cos terms ., combinations of two progressive waves.
(c) The equation y = 10 cos [ (252 – 250) πt ] cos [ (252+250)πt ] involving sum and difference of two near by frequencies 252 and 250 have this equation represents beats formation.
(d) As the equation y = y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2) involves negative sign with x, have if represents a travelling wave along
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
we know that rms speed of molecules of a gas
C=
Where M is the molar mass of the gas
Speed of sound wave in gas v=
On dividing above equation we get
c/v =
c/v =
where = adiabatic constant for diatomic gas
c/v=constant
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Speed of wave in solid =8km/s
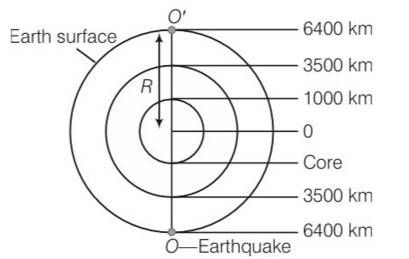
Speed of wave in liquid = 5km/s
Required time = [ ]
= [ ]
= [125+500+362.5] =1975 (diameter = radius )
As we are considering at diametrically opposite point, hence there is a multiplication of 2
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b, c, d) velocity of ball before collision =10+1=11m/s
Speed after collision= 10-1=9m/s
As the speed is changing after travelling 10 m and speed is 1m/s hence, time duration of the changing speed is 10
Since the collision of the ball is perfectly elastic there is no dissipation of energy hence, total momentum and kinetic energy are conserved.
Since the train is moving with constant velocity hence, it will act as inertial frame of reference as that of earth and acceleration will be same in both cases.
As the collision is perfectly elastic so momentum and total energy (K.E and
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
