The p-Block Elements
Get insights from 81 questions on The p-Block Elements, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about The p-Block Elements
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Aluminium reacts with acid as well as base. This shows amphoteric nature of aluminium.
2Al (s) + 6HCl (dil.) →2AlCl3 (aq) + 3H2 (g)
2Al (s) + 2NaOH (aq) + 6H2O (l) →2Na+ [Al (OH)4]– (aq) + 3H2 (g)
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
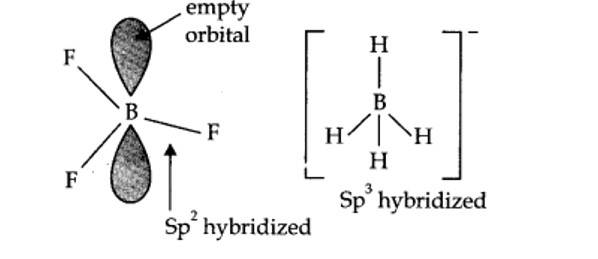
In BF3, boron is sp2 hybridized.
? shape of BF3 = planar.
In [BH4]–, boron is sp3 hybridized, thus the shape is tetrahedral.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
On heating boric acid above 370 K, it forms metaboric acid, HBO2 which on further heating yields boric oxide B2O3.
H3B2O3 → HBO2 → B2O3
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Boric acid is a Lewis acid since it accepts electrons from hydroxyl ion of H2O molecule. It is not a protic acid.
B (OH)3 + 2HOH → [B (OH)4]– + H3O+
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
In BCl3, there is only six electrons in the valence shell of B atom. Thus, the octet is incomplete and it can accept a pair of electrons from water and hence BCl3 undergoes hydrolysis. Whereas, in CCl4, C atom has 8 electrons and its octet is complete. That's why it has no tendency to react with water.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
In BF3, central atom has only six electrons after sharing with the electrons of the F
atoms. It is an electron-deficient compound and thus behaves as a Lewis acid.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
BCl3 is quite stable. Because there is absence of d- and f-electrons in boron three valence electrons (2s2 2px1) are there for bonding with chlorine atom. In Tl the valence s-electron (6s2) are experiencing maximum inert pair effect. Thus, only 6p1 electron is available for bonding. Therefore, BCl3 is stable but TlCl3 is comparatively unstable.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) B to Tl
Common oxidation states are +1 and +3. The stability of +3 oxidation state decreases from B to Tl while +1 oxidation state increases from B to Tl.
(ii) C to Pb
The common oxidation states are +4 and +2. Stability of +4 oxidation state decreases from C to Pb.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 8
Yes, NCERT solutions are enough to prepare for the exam. However, solving the Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 textbook solutions are also important to build the conceptual knowledge.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 8
The link to download the Class 11 Chemistry Ch 11 ncert solutions pdf is activated on this article. Students need to provide basic information to download the solutions.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
