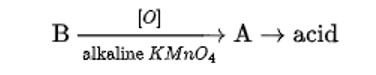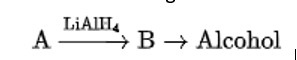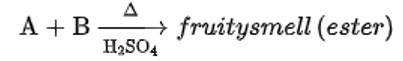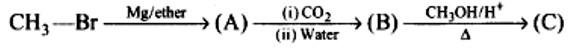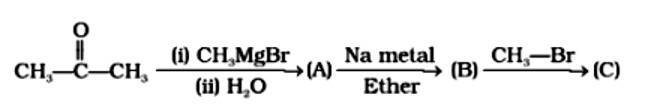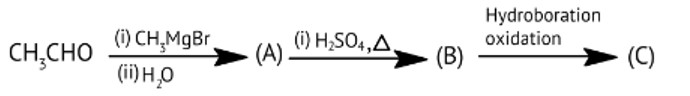- Long answer type questions
- JEE Mains Solutions 2020, 4th september, chemistry, second shift
- JEE Mains Solutions 2020, 4th september, chemistry, First shift
- 25th June 2022 first shift
Long answer type questions
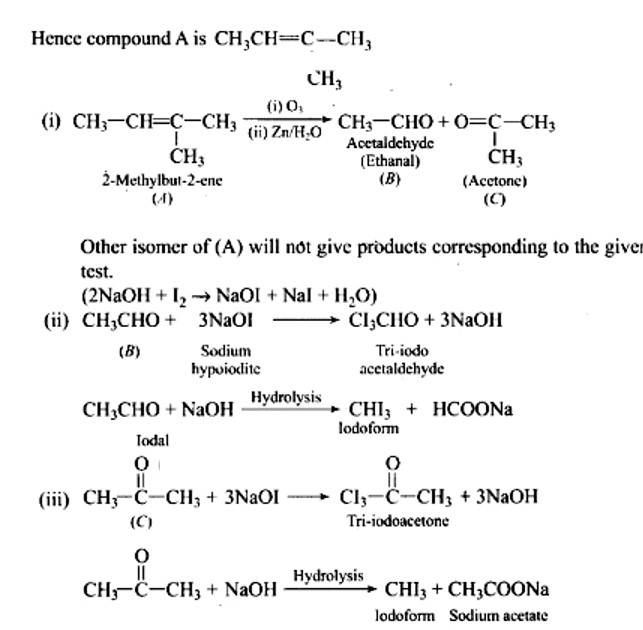
| 1. An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula C5H10 on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and forms an iodoform on treatment with I2 and NaOH. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms an iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C. |
| Ans: Fehling's test is positive when compound 'B' is used. It gives an iodoform test and proves that it is an aldehyde. Because it fails Fehling's test, compound 'C' is a ketone.
|
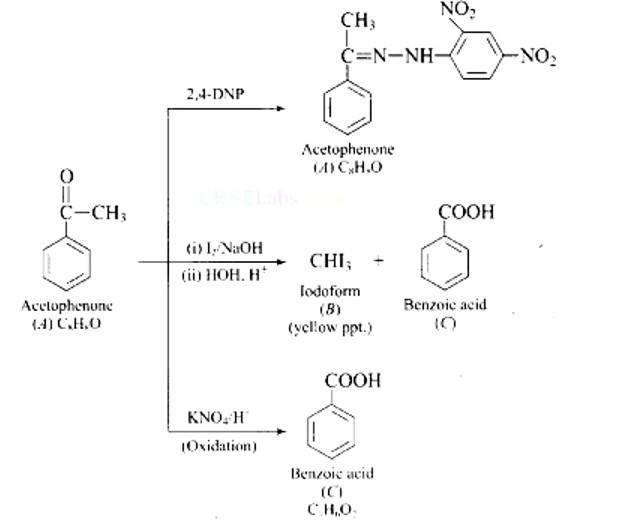
| 2. An aromatic compound ‘A’ (Molecular formula C8H8O]) gives a positive 2, 4-DNP test. It gives a yellow precipitate of compound ‘B’ on treatment with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution. Compound ‘A’ does not give Tollen’s or Fehling’s test. On drastic oxidation with potassium permanganate it forms a carboxylic acid ‘C’ (Molecular formula C7H6O2), which is also formed along with the yellow compound in the above reaction. Identify A, B and C and write all the reactions involved. |
| Ans: The aromatic compound ‘A’ does not give Tollen’s reagent test, it is not an aromatic aldehyde. As it responds to an iodoform test called methyl ketone.
|
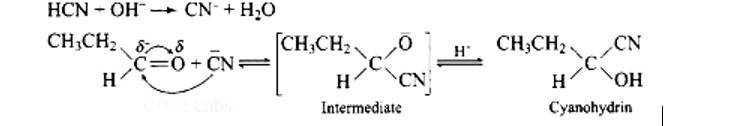
| 3. Write down functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C3H6O. Which isomer will react faster with HCN and why? Explain the mechanism of the reaction also. Will the reaction lead to the completion with the conversion of whole reactant into product at reaction conditions? If a strong acid is added to the reaction mixture what will be the effect on concentration of the product and why? |
| Ans: Functional isomers
|
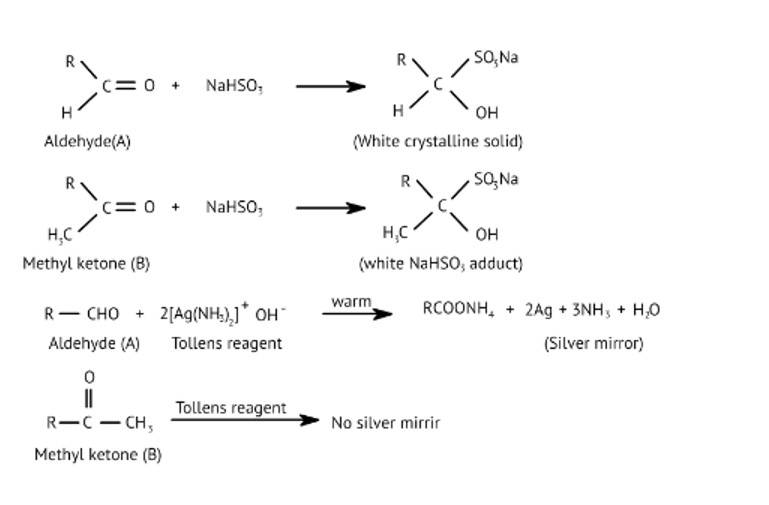
| 4. When liquid ‘A’ is treated with a freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution, it gives bright silver mirror. The liquid forms a white crystalline solid on treatment with sodium hydrogensulphite. Liquid ‘B’ also forms a white crystalline solid with sodium hydrogensulphite but it does not give test with ammoniacal silver nitrate. Which of the two liquids is aldehyde? Write the chemical equations of these reactions also. |
| Ans: Liquid ‘A’ reduces ammoniacal silver nitrate and ‘B’ is a ketone which forms white crystalline solid on treatment with hydrogen sulphite
|
Commonly asked questions
An alkene ‘A’ (Mol. formula C5H10 on ozonolysis gives a mixture of two compounds ‘B’ and ‘C’. Compound ‘B’ gives positive Fehling’s test and forms an iodoform on treatment with I2 and NaOH. Compound ‘C’ does not give Fehling’s test but forms an iodoform. Identify the compounds A, B and C. Write the reaction for ozonolysis and formation of iodoform from B and C.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
Fehling's test is positive when compound 'B' is used. It gives an iodoform test and proves that it is an aldehyde. Because it fails Fehling's test, compound 'C' is a ketone.
An aromatic compound ‘A’ (Molecular formula C8H8O]) gives a positive 2, 4-DNP test. It gives a yellow precipitate of compound ‘B’ on treatment with iodine and sodium hydroxide solution. Compound ‘A’ does not give Tollen’s or Fehling’s test. On drastic oxidation with potassium permanganate it forms a carboxylic acid ‘C’ (Molecular formula C7H6O2), which is also formed along with the yellow compound in the above reaction. Identify A, B and C and write all the reactions involved.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The aromatic compound 'A' does not give Tollen's reagent test, it is not an aromatic aldehyde. As it responds to an iodoform test called methyl ketone.
Write down functional isomers of a carbonyl compound with molecular formula C3H6O. Which isomer will react faster with HCN and why? Explain the mechanism of the reaction also. Will the reaction lead to the completion with the conversion of whole reactant into product at reaction conditions? If a strong acid is added to the reaction mixture what will be the effect on concentration of the product and why?
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Functional isomers

Compound I will react faster with HCN due to less steric hindrance and greater positive charge on carbon atom of carbonyl group. Two methyl groups increase electron density on carbonyl carbon in compounds II hence the rate of nucleophilic attack is less.
Mechanism of the reaction:
When liquid ‘A’ is treated with a freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution, it gives bright silver mirror. The liquid forms a white crystalline solid on treatment with sodium hydrogensulphite. Liquid ‘B’ also forms a white crystalline solid with sodium hydrogensulphite but it does not give test with ammoniacal silver nitrate. Which of the two liquids is aldehyde? Write the chemical equations of these reactions also.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Liquid 'A' reduces ammoniacal silver nitrate and 'B' is a ketone which forms white crystalline solid on treatment with hydrogen sulphite
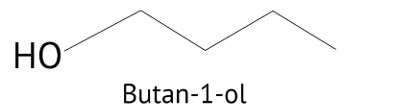
Why is there a large difference in the boiling points of butanal and butan-1-ol?
Butanol is a four-carbon aldehyde, with the aldehyde group on the fourth carbon. It has a functional group and a carbonyl group that interacts dipole-dipole. Because butanol possesses a polar O-H bond, it exhibits intermolecular H bonding, which is not feasible in butanal due to the lack of a polar bond. The boiling point of butanol is higher than that of butan-1-ol.
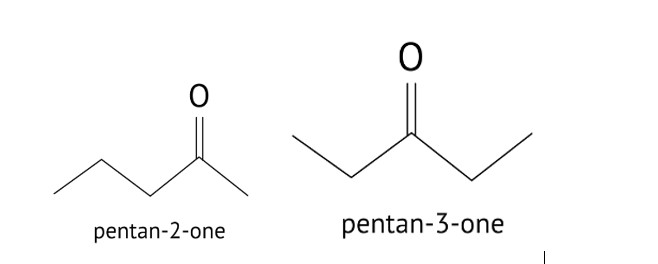
Write a test to differentiate between pentan-2-one and pentan-3-one
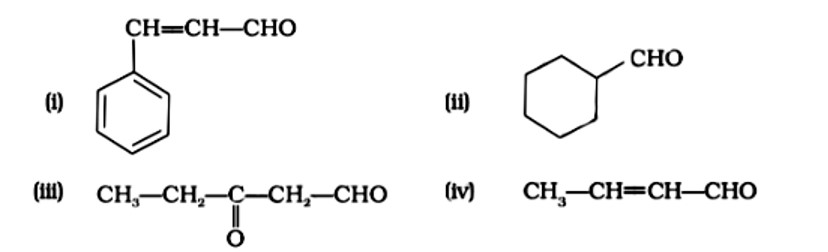
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) 3-Phenylprop-2-ene-1-al.
(ii) Cyclohexanecarbaldehyde
(iii) 3-Oxopentan-1-al
(iv) IUPAC name: But-2-enal
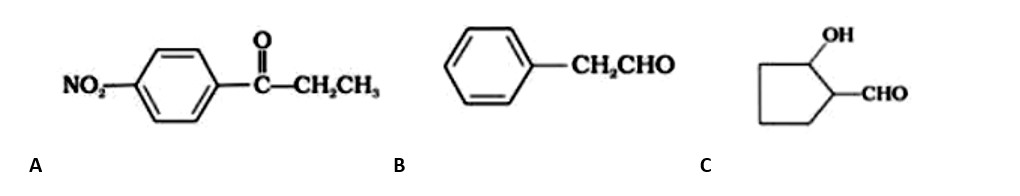
Give the structure of the following compounds.
A: 4-Nitropropiophenone
B: 2-Hydroxycyclopentanecarbaldehyde
C: Phenyl acetaldehyde
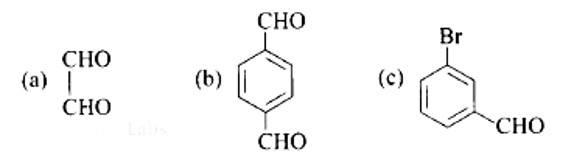
Write IUPAC names of the following structures
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
A: Ethane-1, 2-dial
B: Benzene-1, 4-carbaldehyde
C: 3-Bromobenzaldehyde
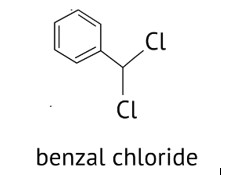
Benzaldehyde can be obtained from benzal chloride. Write reactions for obtaining benzalchloride and then benzaldehyde from it
Benzal chloride can be made by chlorinating toluene in the presence of sunshine and then using the hydrolysis process to obtain benzaldehyde. This method can be used to make benzaldehyde in a commercial setting.
Name the electrophile produced in the reaction of benzene with benzoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3. Name the reaction also.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The electrophile formed when benzene reacts with benzoyl chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 is benzoylinium cation, and the resultant product is benzophenone. Friedel Crafts acylation reaction is the name for this reaction.
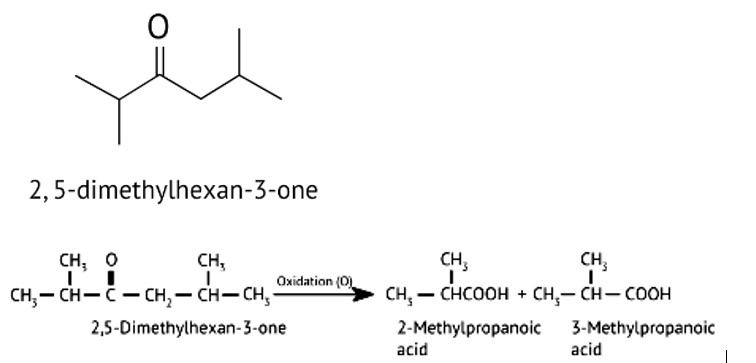
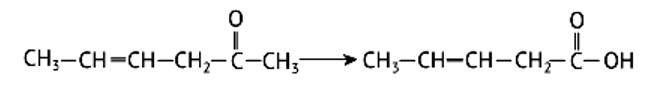
Oxidation of ketones involves carbon-carbon bond cleavage. Name the products formed on oxidation of 2, 5-dimethylhexan-3-one.
Arrange the following in decreasing order of their acidic strength and give reason for your Ans:.
CH3CH2OH, CH3COOH, ClCH2COOH, FCH2COOH, C6H5CH2COOH
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
ClCH2COOH > FCH2COOH > C6H5CH2COOH > , CH3COOH > CH3CH2OH
When compared to other alcohols, CH3CH2OH is the least acidic. Because of the halogen, FCH2COOH is quite acidic. It is either an electron donating group or an electron receiving group in acidic strength. Acidic strength increases as the number of electron withdrawing groups increases. The acidic strength of electron donating groups diminishes.
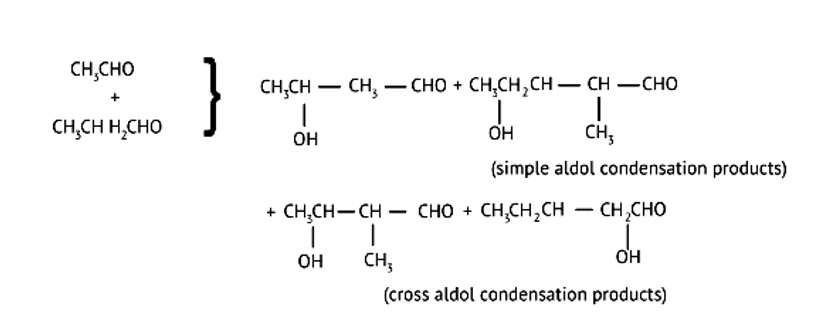
What product will be formed on reaction of propanal with 2-methylpropanal in the presence of NaOH? What products will be formed? Write the name of the reaction also?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
It's referred to as cross Aldol Condensation.Cross aldol condensation occurs when two separate aldehydes or ketones combine to form a single molecule.
Compound ‘A’ was prepared by oxidation of compound ‘B’ with alkaline KMnO4. Compound ‘A’ on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride gets converted back to compound ‘B’. When compound ‘A’ is heated with compound B in the presence of H2SO4 it produces a fruity smell of compound C to which family the compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ belong to?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When alkaline KMnO4 oxidises compound "B" with compound "A," acid is formed.
Arrange the following in decreasing order of their acidic strength. Give for the arrangement.
C6H5COOH, FCH2COOH, NO2CH2COOH
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
NO2CH2COOH > FCH2COOH > C6H5COOH
To begin, determine whether it has an acidic strength associated with it, and whether it is an electron donating or electron withdrawing group. Acidic strength increases as the number of electron withdrawing groups increases. The acidic strength reduces as the electron donating group increases. In decreasing order, the most influential acidic strength is −NO2> −F> −C6H5.
Alkenes (
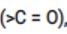
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
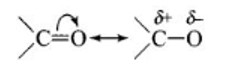
Solution: Carbonyl group is polar in nature. Due to larger electronegativity of oxygen as compared to carbon, carbon acquires partial positive charge while O acquires partial negative charge.
Carboxylic acids contain carbonyl group but do not show the nucleophilic addition reaction like aldehydes or ketones. Why?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The presence of a lone pair of electrons on an atom of the OH group diminishes the electrophilic character of C through resonance; carboxylic acids contain a carbonyl group. As a result, the carbonyl atom's partial positive charge is lowered.
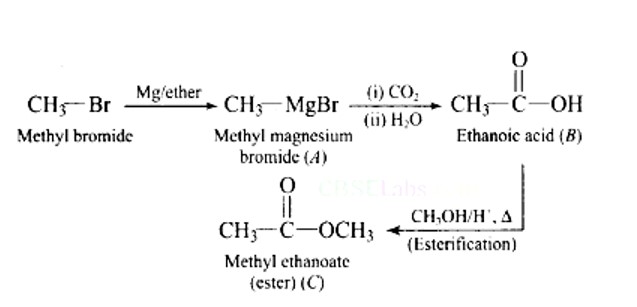
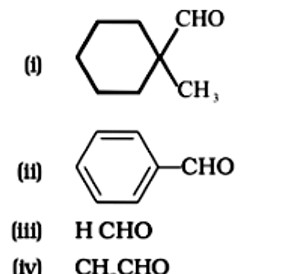
Identify the compounds A, B and C in the following reaction.
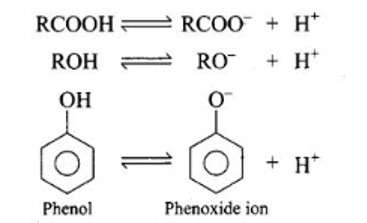
Why are carboxylic acids more acidic than alcohols or phenols although all of them have hydrogen atom attached to a oxygen atom (—O—H)?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Although all of them have a hydrogen atom connected to an oxygen atom (—O—H), carboxylic acids are more acidic than alcohols or phenols. This can be explained by the conjugate base's stability after H+ ions have been removed from the acid and phenol.
This resonance hybrid may be presented as:-
Complete the following reaction sequence.
Ethylbenzene is generally prepared by acetylation of benzene followed by reduction and not by direct alkylation. Think of a possible reason.
Due to the development of polysubstitution products, ethylbenzene is usually made through acetylation of benzene followed by reduction and direct alkylation.
Due to resonance, the benzene ring must be deactivated. The electrophilic attacking agent is rarely produced by the benzene ring.
Can Gatterman-Koch reaction be considered similar to Friedel Craft’s acylation? Discuss.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Yes, both reactions look to be the same, but they are not. To convert benzene to benzaldehyde, the Gatterman-Koch reaction is performed. Benzene is treated with an acid chloride in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3 in acylation processes. The Gatterman-Koch reaction is used to make HCOCl in situ by reacting CO with HCl gas in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3.
Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of Hg2+ ions as a catalyst. Which of the following products will be formed in addition to water to but-1-yne under these conditions?
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
CH3−CH2−C≡CH + H2O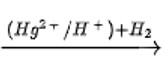
Butan-2-one is produced when butyne is hydrated in the presence of Hg ions as a catalyst. The ketone is the product. After the triple bond is broken, the OH group attaches to the secondary carbocation.
Which of the following compounds is most reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions?
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B or (ii)
In nucleophilic addition processes, the reactivity of aldehydes and ketones are steric factors. The carbonyl group with the highest positive charge will be the most reactive, and if these groups have a positive inductive impact, the attack tendency will be reduced.
The correct order of increasing acidic strength is _____________.
A: Phenol < Ethanol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
B: Ethanol < Phenol < Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid
C: Ethanol < Phenol < Acetic acid < Chloroacetic acid
D: Chloroacetic acid < Acetic acid < Phenol < Ethanol
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: C
Because the phenoxide ion produced is stabilised by resonance, phenol is more acidic than ethanol. When it comes to ethanol, resonance does not help to stabilise the phenoxide ion. The acidity of chloroacetic acid is higher than that of acetic acid. Alcohols and phenols are less acidic than carboxylic acids.
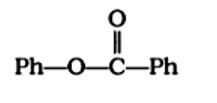
Compound
can be prepared by the reaction of _____________.
A: Phenol and benzoic acid in the presence of NaOH
B: Phenol and benzoyl chloride in the presence of pyridine
C: Phenol and benzoyl chloride in the presence of ZnCl2
D: Phenol and benzaldehyde in the presence of palladium
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
When phenol reacts with acid chloride in the presence of an alkali, the alkali is pyridine, and the acid chloride is benzoyl chloride, compound C6H5OCOC6H5 is formed. During this process, pyridine is utilised to neutralise 4HCl.
The reagent which does not react with both acetone and benzaldehyde.
A: Sodium hydrogen sulphite
B: Phenyl hydrazine
C: Fehling’s solution
D: Grignard reagent
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: C
Acetones belong to the ketonic functional category. To distinguish between aldehyde and ketone, utilise Fehling's solution. Carbonyl groups are found in sodium hydrogen sulphite, phenyl hydrazine, and Grignard reagent. Ketones and aromatic aldehydes do not react with Fehling's solution.
Cannizaro’s reaction is not given by _____________.
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: D
Aldehydes without a - hydrogen atom are the subject of Cannizaro's reaction.
Option D, CH3CHO has 3 alpha hydrogen atoms and it does not give Cannizaro's reaction
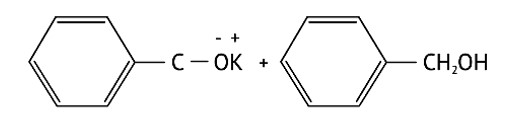
Which product is formed when the compound
is treated with concentrated aqueous KOH solution?
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
In KOH adds to the compound
Due to the production of a stable conjugate base after hydronium is removed from phenol, it is more stable than alcohol.
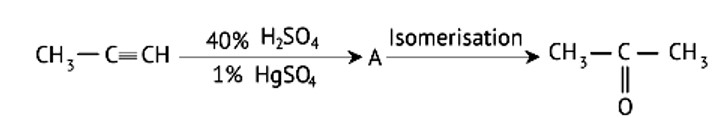
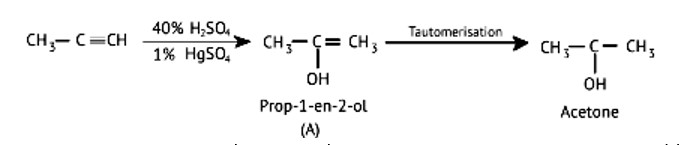
Structure of ‘A’ and type of isomerism in the above reaction are respectively
A: Prop–1–en–2–ol, metamerism
B: Prop-1-en-1-ol, tautomerism
C: Prop-2-en-2-ol, geometrical isomerism
D: Prop-1-en-2-ol, tautomerism
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Correct option: D
Compounds A and C in the following reaction are __________.
A: Identical
B: Positional isomers
C: Functional isomers
D: Optical isomers
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
The position of a functional group in the same carbon chain differs in positional isomerism. The functional group in the chemical or the unsaturated double or triple bond in the compound can help us figure it out.
Which is the most suitable reagent for the following conversion?
A: Tollen’s reagent
B: Benzoyl peroxide
C: I2 and NaOHsolution
D: Sn and NaOH solution
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: C
I2 and NaOH It is an iodoform reaction involving methyl ketones, the solution is the correct reagent. Because the reactants and product have double bonds, double bonds do not work throughout the reaction. There are also ketone and carboxylic groups present. The ketonic group is oxidised under the carboxylic group during the process.
Which of the following compounds will give butanone on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 solution?
A: Butan-1-ol
B: Butan-2-ol
C: Both
D: None of these
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: B
When a primary alcohol, such as Butan-1-ol, reacts with a powerful oxidising agent, such as KMnO4, it produces carboxylic acid, however when a secondary alcohol, such as Butan-2-ol, is oxidised under the pressure of KMnO4, it produces ketone. As a result, option B is right.
In Clemmensen Reduction carbonyl compound is treated with _____________.
A: Zinc amalgam + HCl
B: Sodium amalgam + HCl
C: Zinc amalgam + nitric acid
D: Sodium amalgam + HNO3
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: A
The Clemmensen Reduction method is used to reduce a carbonyl group to CH2. Amalgams are a type of reducing agent that has been around for a long time. In the Clemmensen reduction, hydrogen chloride acts as an acid, protonating the ketone and transferring the electrons from the zinc amalgam to the carbon atoms
Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct
13. Which of the following compounds do not undergo aldol condensation?
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: B and D
Consider the following product CH3 -CHO C and O are broken into positive and negative bonds. C should have one condition: hydrogen must be available; if it isn't, aldol condensation will not occur. When two products are mixed with the availability of - hydrogen, the positive and negative bonds between carbon and hydrogen are exchanged, and water (H20) is eliminated, resulting in aldol condensation.
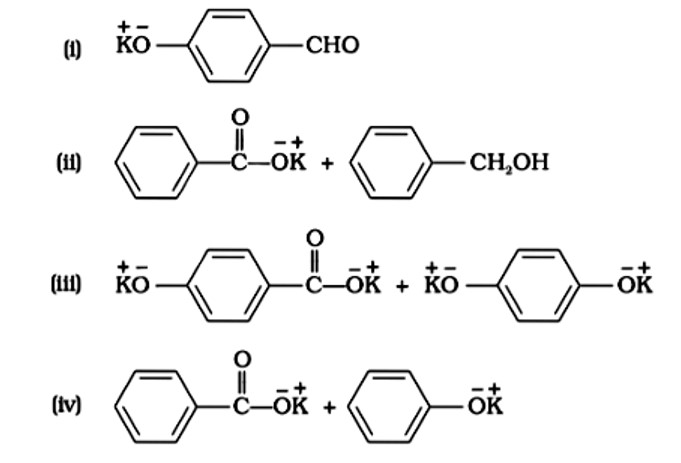
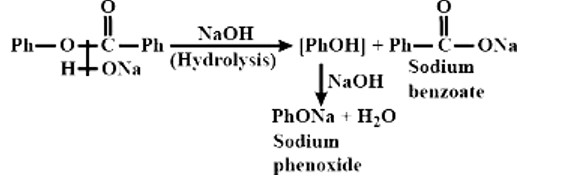
Treatment of compound
with NaOH solution yields
A: Phenol
B: Sodium phenoxide
C: Sodium benzoate
D: Benzophenone
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: B and C
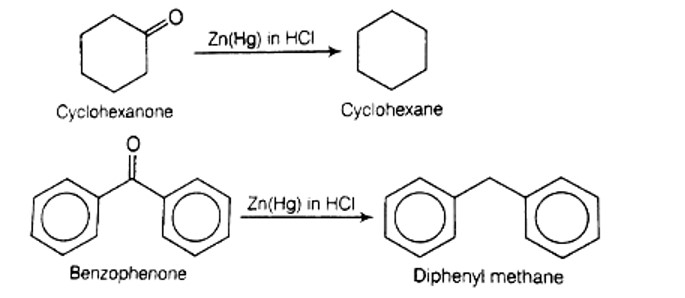
Which of the following conversions can be carried out by Clemmensen Reduction?
(i) Benzaldehyde into benzyl alcohol
(ii) Cyclohexanone into cyclohexane
(iii) Benzoyl chloride into benzaldehyde
(iv) Benzophenone into diphenyl methane
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Solution: (b, d)
Clemmensen reduction is used to convert cyclohexanone into cyclohexane and benzophenone into diphenyl methane .
Through which of the following reactions the number of carbon atoms can be increased in the chain?
A: Grignard reaction
B: Cannizaro’s reaction
C: Aldol condensation
D: HVZ reaction
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct option: A and C
Grignard Reaction is the addition of an organomagnesium halide to form a tertiary or secondary alcohol.
Canizzaro's Reaction involves the base induced disproportionation of two molecules. Aldol Condensation is an organic reaction when an enolate ion reacts with a carbonyl compound to form beta hydroxy ketone with dehydration to give a conjugated enone.
The HVZ reaction involves alpha bromination of carboxylic acids and this reacts with chlorine or bromine in presence of a small amount of red phosphorus to give alpha halo carboxylic acids.
Benzophenone can be obtained by ____________.
A: Benzoyl chloride + Benzene + AlCl3
B: Benzoyl chloride + Diphenyl cadmium
C: Benzoyl chloride + Phenyl magnesium chloride
D: Benzene + Carbon monoxide + ZnCl2
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and B
A: Benzophenone can be obtained by Friedel-craft acylation reaction
B: Benzophenone can also be obtained by the reaction between benzoyl chloride and diphenyl cadmium.
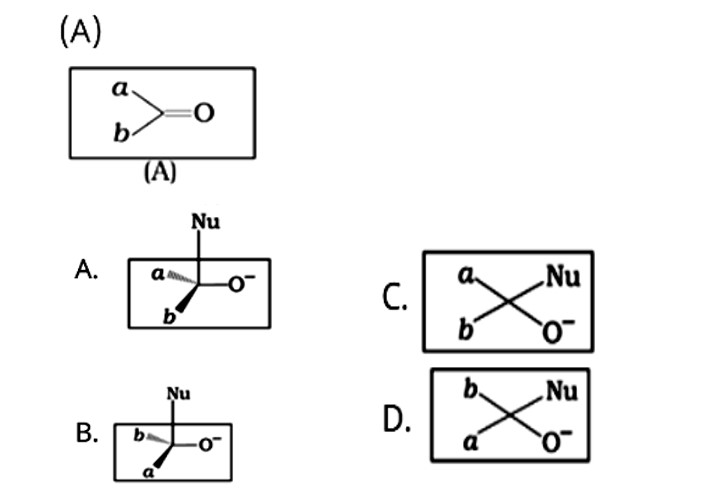
Which of the following is the correct representation for intermediate of nucleophilic addition reaction to the given carbonyl compound
This is a Multiple Choice Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Correct options: A and B
The given compound is a planar molecule with sp2 hybridised carbon. Carbon atoms are attacked by nucleophiles. If the nucleophile approaches from the front, the A and B molecules shift to the front and back positions, respectively, and the carbon becomes tetrahedral. Another alternative is that A and B molecules will be located above and below the plane, respectively. As a result, the choices C and D aren't represented as planar molecules.
Note: In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct Ans: out of the following choices
A: Assertion and reason both are correct, and reason is the correct of assertion.
B: Assertion and reason both are wrong statements
C: Assertion is correct statement, but reason is wrong statement.
D: Assertion is wrong statement, but reason is correct statement
E: Assertion and reason both are correct statements, but reason is not correct of assertion
Assertion: Formaldehyde is a planar molecule.
Reason: It contains sp2 hybridised carbon atom
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: A
The smallest aldehyde is formaldehyde. It features a triangular planar shape with two bond pairs and no lone pairings. C and O share one pair of electrons in their double bond. As a result, the C atom is sp2 hybridised. As a result, both Assertion and Reason are true.
Assertion: Compounds containing - CHO The group is easily oxidised to corresponding carboxylic acids.
Reason: Carboxylic acids can be reduced to alcohols by treatment with LiAlH4
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: E
The two reactions produce different products for different reasons. One involves the oxidation of aldehydes, while the other involves the reduction of carboxylic acids. Aldehydes are easily oxidised by mild oxidising agents, hence compounds containing - CHO are rapidly oxidised.
Assertion: The α-hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is less acidic.
Reason: The anion formed after the loss of α-hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: D
Because of the presence of electron withdrawing carbonyl groups, the alpha hydrogen atom in carbonyl compounds is acidic. In nature, hydrogen is very acidic.
Because the cation is released in the form of H+ , the anion created after the loss of the -hydrogen atom is resonance stabilised.
Assertion: Aromatic aldehydes and formaldehyde undergo Cannizaro reaction.
Reason: Aromatic aldehydes are almost as reactive as formaldehyde
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: C
There is no alpha hydrogen atom in the Cannizaro process. Formaldehyde and aromatic aldehydes do not contain alpha hydrogen. It proceeds through the Cannizaro reaction. Formaldehyde is the most reactive of all aldehydes.
Assertion: Aldehydes and ketones, both react with Tollen’s reagent to form a silver mirror.
Reason: Both, aldehydes and ketones contain a carbonyl group.
This is a Assertion and Reason Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: D
The silver mirror test can be used to determine Tollen's. [Ag (NH3)2] + OH - . Only aldehydes, not ketones, react with Tollen's reagent to create silver.
A silver mirror test is not given with this affirmative test.
The carbonyl group is present in both aldehyde and ketone.
Note: Match the items of Column I and Column II in the following questions.
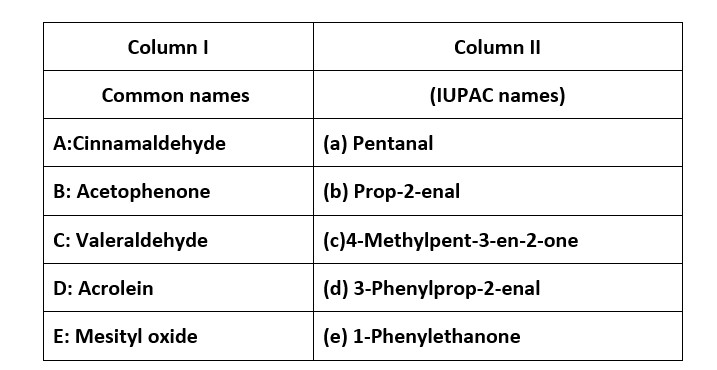
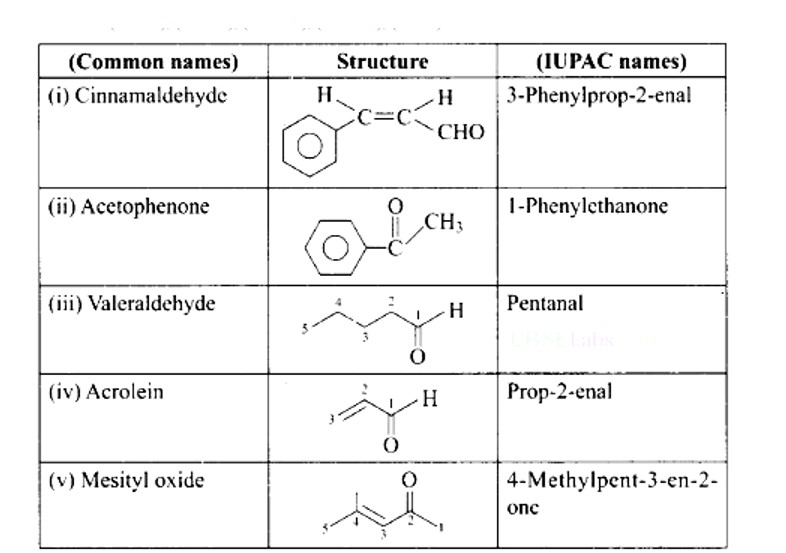
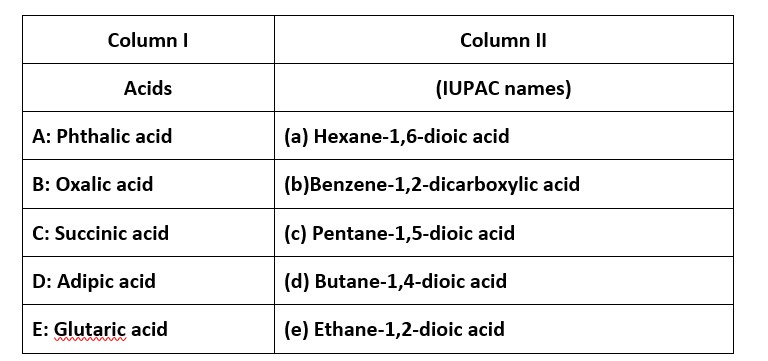
38. Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.
Match the common names given in Column I with the IUPAC names given in Column II.
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) → (d); (ii) → (e); (iii) → (a); (iv) → (b); (v) → (c)
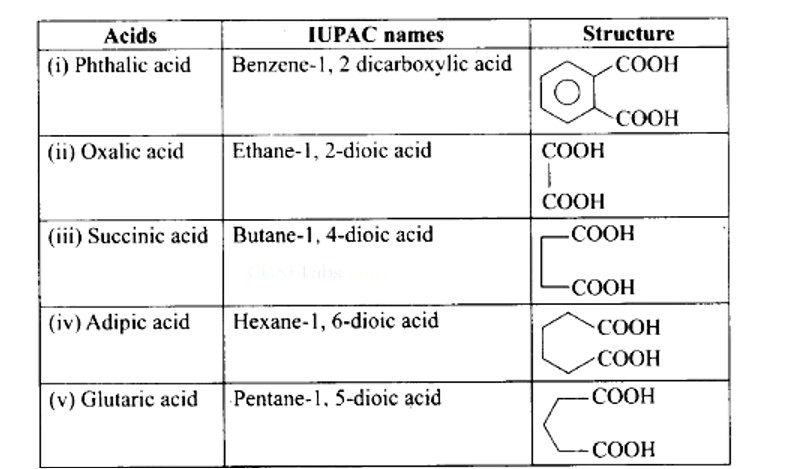
Match the acids given in Column I with their correct IUPAC names given in Column II
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) → (b); (ii) → (e); (iii) → (d); (iv) → (a); (v) → (c)
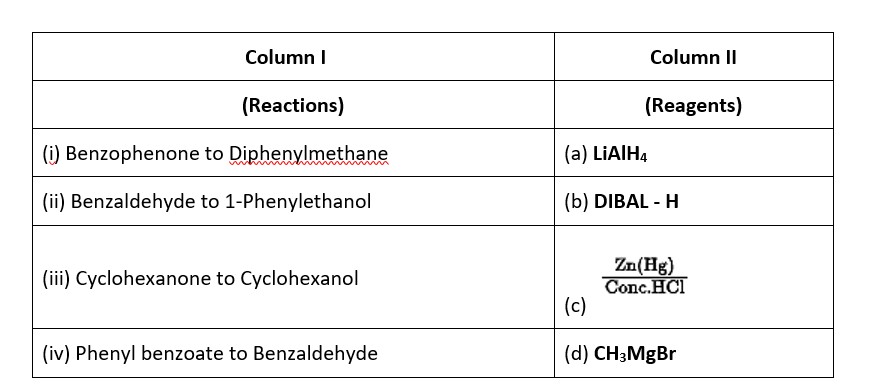
Match the reactions given in Column I with the suitable reagents given in Column II
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) → (c); (ii) → (d); (iii) → (a); (iv) → (b).
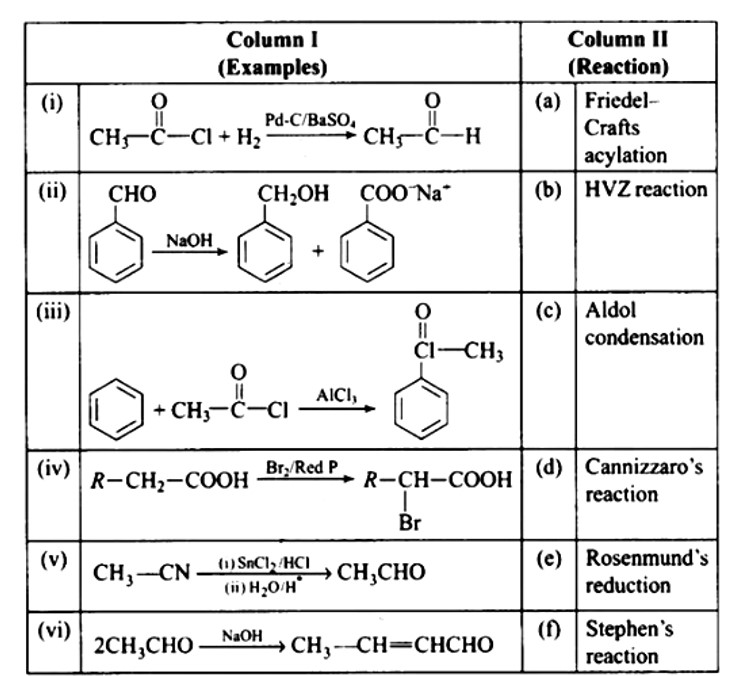
Match the example given in Column I with the name of the reaction in Column II.
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) — (e); (ii) — (d); (iii) — (a); (iv) — (b); (v) — (f); (vi) — (c)
JEE Mains Solutions 2020, 4th september, chemistry, second shift
JEE Mains Solutions 2020, 4th september, chemistry, second shift
Commonly asked questions
The Crystal Field Stabilization Energy (CFSE) of is :
Sol. (a) In extraction of iron lime stone is added on a flux
The processes of calcination and roasting in metallurgical industries, respectively, can lead to:
Sol. Reactivity towards depend on stability of carbocation formed
of a waste solution obtained from the workshop of a goldsmith contains and . The solution was electrolyzed at by passing a current of for 15 minutes. The metal/metals electrodeposited will be :
Sol. Balmer series lies in the visible region.
If the equilibrium constant for is and that of is , the equilibrium constant for is:
Among the following compounds, which one has the shortest bond?
Sol. and both have 4 unpaired electrons.
The process that is NOT endothermic in nature is:
Sol.
colourless
Oxidation state in is +3
The shortest wavelength of atom in the Lyman series is . The longest wavelength in the Balmer Series of is:
Kindly go through the solution
Which of the following compounds will form the precipitate with aq. solution most readily?
Sol. . Greater the Zeff, smaller is size.
In the following reaction sequence, is:
Sol. A - B has the lowest potential energy and it means it has stronger bond.
The major product in the following sequence of reactions is:
Kindly go through the solution
Sol.
The major product in the following reaction sequence will be:
Sol. At equilibrium rate of forward and backward reaction becomes equal.
The major product in the following reactions is:
Kindly go through the solution
Sol.
The mechanism of action of "Terfenadine" (Seldane) is :
Sol. , cell reaction is reversed
i.e. anode
cathode
An alkaline earth metal ' ' readily forms water soluble sulphate and water insoluble hydroxide. Its oxide is very stable to heat and does not have rock-salt structure. is:
Both contains group
The incorrect statement(s) among (a) - (c) is (are):
(a) is more stable than .
(b) In the presence of , permanganate titrations provide satisfactory results.
Sol. (i) Foam - Froth (e)
(ii) Gel - Jellies (c)
(iii) Aerosol - smoke (a)
(iv) Emulsion - milk (f)
The molecule in which hybrid MOs involve only one d-orbital of the central atom is :
Sol. and are temperature dependent
(for 1 mole of ideal gas)
The reaction in which hybridization of the underlined atom is affected is:
Sol. oxide
peroxide
superoxide
Five moles of an ideal gas at 1 bar and is expanded into vacuum to double the volume. The work done is :
Sol. belong to actinoids
104 belong to group 4
The number of molecules with energy greater than the threshold energy for a reaction increases five fold by a rise of temperature from to . Its energy of activation in is (Take in )(Kinetics)
Sol.
ATQ
Consider the following equations :
(in basic medium)
(in acidic medium)
(in acidic medium)
The sum of the stoichiometric coefficients and for products and , respectively, is
Sol. first order reaction
The number of chiral centres present in threonine is(Biomolecules)
A solution was made by adding of . The normality of the solution is . The value of is (The atomic mass of is )
Kindly go through the solution
The osmotic pressure of a solution of is and that of a glucose solution is . The osmotic pressure of a solution formed by mixing of the sodium chloride solution with of the glucose solution is is (nearest integer)(Solutions)
eq of eq of
JEE Mains Solutions 2020, 4th september, chemistry, First shift
JEE Mains Solutions 2020, 4th september, chemistry, First shift
Commonly asked questions
Among statements (a) - (d), the correct ones are:
(a) Lime stone is decomposed to during the extraction of iron from its oxides.
(b) In the extraction of silver, silver is extracted as an anionic complex.
(c) Nickel is purified by Mond's process.
(d) Zr and Ti are purified by Van Arkel method.
(a) In extraction of iron lime stone is added on a flux
(b) Extraction of silver
(c) Nickel is purified by Mond's process
(d) and are purified by Van Arkel method by converting to volatile iodide.
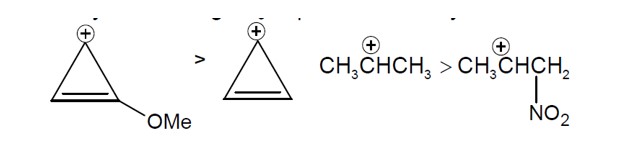
The decreasing order of reactivity of the following organic molecules towards solution is:
Reactivity towards depend on stability of carbocation formed
The region in the electromagnetic spectrum where the Balmer series lines appear is:
Balmer series lies in the visible region.
The pair in which both the species have the same magnetic moment (spin only) is:
and both have 4 unpaired electrons.
On heating, lead (II) nitrate gives a brown gas (A). The gas (A) on cooling changes to a colourless solid/liquid (B). (B) on heating with NO changes to a blue solid (C). The oxidation number of nitrogen in solid is:
colourless
Oxidation state in is +3
The ionic radii of and are in the order:
. Greater the Zeff, smaller is size.
The intermolecular potential energy for the molecules A, B, C and D given below suggest that:
A - B has the lowest potential energy and it means it has stronger bond.
The IUPAC name of the following compound is:
Correct IUPAC name is 4-Bromo-2-methylcyclopentane carboxylic acid
What are the functional groups present in the structure of maltose?
Kindly go through the solution
Identify the incorrect statement from the options below for the above cell:
, cell reaction is reversed
i.e. anode
cathode
Which of the following will react with alc. ?
Both contains group
Match the following:
(i) Foam - Froth (e)
(ii) Gel - Jellies (c)
(iii) Aerosol - smoke (a)
(iv) Emulsion - milk (f)
For one mole of an ideal gas, which of these statements must be true?
and each depends only on temperature
Compressibility factor is not equal to 1
for any process
and are temperature dependent
(for 1 mole of ideal gas)
On combustion of and in excess of air, the major oxides formed, respectively, are:
oxide
peroxide
superoxide
The elements with atomic numbers 101 and 104 belong to, respectively:
belong to actinoids
104 belong to group 4
At , the vapour pressure of a solution containing 1 mole of -hexane and 3 moles of -heptane is of . At the same temperature, if one more mole of -heptane is added to this solution, the vapour pressure of the solution increases by of . What is the vapour pressure in of -heptane in its pure state ?
ATQ
If of a first order reaction was completed in 90 minutes, of the same reaction would be completed in approximately (in minutes)
(Take: )(Kinetics)
First order reaction
The mass of ammonia in grams produced when of dinitrogen quantitatively reacts with of dihydrogen is(Mole Concept)
The number of chiral centres present in is
Kindly go through the solution
At solution containing impure reacts completely with of in acid solution. The purity of (in %) is (mol. wt. of ; mol. wt. of )
eq of eq of
on treatment with in produced a single isomer while heating with sodalime gave toluene. The compound is:
Kindly go through the solution
An organic compound (A) (molecular formula ) was hydrolysed with dil. to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). ' ' gives white turbidity immediately when treated with anhydrous and conc. . The organic compound is:
Kindly go through the solution
For the equilibrium , the variation of the rate of the forward (a) and reverse (B) reaction with time is given by:
At equilibrium rate of forward and backward reaction becomes equal.
When neopentyl alcohol is heated with an acid, it slowly converted into an 85:15 mixture of alkenes and , respectively. What are these alkenes?
Kindly go through the solution
25th June 2022 first shift
25th June 2022 first shift
Commonly asked questions
Bonding in which of the following diatonic molecule(s) become(s) stronger, on the basis of MO Theory, by removal of an electron?
(A) NO
(B) N2
(C) O2
(D) C2
(E) B2
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
Bond strength Bond order
NO Number of electron = 7 + 8 = 15
B.O. Similar to
B.O. of N2 = 3B.O of C2 =
Removal of e form antibonding molecular orbital increases bond order.
In NO & O2 has valance e in orbital.
Incorrect statement for Tyndall effect is:
→ number of electrons = 10
Br → number of electrons = 36
→ number of electrons = 2
→ number of electrons = 18
→ number of electrons = 2
→ number of electrons = 18
K+ → number of electrons = 18
O-2 → number of electrons = 10
Mg+2 → number of electrons = 10
O-2 & Mg+2 are isoelectronic with Al+3
Leaching of gold with dilute aqueous solution of NaCN in presence of oxygen gives complex [A], which on reaction with zinc forms the elemental gold an another complex [B], [A] and [B], respectively are
Au + NaCN + O2 → Na [Au (CN)2]
Number of electron deficient molecules among the following PH3, B2H6, CCl4, NH3, LiH and BCl3 is
Number of electrons in
are e- deficient molecules. B2H6 is dimer of BH3, both compound has 6e- only.
Which one of the following alkaline earth metal has the highest ionic mobility in its aqueous solution?
Size of hydrated ion
Size of hydrated ions
Size of hydrated ions ;
Ionic mobility ;
White precipitate of AgCl dissolves in aqueous ammonia solution due to formation of
Cerium (IV) has a noble gas configuration. Which of the following is correct statement about it?
Cerium exists in two oxidation states (+3) and (+4)
It exist as Ce+4 and acts like a strong oxidizing agent by gaining electrons
Among the following, which is the strongest oxidizing agent?
the strongest oxidizing agent have the highest reduction potential. So Mn3+ is the strongest oxidizing agent.
The eutrophication of water body results in
Eutrophication of water body results in loss of biodiversity.
Phenol on reaction with dilute nitric acid, gives two products. Which method will be most efficient for large scale separation?
Ortho product has intramolecular H- bonding & para product has intermolecular H- bonding. Thus it can be separated by steam distillation due to difference in B.
The number of N atoms in 681 g of C7H5N3O6 is x × 1021. The value of x is___________.
(NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol-1) (Nearest Integer)
Molar mass of C7H5N3O6 = 12 × 7 + 1 × 5 + 14 × 3 + 16 × 6 = 84 + 42 + 96 = 227 g/mol
Number of moles =
number of N-atoms
The longest wavelength of light that can be used for the ionization of lithium atom (Li) in its ground state is x × 10-8m. The value of x is_________. (Nearest Integer)
m
The standard entropy change for the reaction
[Given: The standard enthalpy change for the reaction is -165 kJ mol-1]. The temperature in K at which the reaction attains equilibrium is__________.
[Nearest Integer)
T =?
At equilibrium ;
1L aqueous solution of H2SO4 contains 0.02m mol H2SO4. 50% of this solution is dilutd with deionized water to give 1L solution (A). In solution (A), 0.01m mol of H2SO4 are added. Total m mols of H2SO4 in the final solution is ________× 103 m mols
1000 ml solution contains 0.02 milli mole (mm)
500 ml solution contains 0.02 m.m
Solution made 1000 ml with H2O
m.m in final solution = 0.01 mm
Solution (A) + 0.01 m. m H2SO4
= 0.01 + 0.01
= 0.02 m.m
= 0.00002 × 103 mm
The standard free energy change for 50% dissociation of N2O4 into NO2 at and 1 atm pressure is -xJ mol-1. The value of x is_________. (Nearest Integer)
[Given: R= 8.31 J k-1 mol-1, log 1.33 = 0.1239, In 10 = 2.3]
In a cell, the following reactions take place
Fe2+ → Fe3+
2I- → I2 + 2e-
The standard electrode potential for the spontaneous reaction in the cell is x × 10-2 V 298 K. The value of x is________(Nearest Integer)
Fe+2 undergoes reduction & I2 undergoes oxidation.
= (0.77 – 0.54) V = 0.23 V
= 23 × 10-2 V
For a given chemical reaction
Concentration of C charges form 10 mmol dm-3 to 20 mmol dm-3 in 10 second. Rate of appearance of D is 1.5 times the rate of disappearance of B which is twice the rate of disappearance A. The rate of appearance of D has been experimentally determined to be 9 mmol dm-3 s-1. Therefore the rate of reaction is_____________mmol dm-3 s-1 (Nearest Integer)
rate of reaction = = 1m.m dm-3 S-1
If absorbs a light of wavelength 600nm d-d transition, then the value of octahedral crystal field splitting energy for will be_________× 10-21J. (Nearest Integer)
(Given: h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js and c = 3.08 × 108 ms-1)
J
J
Number of grams of bromine that will completely react with 5.0g of pent-1-ene is_____________×10-2g. (Atomic mass of Br = 80 g/mol) (Nearest Integer)
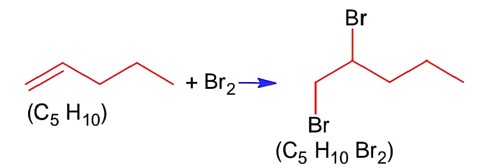
Moles of Br2= moles of C5H10=
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Twelve Exam