Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Get insights from 93 questions on Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
In KOH adds to the compound
Due to the production of a stable conjugate base after hydronium is removed from phenol, it is more stable than alcohol.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: D
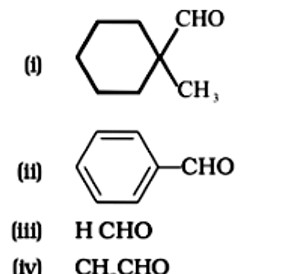
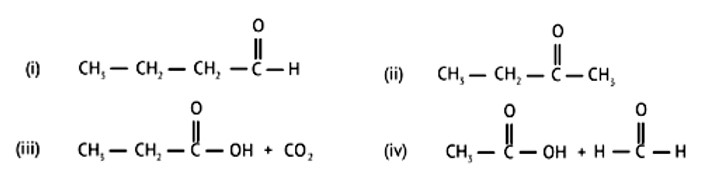
Aldehydes without a - hydrogen atom are the subject of Cannizaro's reaction.
Option D, CH3CHO has 3 alpha hydrogen atoms and it does not give Cannizaro's reaction
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: C
Acetones belong to the ketonic functional category. To distinguish between aldehyde and ketone, utilise Fehling's solution. Carbonyl groups are found in sodium hydrogen sulphite, phenyl hydrazine, and Grignard reagent. Ketones and aromatic aldehydes do not react with Fehling's solution.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
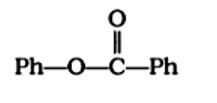
When phenol reacts with acid chloride in the presence of an alkali, the alkali is pyridine, and the acid chloride is benzoyl chloride, compound C6H5OCOC6H5 is formed. During this process, pyridine is utilised to neutralise 4HCl.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: C
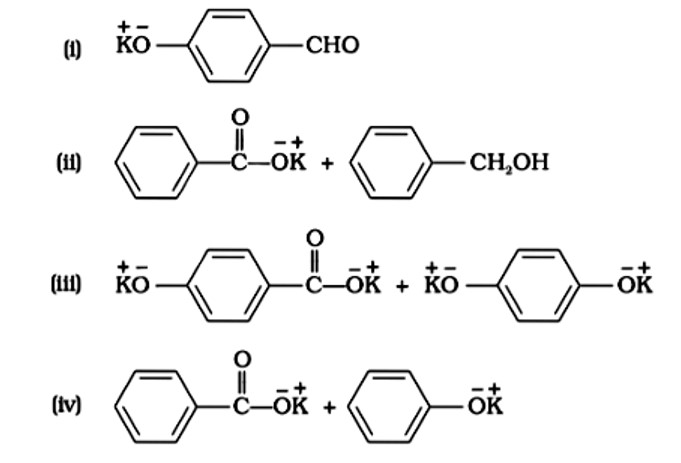
Because the phenoxide ion produced is stabilised by resonance, phenol is more acidic than ethanol. When it comes to ethanol, resonance does not help to stabilise the phenoxide ion. The acidity of chloroacetic acid is higher than that of acetic acid. Alcohols and phenols are less acidic than carboxylic acids.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
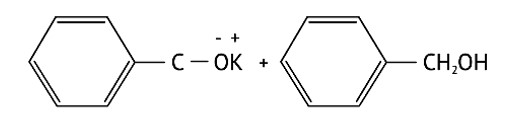
Correct option: B or (ii)
In nucleophilic addition processes, the reactivity of aldehydes and ketones are steric factors. The carbonyl group with the highest positive charge will be the most reactive, and if these groups have a positive inductive impact, the attack tendency will be reduced.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
CH3−CH2−C≡CH + H2O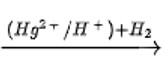
Butan-2-one is produced when butyne is hydrated in the presence of Hg ions as a catalyst. The ketone is the product. After the triple bond is broken, the OH group attaches to the secondary carbocation.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Yes, both reactions look to be the same, but they are not. To convert benzene to benzaldehyde, the Gatterman-Koch reaction is performed. Benzene is treated with an acid chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 in acylation processes. The Gatterman-Koch reaction is used to make HCOCl in situ by reacting CO with HCl gas in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
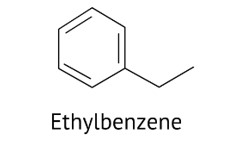
Due to the development of polysubstitution products, ethylbenzene is usually made through acetylation of benzene followed by reduction and direct alkylation.
Due to resonance, the benzene ring must be deactivated. The electrophilic attacking agent is rarely produced by the benzene ring.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers