Physics
Get insights from 5.6k questions on Physics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
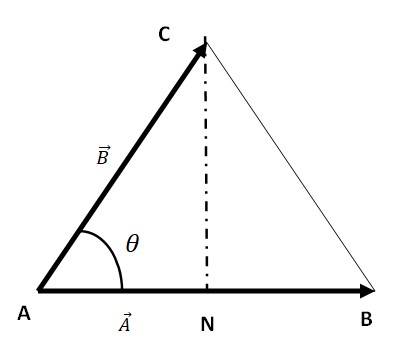
Let AB is equal to the vector a and AC be equal to the vector b.
Consider two vectors = =
= inclined at an angle
MN =
| | = | | |
The area of ΔABC, we can write the relation
Area of Δ ABC = AB =
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The child is sitting on the trolley and there is no external force, hence it is a single system. The velocity of the centre of mass will not change, irrespective of any internal motion.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
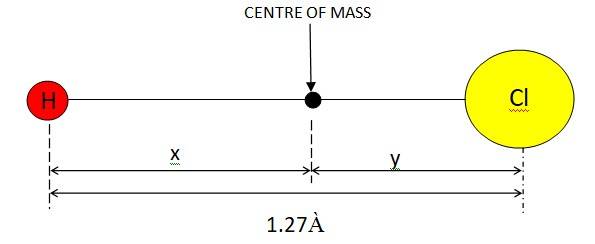
If mass of the H atom = m, mass of the Cl atom = 35.5m
Given x + y = 1,27 À
Let us assume that the centre of mass of the given molecule lies at the origin. Therefore,
We can have, : (my+35.5mx)/ (m+35.5m) = 0
mx + 35.5my = 0
x = 35.5 (1.27 – x)
x = 1.24 À
So the centre of mass lies 1.24 À from H atom
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
All the structures specified are symmetric bodies with uniform mass density. For all these bodies, their centre of mass will lie in their geometric centres.
Not necessarily, the centre of gravity of a circular ring is at the imaginary centre of the ring.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
9.32 Focal length of the convex lens, = 30 cm
The liquid acts as a mirror, focal length of the liquid =
Focal length of the system (convex lens + liquid), = 45 cm
For a pair of optical systems placed in contact, the equivalent focal length is given as
= + or = -
- 90 cm
Let the refractive index of the lens be and the radius of curvature of one surface be R
Hence, the radius of curvature of the other surface is –R
R can be obtained by using the relation
= ( + ) = (1.5 – 1)(
= , so R =
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
9.31 Angle of deflection, = 3.5
Distance of the screen from the mirror, D = 1.5 m
The reflected rays get deflected by an amount twice the angle of deflection, i.e. 2
The displacement (d) of the reflected spot of light on the screen is given as:
=
d = 1.5 tan 7 = 0.184 m = 18.4 cm
Hence, the deflection of the reflected spot of light is 18.4 cm.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
9.30 Distance between the objective mirror and the secondary mirror, d = 20 mm
Radius of curvature of objective mirror, = 220 mm
Hence focal length of the objective mirror, = = 110 mm
Radius of curvature of secondary mirror, = 140 mm
Hence focal length of the objective mirror, = = 70 mm
The image of an object placed at infinity, formed by the objective mirror, will act as a virtual object for the secondary mirror. Hence, the virtual object distance for the secondary mirror,
u = = 110 – 20 = 90 mm
Applying the mirror formula for the secondary mirror, we can cal
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
9.29 Focal length of the objective lens, = 140 cm
Focal length of the eyepiece, = 5 cm
Least distance of distinct vision, d = 25 cm
In normal adjustment, the separation between the objective lens and the eyepiece
=
Height of the tower
Distance of the tower (object) from the telescope, u = 3 km = 3000 m
The angle subtended by the tower at the telescope is given as : = = rad
The angle subtended by the image produced by the objective lens is given as , where = height of the image of the tower formed by the objective lens
So, = = &nbs
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
9.28 Focal length of the objective lens, = 140 cm
Focal length of the eyepiece, = 5 cm
Least distance of distinct vision, d = 25 cm
When the telescope is in normal adjustment, its magnifying power is given as:
= = = 28
When the final image is formed at d, the magnifying power of the telescope is given as:
= ] = 28 ] = 33.6
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
9.27 Focal length of the objective lens, = 1.25 cm
Focal length of the eyepiece, = 5 cm
Least distance of distinct vision, d = 25 cm
Angular magnification of the compound microscope = 30X
Total magnifying power of the compound microscope, m = 30
The angular magnification of the eyepiece is given by the relation:
= (1 + ) = (1 + = 6
The angular magnification of the objective lens ( ) is related to by the equation
m = or
= = = 5
We also have relation
5 = or ……….(1)
Applying lens formula for the objective lens
&nbs
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers



