Waves
Get insights from 109 questions on Waves, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Waves
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
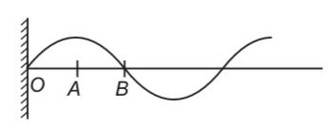
during propagation of a plane progressive mechanical wave
(i) clearly the particles O, A and B are having different phase.
(ii) Particles of the wave are having up and SHM.
(iii) For a progressive wave propagating in a fluid
V= , V=
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c, d) Speed of sound waves in a fluid is given by
V=
V= V so when we increase velocity bulk modulus also increases.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b, c) y (x, t) = 0.06 sin (2πx/3) cos (120πt)
(a) y (x, t)=asinkxcoswt
(b) w=120 , f=60hz
(c) k=2 , v =60 (3)=180m/s
(d) since in stationary wave all particles of the medium executes SHM with varying amplitude nodes.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, c) y (x, t)=30sin (36t+0.018x+ )
Y=asin (wt+kx+ )
(a) as the equation involves positive sign with x . hence the wave is travelling from right to left. Hence option a is correct.
(b) W=36
2
=
w/v=0.018
v=2000cm/s=20m/s
(c) 2
= 5.7Hz
(d) , /0.0018cm=3.48cm
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) Let frequency of the source is no
Let the speed of sound wave in the medium is v
As observer is stationary
Apparent frequency na=
When the train is going away from the observer
Apparent frequency na= =
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
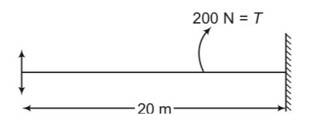
(b) m=2.5kg
mass per unit length
=m/l =2.5/20=125/10=0.125kg/m
V=
L=v
20=
= 20
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Amplitude of reflected wave
Af= =2 (0.6)/3=0.4 units
Equation of incident wave
Yi=0.6sin2
For reflected wave
yr=Arsin2 (t+x/2+ )
Yr=-0.4sin2
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(d) Due to compression and rarefactions density of the medium changes.at compressed regions density is maximum and at rarefactions density is minimum
As density is changing so boyle, s law not obeyed
Bulk modulus remains same
The time of compression and rarefaction is too small so no transfer of heat.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) When mechanical transverse wave propagates through a medium, the constituents of the medium oscillate perpendicular to wave motion causing change in shape. That is each element of the medium is subjected to shearing stress. Solids and strings have shear, that is why tey bear stress. But in fluids there is no fixed shape so transverse waves does not formed in fluid.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b) Propagation of longitudinal waves through a medium leads to transmission of energy through the medium without matter being transmitted. So no movement of energy and matter hence momentum
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers