Waves
Get insights from 109 questions on Waves, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Waves
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) The equation y = 100 cos (100πt + 0.5x ) is representing a travelling wave along x-direction
(b) The equation y = 5 cos (4x ) sin (20t) represents a stationary wave, because it contains sin cos terms ., combinations of two progressive waves.
(c) The equation y = 10 cos [ (252 – 250) πt ] cos [ (252+250)πt ] involving sum and difference of two near by frequencies 252 and 250 have this equation represents beats formation.
(d) As the equation y = y = 4 sin (5x – t/2) + 3 cos (5x – t/2) involves negative sign with x, have if represents a travelling wave along
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
we know that rms speed of molecules of a gas
C=
Where M is the molar mass of the gas
Speed of sound wave in gas v=
On dividing above equation we get
c/v =
c/v =
where = adiabatic constant for diatomic gas
c/v=constant
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Speed of wave in solid =8km/s
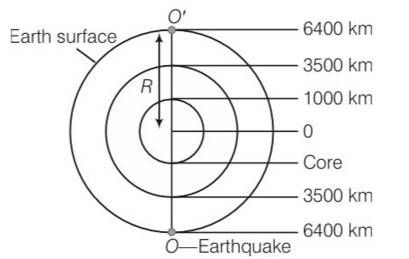
Speed of wave in liquid = 5km/s
Required time = [ ]
= [ ]
= [125+500+362.5] =1975 (diameter = radius )
As we are considering at diametrically opposite point, hence there is a multiplication of 2
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ultrasonic beep frequency emitted by bat, = 40 kHz
Velocity of the bat, = 0.03v, where v = velocity of sound in air
The apparent frequency of the sound striking the wall is given as:
) = ) = kHz = 41.24 kHz
This frequency is reflected by the stationary wall ( towards the bat
The frequency (
) = ( ) = 1.03 = 42.47 kHz
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let and be the velocities and and be the time taken to reach the seismograph from the epicentre of S and P waves respectively.
Let L be the distance between the epicentre and the seismograph.
We have:
L = …. (i)
L = …. (ii)
It is given, = 4 km/s and = 8 km/s
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
4 = 8 or 2 …. (iii)
It is also given,
so
From equation (ii), we get, L = 8 = 1920 km
Hence, the earthquake occurred at a distance of 1920 km from the seismograph.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Operating frequency of the SONAR system, = 40 kHz
Speed of enemy submarine, 360 km/h = 100 m/s
Speed of sound in water, v = 1450 m/s
The source is at rest and the observer (enemy submarine) is moving towards it. Hence, the apparent frequency (f') received and reflected by the submarine is given by the relation:
f = ( ( = 42.76 kHz
The frequency (f') received by the enemy submarine is given by the relation:
f' = ( )f = ( ) = 45.93 kHz
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The equation of a travelling wave propagating along the positive y- direction is given by the displacement equation:
y (x, t) = a sin ( ……… (i)
Linear mass density 8.0 kg/m and frequency of the tuning fork, = 256 Hz
Amplitude of the wave, a= 5.0 cm = 0.05 m …. (ii)
Mass of the pan, m = 90 kg and tension of the string, T = mg = 90 = 882 N
The velocity of the transverse wave, v is given by the relation:
v = = = 332 m/s
Angular frequency, = 2 = 2 = 1608.5 rad/s = 1.6 rad/s
Wavelength, = = &
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The narrow sound pulse does not have a fixed wavelength or frequency. However, the speed of the sound pulse remains the same, which is equal to the speed in that medium. The short pip produced after 20 s does not mean that the frequency of the whistle is 0.05 Hz. It means that 0.05 Hz is the frequency of repetition of the pip of the whistle. So the answers are
(a)
(i) No
(ii) No
(iii) Yes
(b) No
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) The given harmonic wave is
y(x, t) = 7.5 sin (0.0050x +12t + /4)
For x = 1 cm and t = 1 s
y(1, 1) = 7.5 sin (0.0050 +12+ /4)
= 7.5 sin( 12.0050 + )
= 7.5 sin (12.0050 + 0.7854)
= 7.5 sin (732.84 )
= 7.5 sin (90 12.81)
= 7.5 sin 12.81
=1.6629 cm
The velocity of the oscillation at a given point and the time is given as:
v = y(x,t) =
= 7.5 )
At x= 1 cm and t= 1 s
v= y (1,1) = 90 cos (12.005 + ) = 90 cos(12.81 ) = 87.75 cm/s
Now the equation of a propagating wave is given by
Y(x, t) = a sin (kx + t + , where
k =&nbs
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) For the stationary observer:
Frequency of the sound produced by the whistle, = 400 Hz
Speed of sound = 340 m/s
Velocity of wind, v = 10 m/s
As there is no relative motion between the source and the observer, the frequency of the sound heard by the observer will be the same as that produced by the source, i.e. 400 Hz. The wind is blowing towards the observer. Hence, the effective speed of the sound increases by 10 units, i.e.
Effective speed of the sound, = 340 + 10 = 350 m/s
The wavelength ( heard by the observer is given by the relation:
= = 0.875 m
(b) For the running Observer:
,&nb
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
