The p-Block Elements
Get insights from 81 questions on The p-Block Elements, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about The p-Block Elements
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
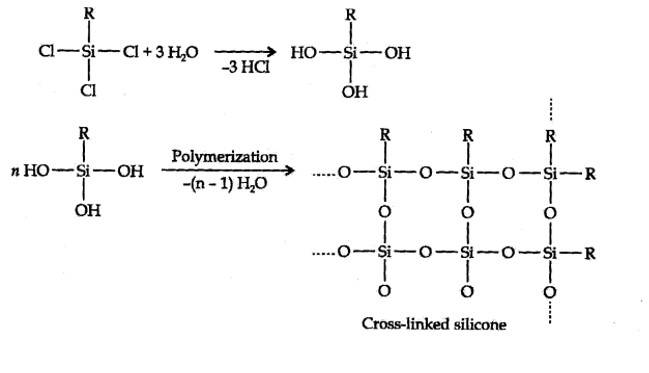
Hydrolysis of aikyltrichlorosilanes gives cross-linked silicones.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Due to inert pair effect, elements of group 14 exhibit oxidation states of +2 and +4. Thus, option (b) is correct.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Thermodynamically the most stable form of carbon is graphite, i.e., option (b) is correct.
New answer posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Boric acid is polymeric due to the presence of H-bonds. Therefore, option (b) is correct.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Borax is a salt of a strong base (NaOH) and a weak acid (H3BO3), therefore, it is basic in nature, i.e., option (c) is correct.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Laboratory preparation of carbon monoxide:
Formic acid is dehydrated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 373 K.
HCOOH → H2O + CO↑
Commercial preparation of CO:
Steam is passed over hot coke.
C + H2O → CO + H2
Laboratory preparation of carbon dioxide:
Calcium carbonate reacts with dilute HCl to form carbon dioxide.
CaCO3 + 2HCl → CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
Industrial preparation of carbon dioxide:
Limestone is heated to produce carbon dioxide.
CaCO3 →→CaO + CO2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The balanced equations are given below:
(i) 2BF3 + 6LiH → B2H6 + 6LiF
(ii) B2H6 + 6H2O → 2H3BO3 (orthoboric acid)
(iii) 2NaH + B2H6 →2Na [BH4] (sodium borohydride)
(iv) H3BO3 →HBO2 (metaboric acid) + H2O
4HBO2 →H2B4O7→ 2B2O3 (boron trioxide) + H2O
(v) Al+3NaOH→Al (OH)3 + 3Na
3 B2H6 + 6NH3 → 2B3N3H6 + 12H2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The compounds X, Y and Z are borax, sodium metaborate + boric anhydride and boric acid respectively.
When borax is heated, it first swells and then forms a transparent glass like bead of sodium meta borate and boric anhydride.
Na2B4O7 à2NaBO2+B2O3+10H2O
(Borax) (sodium metaborate) (Boric anhydride)
Aqueous solution of borax is alkaline due to formation of strong base NaOH.
Hence, it turns red litmus blue.
Na2B4O7 +7 H2O → 4H3BO3 + 2NaOH
Borax reacts with sulphuric acid to form boric acid and sodium sulphate.
Na2B4O7 + H2SO4 + 5 H2O → 4H3BO3 + Na2SO4
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) Inert pair effect: When the pair of electrons in the valence shell does not take part in bond formation, then this effect is called as inert pair effect.
(b)Allotropy: It is the property of the element by which an element can exist in two or more forms which have same chemical properties but different physical properties due to their structures.
(c)Catenation: The tendency to link with one another through covalent bonds to form chains and rings. This property is called catenation.
For example, carbon forms chains with (C-C) single bonds and also with multiple bonds (C = C or C = C).
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
