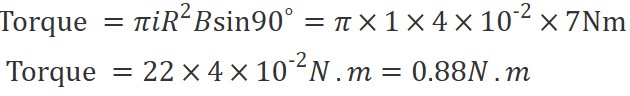- Waves Questions and Answers
- JEE Mains 2022
- 01 Mock Test 2025
- 01 Oct 2025
- NEET 2025
Waves Questions and Answers
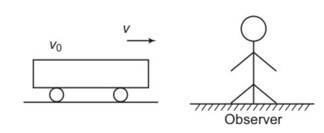
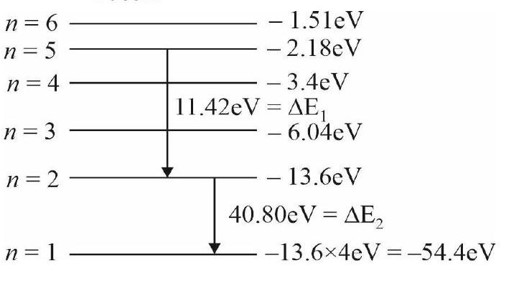
| 15.1 The earth has a radius of 6400 km. The inner core of 1000 km radius is solid. Outside it, there is a region from 1000 km to a radius of 3500 km which is in molten state. Then again from 3500 km to 6400 km the earth is solid. Only longitudinal (P) waves can travel inside a liquid. Assume that the P wave has a speed of 8 km s-1 in solid parts and of 5 km s-1 in liquid parts of the earth. An earthquake occurs at some place close to the surface of the earth. Calculate the time after which it will be recorded in a seismometer at a diametrically opposite point on the earth if wave travels along diameter? |
| Explanation- Speed of wave in solid =8km/s Speed of wave in liquid = 5km/s Required time = [ ] =[ ] =[125+500+362.5] =1975 (diameter = radius ) As we are considering at diametrically opposite point, hence there is a multiplication of 2 |
| 15.2 If c is r.m.s. speed of molecules in a gas and v is the speed of sound waves in the gas, show that c/v is constant and independent of temperature for all diatomic gases. |
| Explanation- We know that rms speed of molecules of a gas C= Where M is the molar mass of the gas Speed of sound wave in gas v= On dividing above equation we get c/v = c/v = where = adiabatic constant for diatomic gas
c/v=constant |
| 15.3 Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement of an elastic wave. (a) y = 5 cos (4x ) sin (20t) (b) y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2) (c) y = 10 cos [(252 – 250) πt ] cos [(252+250)πt ] (d) y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x ) State which of these represent (a) A travelling wave along –x direction (b) A stationary wave (c) Beats (d) A travelling wave along +x direction. Given reasons for your answers. |
| Explanation- (a) the equation y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x ) is representing a travelling wave along x-direction (b) the equation y = 5 cos (4x ) sin (20t) represents a stationary wave , because it contains sin cos terms ., combinations of two progressive waves. (c) the equation y = 10 cos [(252 – 250) πt ] cos [(252+250)πt ] involving sum and difference of two near by frequencies 252 and 250 have this equation represents beats formation. (d) as the equation y = y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2) involves negative sign with x , have if represents a travelling wave along x – direction. |
| 15.4 In the given progressive wave y = 5 sin (100πt – 0.4πx ) where y and x are in m, t is in s. What is the (a) Amplitude (b) Wave length (c) Frequency (d) Wave velocity (e) Particle velocity amplitude. |
| Explanation- standard equation of a progressive wave is given by Y=asin(wt-kx+ ) This is travelling along positive x- direction Given equation is y=5sin(100 ) Comparing with standard equation (a) amplitude =5m (b) k=2 =0.4x wavelength =2 = (c) w=10 w=2 frequency v= 100 =50Hz (d) wave velocity =100 =1000/4 250m/s (e) y= 5sin(100 ) dy/dt = particle velocity dy/dt = 5(100 cos[100 ] for particle velocity amplitude (dy/dt)max which will be for cos[100 ]max=1 so particle velocity amplitude =(dy/dt)max =5(100 ) =550 m/s |
Commonly asked questions
The earth has a radius of 6400 km. The inner core of 1000 km radius is solid. Outside it, there is a region from 1000 km to a radius of 3500 km which is in molten state. Then again from 3500 km to 6400 km the earth is solid. Only longitudinal (P) waves can travel inside a liquid. Assume that the P wave has a speed of 8 km s-1 in solid parts and of 5 km s-1 in liquid parts of the earth. An earthquake occurs at some place close to the surface of the earth. Calculate the time after which it will be recorded in a seismometer at a diametrically opposite point on the earth if wave travels along diameter?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Speed of wave in solid =8km/s
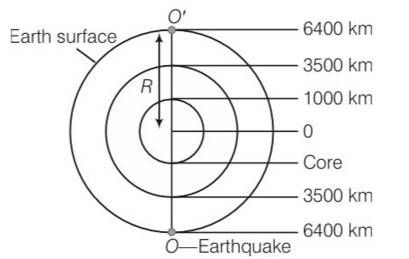
Speed of wave in liquid = 5km/s
Required time = [ ]
= [ ]
= [125+500+362.5] =1975 (diameter = radius )
As we are considering at diametrically opposite point, hence there is a multiplication of 2
If c is r.m.s. speed of molecules in a gas and v is the speed of sound waves in the gas, show that c/v is constant and independent of temperature for all diatomic gases.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
we know that rms speed of molecules of a gas
C=
Where M is the molar mass of the gas
Speed of sound wave in gas v=
On dividing above equation we get
c/v =
c/v =
where = adiabatic constant for diatomic gas
c/v=constant
Given below are some functions of x and t to represent the displacement of an elastic wave.
(a) y = 5 cos (4x ) sin (20t)
(b) y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2)
(c) y = 10 cos [(252 – 250) πt ] cos [(252+250)πt ]
(d) y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x )
State which of these represent
(a) A travelling wave along –x direction
(b) A stationary wave
(c) Beats
(d) A travelling wave along +x direction.
Given reasons for your answers.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) The equation y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x ) is representing a travelling wave along x-direction
(b) The equation y = 5 cos (4x ) sin (20t) represents a stationary wave, because it contains sin cos terms ., combinations of two progressive waves.
(c) The equation y = 10 cos [ (252 – 250) πt ] cos [ (252+250)πt ] involving sum and difference of two near by frequencies 252 and 250 have this equation represents beats formation.
(d) As the equation y = y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2) involves negative sign with x, have if represents a travelling wave along x – direction.
In the given progressive wave y = 5 sin (100πt – 0.4πx ) where y and x are in m, t is in s. What is the
(a) Amplitude
(b) Wave length
(c) Frequency
(d) Wave velocity
(e) Particle velocity amplitude.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
standard equation of a progressive wave is given by
Y=asin(wt-kx+ )
This is travelling along positive x- direction
Given equation is y=5sin(100 )
Comparing with standard equation
(a) amplitude =5m
(b) k=2 =0.4x
wavelength =2 =
(c) w=10
w=2
frequency v= 100 =50Hz
(d) wave velocity
=100 =1000/4
250m/s
(e) y= 5sin(100 )
dy/dt = particle velocity
dy/dt = 5(100 cos[100 ]
for particle velocity amplitude (dy/dt)max which will be for cos[100 ]max=1
so particle velocity amplitude =(dy/dt)max =5(100 ) =550 m/s
For the harmonic travelling wave y = 2 cos 2π (10t–0.0080x + 3.5) where x and y are in cm and t is second. What is the phase difference between the oscillatory motion at two points separated by a distance of
(a) 4 m
(b) 0.5 m
(c) 2 λ
(d) 3 4 λ (at a given instant of time)
(e) What is the phase difference between the oscillation of a particle located at x = 100cm, at t = T s and t = 5 s
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Wave functions y= 2cos2 (10t-0.0080x + 3.5)
= 2cos(20 )
Now standard equation of travelling wave can be written as
Y= a cos (wt-kx+ )
So by comparing with above equation
a= 2cm
w=20
k=0.016
path difference =4cm
(a) phase difference path difference
(e) T= /w=2 /20
At x=100cm
t=T
=20
= 20
Again at x=100cm t=5s
=20
=100
From above two equation phase difference
=(100 )-
= 100
A sonometer wire is vibrating in resonance with a tuning fork. Keeping the tension applied same, the length of the wire is doubled. Under what conditions would the tuning fork still be is resonance with the wire?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Wire of twice the length vibrates in its second harmonic . thus, if the tuning fork resonates at L, it will resonate at 2L
So the sonometer frequency is
Now if it vibrates with length L we assume
n=n1
When length is doubled then
Dividing above equations
To Keep the resonance
n2=2n1 so it resonates 2nd harmonic.
An organ pipe of length L open at both ends is found to vibrate in its first harmonic when sounded with a tuning fork of 480 Hz. What should be the length of a pipe closed at one end, so that it also vibrates in its first harmonic with the same tuning fork?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As the organ pipe is open at both ends, hence for first harmonic
l=
V=c/2l
For pipe closed at one end
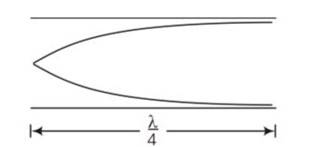
V’=c/4L’
Hence v=v’
c/2L =c/4L’
L’/L=2/4=1/2
L’=L/2
A tuning fork A, marked 512 Hz, produces 5 beats per second, where sounded with another unmarked tuning fork B. If B is loaded with wax the number of beats is again 5 per second. What is the frequency of the tuning fork B when not loaded?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Frequency of tuning fork A
Hz
Probable frequency of tuning fork B
Hz or 507Hz
When B is loaded its frequency reduces .
If it is 517Hz it might reduced to 507Hz given again a beat of 5Hz
If it 507Hz reduction will always increase the beat frequency, hence Hz
The displacement of an elastic wave is given by the function
y = 3 sin ωt + 4 cos ωt.
where y is in cm and t is in second. Calculate the resultant amplitude.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Displacement of an elastic wave y =3sinwt+4coswt
3= acos
4=asin
On dividing above equation
tan =4/3
a2cos2 +a2sin2 = 32+42
a2 (cos2 )=25
a2.1=25
a=5
Y= 5cos +5sin
= 5 [cos ]=5sin (wt+ )
Hence amplitude =5cm
A sitar wire is replaced by another wire of same length and material but of three times the earlier radius. If the tension in the wire remains the same, by what factor will the frequency change?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Frequency of vibrations produced by a stretched wire
Mass per unit length = mass/length =
so when radius is tripled v will be 1/3 rd of previous value.
At what temperatures (in 0C) will the speed of sound in air be 3 times its value at OoC?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
we know the speed of air v
3/1 =
TT=273
=2457-273=2184 oC
When two waves of almost equal frequencies n1 and n2 reach at a point simultaneously, what is the time interval between successive maxima?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let n1>n2 beat frequency
As we know time per beats = 1/frequency
Time period beats = Tb= 1/
A steel wire has a length of 12 m and a mass of 2.10 kg. What will be the speed of a transverse wave on this wire when a tension of 2.06 × 104 N is applied?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Given that length of wire l=12m
Mass of the wire m=2.10kg
T= 2.06
Speed of transverse wave v= =
A pipe 20 cm long is closed at one end. Which harmonic mode of the pipe is resonantly excited by a source of 1237.5 Hz ?(sound velocity in air = 330 m/s)
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
length of pipe
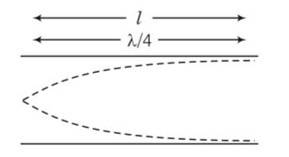
L=20cm =20
=3
Hence 3rd harmonic node of the pipe is resonantly excited by the source of the given frequency.
A train standing at the outer signal of a railway station blows a whistle of frequency 400 Hz still air. The train begins to move with a speed of 10 m/s towards the platform. What is the frequency of the sound for an observer standing on the platform? (sound velocity in air = 330 m/s)
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As the source is moving towards the observer hence apparent frequency observed is more than the natural frequency
Frequency of whistle
Speed of train = vt= 10m/s
Velocity of sound in air =v= 330m/s
Apparent frequency when source is moving vapp= (v/v-vt)v
= (
=
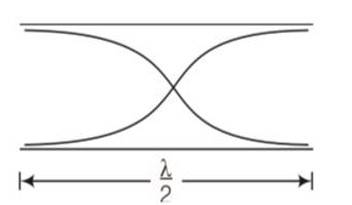
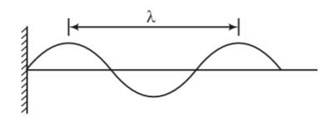
The wave pattern on a stretched string is shown in Fig. Interpret what kind of wave this is and find its wavelength
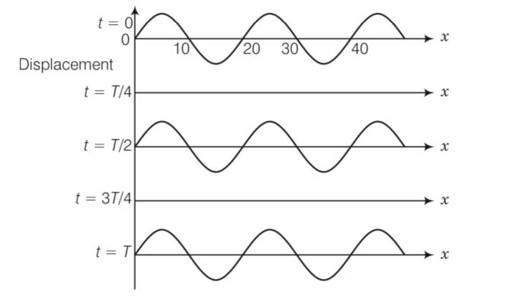
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
We have to observe the displacement and position of different points, then accordingly nature of two waves decided
Points on positions x= 10,20,30,40 never move, always at mean position with respect to time . these are forming nodes which forms a stationary wave
Distance between two successive nodes =
node to node distance)
=2 (20-10)
= 2 (10)=20cm
The pattern of standing waves formed on a stretched string at two instants of time are shown in Fig. The velocity of two waves superimposing to form stationary waves is 360 ms–1 and their frequencies are 256 Hz
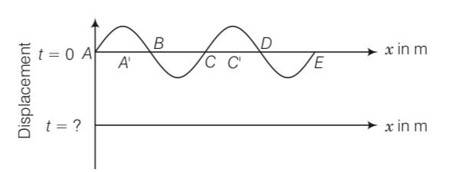
(a) Calculate the time at which the second curve is plotted.
(b) Mark nodes and antinodes on the curve.
(c) Calculate the distance between A′ and C′ .
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Given frequency of the wave v=256Hz
T=
(a) time taken to pass through mean position is
t=T/4=1/40 =3.9 9.8 10-4s
(b) nodes are A, B, C, D, E (having zero displacement)
antinodes are A’ and C’ (having maximum displacement)
(c) it is clear from diagram A’ and C’ are forming antinodes have separation= v/v’=360/256=1.41m
A tuning fork vibrating with a frequency of 512Hz is kept close to the open end of a tube filled with water (Fig. 15.4). The water level in the tube is gradually lowered. When the water level is 17cm below the open end, maximum intensity of sound is heard. If the room temperature is 20° C, calculate
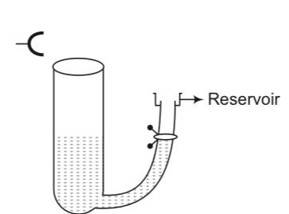
(a) Speed of sound in air at room temperature
(b) Speed of sound in air at 0° C
(c) If the water in the tube is replaced with mercury, will there be any difference in your observations?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
consider the frequency of tuning fork= 512Hz
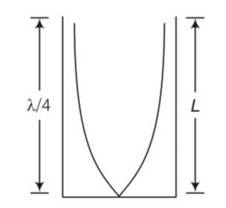
(a) L=
V= = 512
= 348.16m/s
(b) we know that v
=
Vo=
(c) Resonance will be observed at 17cm length of air column only intensity of sound heard may be greater due to more complete reflection of the sound waves at the mercury surface because mercury is more denser than water.
Show that when a string fixed at its two ends vibrates in 1 loop, 2 loops, 3 loops and 4 loops, the frequencies are in the ratio 1:2:3:4.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let there are n number of loops in the string
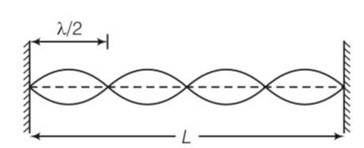
length corresponding each loop is
So we can write L=
v/ =2L/n
so frequency v=
v
so
= 1:2:3:4
Water waves produced by a motor boat sailing in water are
(a) Neither longitudinal nor transverse.
(b) Both longitudinal and transverse.
(c) Only longitudinal.
(d) Only transverse.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Water waves produced by a motorboat are both longitudinal and transverse because it produce both lateral and transverse wave In the medium.
Sound waves of wavelength λ travelling in a medium with a speed of v m/s enter into another medium where its speed is 2v m/s. Wavelength of sound waves in the second medium is
(a) λ
(b) 2 λ
(c) 2λ
(d) 4λ
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) Let frequency of the two will be and it is same in both medium
So v/ = v’/
= v’ /v
= 2v /v=2
Where and ’ and v and v’ are wavelength and speeds of first and second medium respectively
Speed of sound wave in air
(a) Is independent of temperature.
(b) Increases with pressure.
(c) Increases with increase in humidity.
(d) Decreases with increase in humidity.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) Due to presence of moisture density of air decreases.
As we know speed of sound in air v=
So v
v2/v1=
2 (moist air)< 1 (dry air)
So v2>v1
So speed of sound wave increases with increase in humidity
Change in temperature of the medium changes
(a) Frequency of sound waves.
(b) Amplitude of sound waves.
(c) Wavelength of sound waves.
(d) Loudness of sound waves.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) Speed of sound wave in a medium v
Clearly when temperature changes speed also changes
As v= as frequency remains constant and speed changes so wavelength changes
With propagation of longitudinal waves through a medium, the quantity transmitted is
(a) Matter.
(b) Energy.
(c) Energy and matter.
(d) Energy, matter and momentum.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Propagation of longitudinal waves through a medium leads to transmission of energy through the medium without matter being transmitted. So no movement of energy and matter hence momentum
Which of the following statements are true for wave motion?
(a) Mechanical transverse waves can propagate through all mediums.
(b) Longitudinal waves can propagate through solids only.
(c) Mechanical transverse waves can propagate through solids only.
(d) Longitudinal waves can propagate through vacuum.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) When mechanical transverse wave propagates through a medium, the constituents of the medium oscillate perpendicular to wave motion causing change in shape. That is each element of the medium is subjected to shearing stress. Solids and strings have shear, that is why tey bear stress. But in fluids there is no fixed shape so transverse waves does not formed in fluid.
A sound wave is passing through air column in the form of compression and rarefaction. In consecutive compressions and rarefactions,
(a) Density remains constant.
(b) Boyle’s law is obeyed.
(c) Bulk modulus of air oscillates.
(d) There is no transfer of heat.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) Due to compression and rarefactions density of the medium changes.at compressed regions density is maximum and at rarefactions density is minimum
As density is changing so boyle, s law not obeyed
Bulk modulus remains same
The time of compression and rarefaction is too small so no transfer of heat.
Equation of a plane progressive wave is given by y=0.6sin2 . On reflection from a denser medium its amplitude becomes 2/3 of the amplitude of the incident wave. The equation of the reflected wave is
(a) y=0.6sin2
(b) y=-0.4sin2
(c) y=0.4sin2
(d) 0.4sin2
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Amplitude of reflected wave
Af= =2 (0.6)/3=0.4 units
Equation of incident wave
Yi=0.6sin2
For reflected wave
yr=Arsin2 (t+x/2+ )
Yr=-0.4sin2
A string of mass 2.5 kg is under a tension of 200 N. The length of the stretched string is 20.0 m. If the transverse jerk is struck at one end of the string, the disturbance will reach the other end in
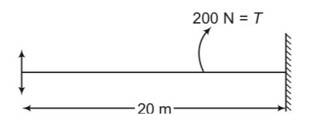
(a) one second
(b) 0.5 second
(c) 2 seconds
(d) data given is insufficient.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) m=2.5kg
mass per unit length
=m/l =2.5/20=125/10=0.125kg/m
V=
L=v
20=
= 20
A train whistling at constant frequency is moving towards a station at a constant speed V. The train goes past a stationary observer on the station. The frequency n′ of the sound as heard by the observer is plotted as a function of time t (Fig) . Identify the expected curve
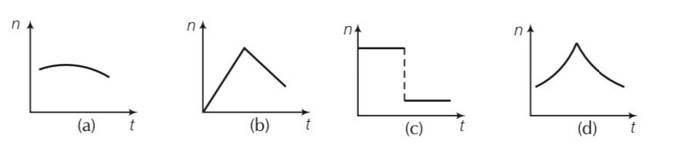
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) Let frequency of the source is no
Let the speed of sound wave in the medium is v
As observer is stationary
Apparent frequency na=
When the train is going away from the observer
Apparent frequency na= =
A transverse harmonic wave on a string is described by y (x,t) = 3.0 sin (36t + 0.018x + π/4) where x and y are in cm and t is in s. The positive direction of x is from left to right.
(a) The wave is travelling from right to left.
(b) The speed of the wave is 20m/s.
(c) Frequency of the wave is 5.7 Hz.
(d) The least distance between two successive crests in the wave is 2.5 cm.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, c) y (x, t)=30sin (36t+0.018x+ )
Y=asin (wt+kx+ )
(a) as the equation involves positive sign with x . hence the wave is travelling from right to left. Hence option a is correct.
(b) W=36
2
=
w/v=0.018
v=2000cm/s=20m/s
(c) 2
= 5.7Hz
(d) , /0.0018cm=3.48cm
The displacement of a string is given by y(x,t) = 0.06 sin (2πx/3) cos (120πt) where x and y are in m and t in s. The length of the string is 1.5m and its mass is 3.0× .
(a) It represents a progressive wave of frequency 60Hz.
(b) It represents a stationary wave of frequency 60Hz.
(c) It is the result of superposition of two waves of wavelength 3 m, frequency 60Hz each travelling with a speed of 180 m/s in opposite direction.
(d) Amplitude of this wave is constant.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b, c) y (x, t) = 0.06 sin (2πx/3) cos (120πt)
(a) y (x, t)=asinkxcoswt
(b) w=120 , f=60hz
(c) k=2 , v =60 (3)=180m/s
(d) since in stationary wave all particles of the medium executes SHM with varying amplitude nodes.
Speed of sound waves in a fluid depends upon
(a) Directly on density of the medium.
(b) Square of Bulk modulus of the medium.
(c) Inversely on the square root of density.
(d) Directly on the square root of bulk modulus of the medium.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c, d) Speed of sound waves in a fluid is given by
V=
V= V so when we increase velocity bulk modulus also increases.
During propagation of a plane progressive mechanical wave
(a) All the particles are vibrating in the same phase.
(b) Amplitude of all the particles is equal.
(c) Particles of the medium executes S.H.M.
(d) Wave velocity depends upon the nature of the medium.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
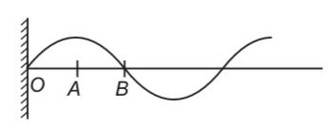
during propagation of a plane progressive mechanical wave
(i) clearly the particles O, A and B are having different phase.
(ii) Particles of the wave are having up and SHM.
(iii) For a progressive wave propagating in a fluid
V= , V=
The transverse displacement of a string (clamped at its both ends) is given by y (x,t) = 0.06 sin (2πx/3) cos (120πt). All the points on the string between two consecutive nodes vibrate with
(a) Same frequency
(b) Same phase
(c) Same energy
(d) Different amplitude.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, d) As we know by y (x, t) = 0.06 sin (2πx/3) cos (120πt)
By comparing the equation with general equation N denotes nodes and A denotes antinodes.
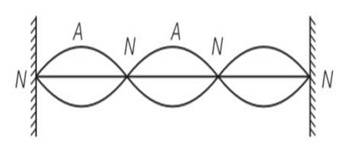
(a) Clearly frequency is common for all the points
(b) Consider all the particles between two nodes they are having same phase at given time
(c) But are having different amplitude of 0.06sin (2 ) and because of different amplitudes they are having different energies.
A train, standing in a station yard, blows a whistle of frequency 400 Hz in still air. The wind starts blowing in the direction from the yard to the station with a speed of 10m/s. Given that the speed of sound in still air is 340m/s,
(a) The frequency of sound as heard by an observer standing on the platform is 400Hz.
(b) The speed of sound for the observer standing on the platform is 350m/s.
(c) The frequency of sound as heard by the observer standing on the platform will increase.
(d) The frequency of sound as heard by the observer standing on the platform will decrease.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b) vo=400Hz, v=340m/s
Vm=10m/s
(a) as both source and observer are stationary, hence frequency observed will be same as natural frequency vo=400Hz
(b) the speed of sound v=v+vw= 340+10=350m/s
(c) there will be on effect on frequency because there is no relative motion between source and observer hence c, d are incorrect.
Which of the following statements are true for a stationary wave?
(a) Every particle has a fixed amplitude which is different from the amplitude of its nearest particle.
(b) All the particles cross their mean position at the same time.
(c) All the particles are oscillating with same amplitude.
(d) There is no net transfer of energy across any plane.
(e) There are some particles which are always at rest.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, d, e) a) clearly every particle at x will have amplitude =asinkx=fixed
b) for mean position =0
coswt=0
wt= (2n-1)
hence for a fixed of n all particles are having same value of time t= (2n-1)
c) amplitude of all the particles are asinkx which is different for different particles at different values of x
d) the energy is a stationary wave is confined between two nodes.
e) particles at different nodes are always at rest.
A particle of mass 'm' is moving in time 't' on a trajectory given by r? = 10αt² i? + 5β(t-5) j?. Where α and β are dimensional constants. The angular momentum of the particle become the same as it was for t = 0 at time t = ______ seconds.
r? = 10αt²î + 5β (t-5)?
v? = dr? /dt = 20αtî + 5β?
As L? = m (r? × v? )
So, at t=0, L=0
given L is same at t=t as at t=0
⇒ r? × v? = 0
⇒ (10αt²î + 5β (t-5)? ) × (20αtî + 5β? ) = 0
⇒ 50αβt² (î×? ) + 100αβt (t-5) (? ×î) = 0
⇒ 50αβt² k? - 100αβt (t-5) k? = 0
⇒ 50t² - 100t (t-5) = 0
⇒ 50t² - 100t² + 500t = 0
⇒ -50t² + 500t = 0
⇒ 50t (10 - t) = 0
⇒ t = 10 second
In the reported figure, two bodies A and B of masses 200g and 800g are attached with the system of springs. Springs are kept in a stretched position with some extension when the system is released. The horizontal surface is assumed to be frictionless. The angular frequency will be _______ rad/s when k = 20 N/m.
ω = √k_eq/μ [μ = (m? )/ (m? +m? ) (Reduced mass)]
k_eq = (k × 4k)/ (k+4k) = 4k/5
ω = √ (4k/5) / (m? / (m? +m? )
= √ (4×20/5) / (0.2×0.8)/ (0.2+0.8)
= √ (16/0.16)
= 10 rad/s
A particle of mass 1 mg and charge q is lying at the mid-point of two stationary particles kept at a distance 2 m when each is carrying same charge q'. If the free charged particle is displaced from its equilibrium position through distance 'x' (x << 1m). The particle executes SHM. Its angular frequency of oscillation will be ______ × 10? rad/s if q' = 1 C.
F_net = -kq²/ (l+x)² + kq²/ (l-x)²
= kq² [ (l+x)² - (l-x)² / (l²-x²)² ]
= kq² [ 4lx / (l²-x²)² ]
For x << l,
ma ≈ -4kq²x / l³
a = - (4kq²/ml³)x
ω² = 4kq²/ml³
ω = √ (4kq²/ml³)
= √ (4 × 9×10? × 10 / (1×10? × 1)
= 6 × 10? rad/s
= 6000 × 10? rad/s
An inductor of 10 mH is connected to a 20 V battery through a resistor of 10 kΩ and a switch. After a long time, when maximum current is set up in the circuit, the current is switched off. The current in the circuit after 1 µs is x/100 mA. Then x is equal to _______. (Take e?¹ = 0.37)
I = I? e? /?
= (20/10000) e^- (1×10? / 10×10? ³)
= 2 × 10? ³ e? ¹
The provided solution calculates as:
= 2 × 10? ³ e? ¹
= 2e? ¹ mA
= 2 × 0.37mA
= 0.74 mA = 74/100 mA
(Note: There seems to be a calculation discrepancy in the source image, the steps shown lead to I = 2e? ¹ mA)
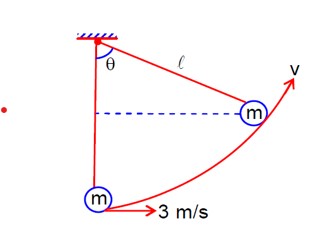
A pendulum bob has a speed of 3 m/s at its lowest position. The pendulum is 50 cm long. The speed of the bob, when the length makes an angle of 60° to the vertical will be _______ m/s. (g = 10 m/s²)
(1/2)mu² = (1/2)mv² + mgl (1-cosθ)
⇒ v² = u² - 2gl (1-cosθ)
⇒ v² = 3² - 2×10×0.5× (1 - 1/2)
⇒ v² = 9 - 5 = 4
v = 2m/s
A body of mass 2 kg moving with a speed of 4 m/s, makes an elastic collision with another body at rest and continues to move in the original direction but with one fourth of its initial speed. The speed of the two body centre of mass is x/10 m/s. Then the value of x is _______ .
From conservation of momentum:
2×4 = 2v? + mv?
Given v? = 1 m/s (interpreted from intermediate steps)
8 = 2 (1) + mv?
mv? = 6 . (i)
From coefficient of restitution (e=1 for elastic collision):
e = (v? - v? )/ (u? - u? )
1 = (v? - v? )/ (4 - 0)
-1 = (v? - v? )/ (0 - 4) (as written in the image)
⇒ 4 = v? - 1
⇒ v? = 5 . (ii)
Put (2) in (1), m (5) = 6
m = 1.2kg
An electric bulb rated as 200 W at 100 V is used in a circuit having 200 V supply. The resistance R that must be put in series with the bulb so that the bulb delivers the same power is _______ Ω.
Given: Power in R_B = 200 W, R_B = 50 Ω, V_source = 200 V
I² R_B = 200
I² (50) = 200
I² = 4 ⇒ I = 2A
Also, I = V_source / (R + R_B)
2 = 200 / (R + 50)
2 (R + 50) = 200
R + 50 = 100
R = 50Ω
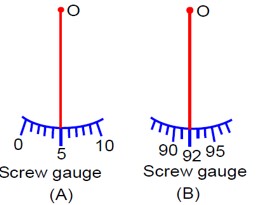
Student A and Student B used two screw gauges of equal pitch and 100 equal circular divisions to measure the radius of a given wire. The actual value of the radius of the wire is 0.322 cm. The absolute value of the difference between the final circular scale readings observed by the students A and B is _______. [Figure shows position of reference 'O' when jaws of screw gauge are closed]. Given pitch = 0.1 cm.
(Figure A shows a positive zero error with the 5th division of the circular scale coinciding with the reference line. Figure B shows a negative zero error with the 92nd division of the circular scale coinciding with the reference line.)
Difference in Reading = Positive Zero Error - Negative Zero Error
= (+5) - [- (100-92)]
= 5 - [-8]
= 13
The value of aluminium susceptibility is 2.2 × 10??. The percentage increase in the magnetic field if space within a current carrying toroid is filled with Aluminium is x/10?. Then the value of x is _______.
We know, μ? = 1 + χ?
B? ∝ μ?
B ∝ μ
(ΔB/B? ) = (B-B? )/B? = (μ-μ? )/μ? = μ/μ? - 1 = μ? - 1 = χ?
% (ΔB/B) = χ? × 100 = 2.2 × 10? × 100 = 22/10?
(Note: The value for χ? in the source image appears to have a typo as 2.2 × 10? , it has been corrected to 2.2 × 10? to match the final answer.)
A circular conducting coil of radius 1 m being heated by the change of magnetic field B passing perpendicular to the plane in which the coil is laid. The resistance of the coil is 2μΩ. The magnetic field is slowly switched off such that its magnitude changes in time as B = (4/π) × 10?³ T [1 - ( t/100 )]. The energy dissipated by the coil before the magnetic field is switched off completely is E = _______ mJ.
ε = |dΦ/dt| = A|dB/dt|
Given B (t), dB/dt = (4/π) × 10? ³ × (-1/100)
ε = (π × 1²) × | (4/π) × 10? ³ × (-1/100)|
= 4 × 10? V
To find when B=0:
B = 0 ⇒ 1 - t/100 = 0
⇒ t = 100 second
Energy Dissipated, E = P × t = (ε²/R) × t
E = (4×10? )² / (2×10? ) × 100 = 80mJ
A double convex lens is made of glass which has its refractive index of 1.55 for violet rays and 1.50 for red rays. If the focal length for violet rays is 20cm, then the focal length for red rays will be cm.
Divide (1) by (2),
A electron collides with a stationary helium ion in its ground state and excites it into higher energy level ![]() . After collision ions emits two photons in succession with a wavelength and to reach its ground state. Quantum number of excited state
. After collision ions emits two photons in succession with a wavelength and to reach its ground state. Quantum number of excited state ![]() is
is
If
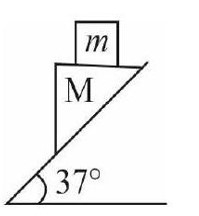
Block of mass M slides down on frictionless incline as shown. The minimum friction coefficient so that block of mass m does not slide with respect to lower block is close to , the nearest integer to I is Take
Acceleration of the combined system along the incline is given by
With respect to block M :
Three points masses and 3m are located at the vertices of an equilateral triangle of side ' a '. The moment of inertia of the system about an axis along the altitude of the triangle passing through m is where N is an integer. The value of N is
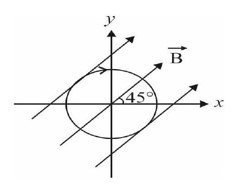
A circular loop of radius R = 20 cm is placed in a uniform magnetic field B = 7 T in x-y plane as shown in figure. The loop carries a current in the direction shown in figure. The magnitude of torque acting on the loop is__ N.m. Take
Kindly consider the following Image
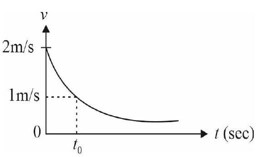
A 1kg particle is moving unidirectionally on a horizontal plane under the action of power , of power supplying energy source. The velocity (v) - time (t) graph that describes the motion of the particle is shown in figure. (Graphs are drawn schematically and are not to scale) The value of ![]() in graph is
in graph is ![]() sec. Find 8x
sec. Find 8x
Kindly consider the following Image
A hot body is being cooled in air according to Newton's law of cooling, the rate of fall of temperature being K times the difference of its temperature with respect to that of surroundings. The time after which the rate of heat loss of the body will be half of the maximum rate of heat loss is (The time is to be counted from the instant t = 0 ). The value of n is
Newton's law of cooling,
A paramagnetic sample shows a net magnetisation of when placed in an external magnetic field of at a temperature of . When the same sample is placed in an external magnetic field of at temperature of 16 k, the net magnetisation will be .
and Curie law ,
or
Two carnot engines operate in series between a heat source at a temperature and heat sink at temperature . There is another reservoir at temperature , as shown, with . The two engines are equally efficient if K ![]()
as
A point object moves towards a concave mirror with a speed along the principal axis. The magnitude of the velocity of object with respect to image when the object is at distance of 15cm from the pole is __ . (Focal length of the mirror kept at rest is 10cm )
Relative velocity
JEE Mains 2022
JEE Mains 2022
Commonly asked questions
Time period of a simple pendulum is T. The time taken to complete oscillations starting from mean position is The value of a is………..
Total oscillation =
= 7
The volume V of a given mass of monoatomic gas changes with temperature T according to the relation The work done when temperature changes by 90 K will be xR. The value of x is……..
[R = universal gas constant]
Work done =
n = 60
Two stream of photons, possessing energies equal to twice and ten times the work function of metal are incident on the metal surface successively. The value of ratio of maximum velocities of the photoelectrons emitted in the two respective cases is x : y. The value of x is………
Case I :-
Case II :-
x = 1
A point source of light S, placed at a distance 60cm infront of the centre of a plane mirror of width 50cm, hangs vertically on a wall. A man walks inform of the mirror along a line parallel to the mirror at a distance 1.2m from it (see in the figure). The distance between the extreme points where he can the image of the light source in the mirror is…………..cm.
Maximum Distance = 3 (x + x) = 6x = 3 × 2x = 3 × 50 = 150 cm
If the highest frequency modulating a carrier is 5 kHz, then the number of AM broadcast stations accommodated in a 90 kHz bandwidth are……….
Band Width = 2 × n × the highest modulation frequency
1 mole of rigid diatomic gas performs a work of when heat Q is supplied to it. The molar heat capacity of the gas during this transformation is The value of x is………
[R = universal gas constant]
A particle executes S.H.M. with amplitude ‘a’ and time period ‘T’. The displacement of the particle when its speed is half of maximum speed is The value of x is…………
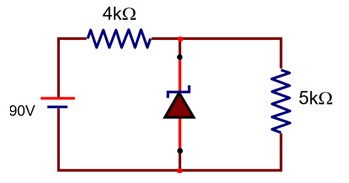
The zener diode has a Vz = 30V. The current passing through the diode for the following circuit is…………mA.
27 similar drops of mercury are maintained at 10V each. All these spherical drops combine into a single big drop. The potential energy of the bigger drop is……… times that of a smaller drop.
With the help of conservation of volume, we can write
With the help of conservation of charge, we can write
Q = 27 q.......(2)
Potential energy of single drop = U1 =
Potential energy of bigger drop =
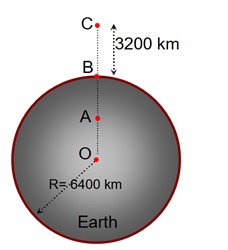
In the reported figure of earth, the value of acceleration due to gravity is same at point A and C but it is smaller than that of its value at point B (surface of the earth). The value of OA: AB will be x : y. The value of x is…………
Consider a uniform cubical box of side a on a rough floor that is to be moved by applying minimum possible force at point above its centre of mass (see figure). If the coefficient of friction is , the maximum possible value of for box not to topple before moving i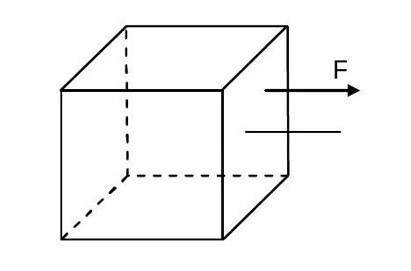
For no toppling
(in limiting case)
But is not possible as maximum value of ![]() can be equal to
can be equal to ![]() only.
only.
grams of steam at is mixed with of ice at its melting point in a thermally insulated container. If it produces liquid water at [heat of vaporization of water is and heat of fusion of ice is ], the value of is
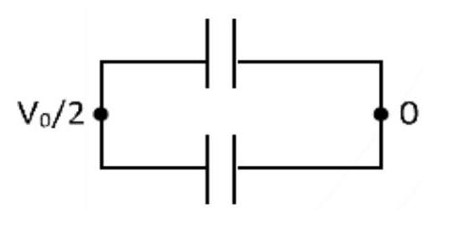
A capacitor is fully charged by a supply. It is then disconnected from the supply and is connected to another uncharged capacitor in parallel. The electrostatic energy that is lost in this process by the time the charge is redistributed between them is (in )
6
Sol. Common potential after connection.
Loss of energy
The balancing length for a cell is in a potentiometer experiment. When an external resistance of is connected in parallel to the cell, the balancing length changes by . If the internal resistance of the cell is , where is an integer then value of is
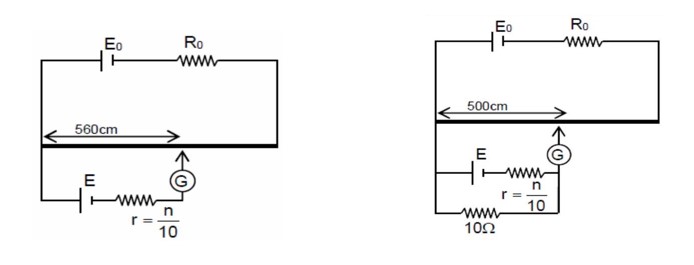
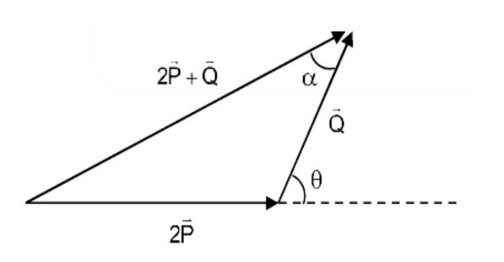
The sum of two forces and is such that . The angle (in degrees) that the resultant of and will make with is,
Sol.
01 Mock Test 2025
01 Mock Test 2025
Commonly asked questions
When monochromatic light of wavelength 620 nm is used to illuminate a metallic surface, the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons emitted is 1 eV. Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectron emitted (in eV) if a wavelength of 155 nm is used on the same metallic surface. (hc = 1240 eV-nm)
In case 1, E? = 2eV; φ? ? = E? - KE? = 1eV
In case 2, E? = 12400/1550 = 8eV; max.KE = 8eV - 1eV = 7eV
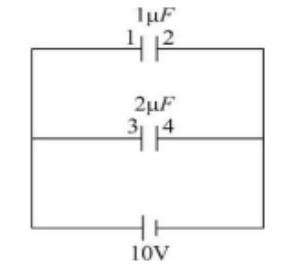
Two capacitros are fully charged by a battery as shown in the figure.
If the capacitors are disconnected from battery and plate 1 is connected to plate 4 & plate 2 to plate 3, then find the potential difference (in volts) across capacitors finally.
Charge initially on capacitor 1=10µC
Charge initially on capacitor 2=20µC
Finally the potential difference across both capacitor will be equal.
Let us assume that to be V.
1V + 2V = +10
V = 10 / 3 = 3.33V
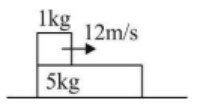
A plank of mass 5 kg in kept on a smooth surface. A block of 1 kg is kept on it and is given a velcoity of 12 m/s. There is friction between the block and the plank. Assuming the plank to be very long, find the magnitude of work done (in Joules) by friction on block till the relative sliding between them stops.
When relative sliding stops, both move with same velocity.
Only friction acts in horizontal direction.
∴ for system no external force, we can apply conservation of momentum.
1 × 12 + 5 × 0 = 6 × v
v = 2 m/s
Now work done by friction on block = change in kinetic energy of block
w = (1/2)m (2² - 12²) = (1/2) (1) (4 - 144) = (1/2) (-140) = -70 J
If the molar specific heat at constant pressure for a polyatomic non-linear gas is x and the molar specific heat at constant volume for a diatomic gas is y, find the value of x y
x = 8R/2 ; y = 5R/2 ; x/y = 8/5 = 1.6
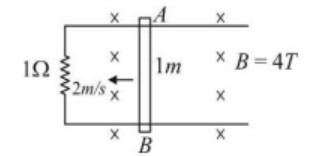
Two fixed long parallel horizontal rails, a distance 1 m apart are joined at one end by a resistance 1Ω . A rod AB of negligible resistance slides towards the resistance. A magnetic field of magnitude 4T perpendicular to the plane of rails exists. Find the current flowing (in Ampere) in the resistance, at an instant when the velocity of the rod is 2 m/s.
EMF induced = BLV = 4 * 2 * 1 = 8V
Current produced = BLV/R = 8/1 = 8A
A radioactive sample decays with a constant of (1/3)logₑ2 s⁻¹. If initially there are 200 nuclei present, find the number of nuclei decayed during the first 9 seconds.
t? , half life = (log?2)/λ = 3 s
Initially 200 nuclei were there
After 3 half-lives, 9 seconds,
No. of nuclei = (1/2³) (200) = 25
Therefore, the number of nuclei that decayed = 200 – 25 = 175
In the colour coding system of carbon resistors, the tolerance (in %) shown by gold band is ____.
Gold band is equal to 5% tolerance
The fundamental frequency of an organ pipe open at one end is 300 Hz. The frequency of 3rd overtone of n Find n.×this organ pipe is 100 Hz
f? = 300 Hz
3rd overtone = 7f? = 2100 Hz
A carnot engine works between temperatures 327°C and 27°C. If the engine takes 1600 J of heat from the higher temperature reservoir, the work done by the engine per cycle (in Joule) is equal to ______.
(Q? - Q? )/Q? = (T? - T? )/T? ; Q = (300/600) × 1600 = 800 J
work done = Q? - Q? = 1600 – 800 = 800J
Consider a p-n junction diode which has a potential drop of 0.5 V which is to be taken independent of current (under forward bias). If we want to use 1.5 V cell to forward bias the diode then what should be the value of resister (in Ω) used in series with the diode so that current may not exceed 10 mA, and hence may work safely.
1R + 0.5 = 1.5
1R = 1
R = 1/10 = 100Ω
A coil of inductance 2H having negligible resistance is connected to a source of supply whose voltage is given by V = 3t volt. (where t is in second). If the voltage is applied when t = 0, the energy stored in the coil after 4s is…………… J.
The potential energy (U) of a diatomic molecule is a function dependent on r (interatomic distance) as
Where, α and β are positive constants. The equilibrium between two atoms will be where α =……………..
For equilibrium,
A mono-atomic gas of mass 4.0u is kept in an insulated container. Container is moving with velocity 30 m/s. If container is suddenly stopped then change in temperature of the gas (R = gas constant) is Value of x is…………….
A small bob tied at one end of a thin string of length 1m is describing a vertical circle so that the maximum and minimum tension in the string are in the ratio 5 : 1. The velocity of the bob at the highest position is ……………… m/s. (Take g = 10 m/s2)
Let v is velocity at the highest position.
The electric field in a region is given by The ratio of flux of reported field through the rectangular surface of are 0.2m2 (parallel to y – z plane) to the of the surface of are 0.3m2 (parallel to x – z plane) is a : b, where a = ……………
[Here are the unit vectors along x, y and z – axes respectively]
01 Oct 2025
01 Oct 2025
Commonly asked questions
The Vernier constant of Vernier calipers is 0.1 mm and it has zero error of (-0.05) cm. White measuring diameter of a sphere, the main scale reading is 1.7 cm and coinciding vernier division is 5. The correct diameter will be__________ × 10-2 cm.
Least count of Vernier = 0.1mm
Reading of Vernier Scale = 5 × 0.1 = 0.5mm
The corrected diameter of sphere = Main Scale Reading + Vernier Scale reading + Zero correction = 1.7 + 0.05 + 0.05 = 1.8cm = 180 × 10-2 cm.
The intensity of the light from a bulb incident on a surface is 0.22 W/m2. The amplitude of the magnetic field in this light – wave is__________ × 10-9 T.
(Given : Permittivity of vacuum speed of light in vacuum c = 3 × 108 ms-1)
B0 = 42.9 × 10-9
42.9 Ans
In a Young’s double slit experiment, an angular width of the fringe is 0.53° on a screen place at 2m away for particular wavelength of 450 nm. The angular width of the fringe, when whole system is immersed in a medium of refractive index 7/5, is The value of a is__________.
we know, =
[with change in medium frequency remain constant]
2=
2
The velocity of a small ball of mass 0.3g and density 8 g/cc when dropped in a container filled with glycerine becomes constant after some time. If the density of glycerine is 1.3 g/cc, then the value of viscous force acting on the ball will be x × 10-4 N, value of x is________. [use g = 10 m/s2]
m = 0.3g density,
Fv + FB = mg.
Þ Fv = mg – FB = .3 × 10-3 × 10 – 1.3 ×
= 2.5 × 10-3N
The position vector of 1kg object is and its velocity The magnitude of is angular momentum is where x is________.
=
A lens is placed between a source of light and screen. It forms real image on screen for two different positions. If height of one image is 20 cm and the other is 80 cm, then the height of source of light (in cm) is_____.
Kindly consider the following figure
Force required to separate two glass plates of area 100cm2 with a thin film of water 0.05 cm thick between them is____. (in N). (Surface tension of water is 70x10-3N / m , consider complete wetting)
Kindly consider the following figure
A source of sound S is moving with a velocity of 50 m/s towards a stationary observer. The observer measures the frequency of the source as 1000 Hz. What will be the apparent frequency (in Hz) of the source when it is moving away from the observer after crossing him? (Take speed of sound in air as 350 m/s)
Kindly consider the following figure
NEET 2025
NEET 2025
Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Fifteen Exam