Physics
Get insights from 5.6k questions on Physics, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.9 The strength of the radioactive source is given as:
= 8.0 mCi = 8 decay/s = 296 decay/s, where
N = Required number of atoms
Given, half life of , = 5.3 years = 5.3 secs = 167 s
For decay constant , we have rate of decay as:
= or
N = , where = = /s = 4.1497
N = = 7.133 atoms
For , mass of 6.023 atoms = 60 gms
Therefore, the mass of 7.133 atoms = 7.133 gms = 7.106 g
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.8 Decay rate of living carbon-containing matter, R = 15 decay / min
Half life of , = 5730 years
Decay rate of the specimen obtained from the Mohenjo-Daro site, R' = 9 decays/min
Let N be the number of radioactive atoms present in a normal carbon-containing matter.
Let N' be the number of radioactive atoms present in the specimen during the Mohenjo-Daro period.
We can relate the decay constant, and time t as:
= =
= =
By taking log (ln) on both sides,
-
t =
Since = =
t = = 4223.5 years
Hence, the appro
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.7 Half life of the radioactive isotope = T years
Original amount of the radioactive isotope =
After decay, the amount of radioactive isotope = N
It is given that only 3.125% of remains after decay. Hence, we can write,
= 3.125% = =
But = , where = decay constant, t = time
Therefore,
By taking log on both sides
=
-
= 0 – 3.465
=
Since =
t = = 5T years
Hence, all the isotopes will take about 5T years to reduce 3.125% of its original value.
After decay, the amount of radioactive isotope = N
It is given
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.5 Mass of the copper coin, m' = 3.0 g
Atomic mass of , m = 62.92960 u
The total number of atoms in the coin, N = , where
= Avogadro's number = 6.023 atoms / g
Mass number = 63 g
Therefore, N = = 2.868 atoms
has 29 protons and (63 – 29) 34 neutrons
Hence the mass defect of the nucleus Δm = 29 + 34 -
Mass of a proton, = 1.007825 u
Mass of a neutron, = 1.008665 u
Δm = 29 + 34 - 62.92960
Δm = 0.591935 u
Mass defect of all the atoms present in the coin, Δm = 0.591935
= 0.591935 2.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.3 Atomic mass of nitrogen , m = 14.00307 u
A nucleus of nitrogen contains 7 protons and 7 neutrons.
Hence, the mass defect of this nucleus, Δm = 7 + 7 - m, where
Mass of a proton, = 1.007825 u
Mass of a neutron, = 1.008665 u
Therefore, Δm = 7 1.007825+ 7 1.008665 – 14.00307 = 0.11236 u
But 1 u = 931.5 MeV/
Δm = 104.66334 MeV/
The binding energy of the nucleus, = Δm , where c = speed of light
(104.66334/ ) = 104.66334 MeV
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
13.2 Atomic mass of neon isotope, = 19.99 u ad the abundance = 90.51 %
Atomic mass of neon isotope, = 20.99 u ad the abundance = 0.27 %
Atomic mass of neon isotope, = 21.99 u ad the abundance = 9.22 %
The average atomic mass of neon is given as:
m = = = = 20.1771 u
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
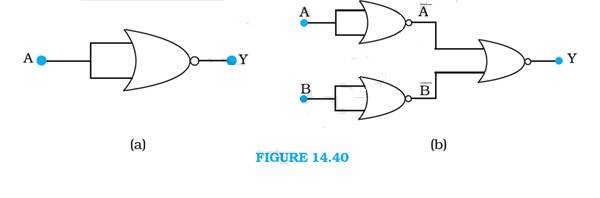
14.15 A acts as two inputs of the NOR gate and Y is the output. As shown in the following figure. Hence the output of the circuit is =
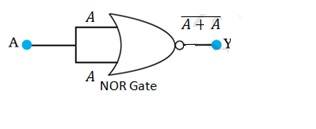
The truth table for the same is given as:
A | Y = ( ) |
0 | 1 |
1 | 0 |
This is the truth table of a NOT gate. Hence, this circuit functions as a NOT gate.
A and B are the inputs and Y is the output of the given circuit. By using the result obtained in solution (a), we can infer that the outputs of the first two NOR gates are and , as shown in the following figure
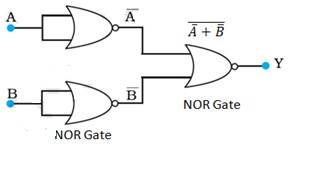
Above is given the inputs for the last NOR gate.
Hence, the output for the circuit can be written as:
Y = = = A.B
The truth table for the same can b
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
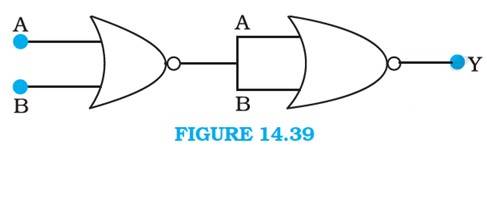
14.14 A and B are the inputs of the given circuit. The output of the first NOR gate is + . It can be observed from the following figure that the inputs of the second NOR gate become the output of the first one.
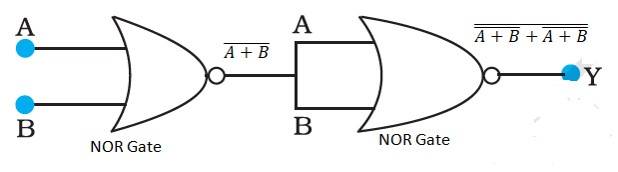
Hence, the output of the combination is given as:
Y = = + = = = + =
The truth table for this operation is given as:
This is the truth table of an or gate. Hence, this circuit functions as an or gate.
A | B | Y ( = A + B) |
0 | 0 | 0 |
0 | 1 | 1 |
1 | 0 | 1 |
1 | 1 | 1 |
This is the truth table of an OR gate. Hence, this circuit functions as an OR gate.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
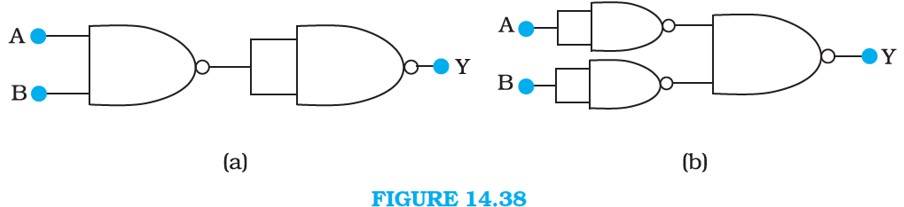
14.13 The output of the left NAND gate will be , as shown in the following figure:
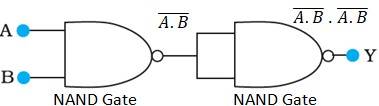
Hence, the output of the combination of two NAND gates is given as:
Y = ( ).( ) = + = AB
Hence the circuit functions as an AND gate.
is the output of the upper left of the NAND gate and is the output of the lower half of the NAND gate, as shown in the following figure.
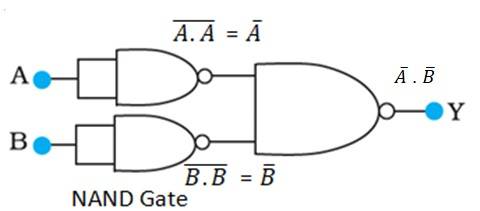
Hence, the output of the combination of the NAND gates will be given as:
Y = . = + = A + B
Hence, this circuit functions as an OR gate.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
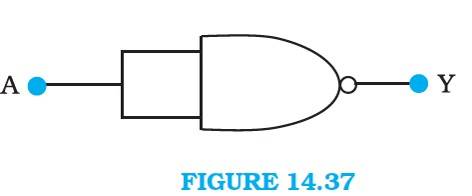
14.12 A acts as the two inputs of the NAND gate and Y is the output, as shown in the following figure.
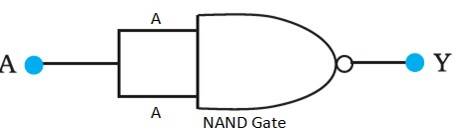
Hence, the output can be written as:
Y = = + = ……………(i)
The truth table for equation (i) can be drawn as:
A | Y = ( ) |
0 | 1 |
1 | 0 |
This circuit functions as a NOT gate. The symbol for this logic circuit is as shown below:
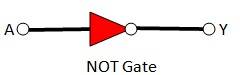
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers