Biomolecules
Get insights from 151 questions on Biomolecules, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Biomolecules
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.18
Open structure of D-glucose could not explain the following reactions:
(i) Despite having the aldehyde group, glucose does not give 2,4 DNP test and Schiff's
(ii) Glucose does not react with sodium hydrogen sulphite to form addition
(iii) The absence of free –CHO group is shown when the penta-acetate of glucose does not react with hydroxyl
(iv) When glucose is heated with methanol in the presence of dry HCl gas, it forms two isomeric monomethyl derivatives known as? -D-glucoside and? -D-glucoside. Since only one molecule of methanol is used for the formation of methyl glucosided, these must be hemiacetals.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.17
When D-glucose is heated and treated with HI for a long period of time, then n-hexane is formed, which shows that all the six-carbon atoms are linked in a straight
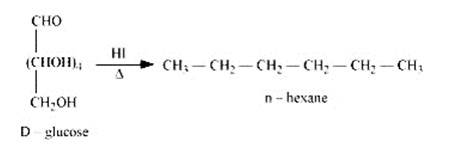
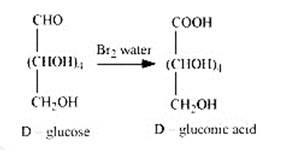
2. When D-glucose is treated with Br2 water i.e., bromine water which is a mild oxidising agent, then we get D-gluconic acid as one of the product. This reaction assures the presence of carbonyl group which is available as an aldehydic group.
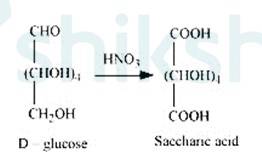
3. On being treated with HNO3, D-glucose get oxidised which gives saccharic acid as final Saccharic acid is a di-carboxylic acid. This reaction confirms the presence of alcoholic group (- OH) in the glucose.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.16
Starch consists of two components – amylase and amylopectin. Amylose is a long linear chain of α–D-(+)-glucose units joined by C1-C4glycosidic linkage (α -link).
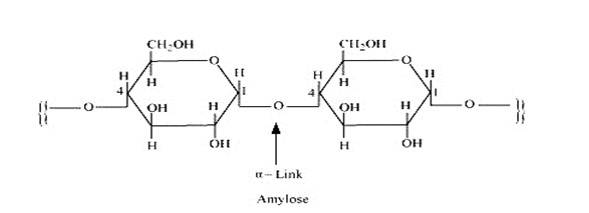
Amylopectin is a branched-chain polymer of –D-glucose units, in which the chain is formed by C1-C4 glycosidic linkage and the branching occurs by C1-C6 glycosidic linkage.

On the other hand, cellulose is the main structural material of tree and other plants. Wood is 50% cellulose, while cotton wool is almost pure cellulose. It is linear chain natural polymers of β-D-glucose units joined by 1, 4-glycosidic linkage (natural linear polymers).

New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.15
Hydrolysis is the process of using water to break down a molecule into two parts. It is usually a type of decomposition reaction where one reactant is water, where water is used to break chemical bonds in the other reactant. It can be considered as reverse of a condensation reaction.
The general formula of a hydrolysis reaction is:
XY + H2O → XH + YOH
(i) On hydrolysis with dilute acids, sucrose yields an equimolecular mixture of α –D glucose and β–D- fructose.
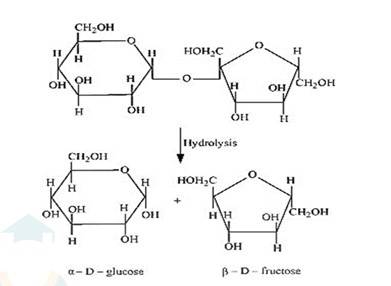
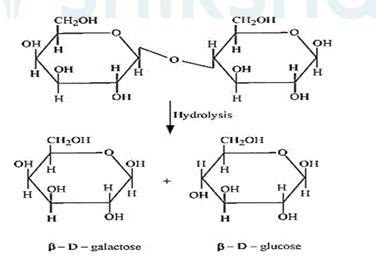
(ii) The hydrolysis of lactose gives β–D-galactose and β–D-glucose as final products.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.14
Glycogen is a polysaccharide-type of carbohydrate. In animals, carbohydrates are stored as glycogen.
But starch is a carbohydrate which consists of two components –amylase (15 -20 %) and amylopectin (80 – 85%). However, glycogen is also like amylopectin but branching will take place after every 5 to 6 glucose unit. Also, glycogen is highly branched.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.13
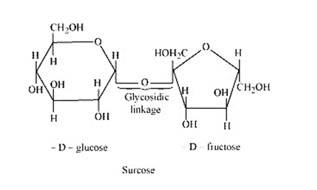
The condensation of the hydroxyl group of two monosaccharides to form a link between them is called glycosidic linkage. In other words, it refers to linkage developed between two different monosaccharide units through an oxygen atom by the loss of a water molecule. For example, in a sucrose molecule, two monosaccharide units, α-glucose and β–fructose, are joined together by a glycosidic linkage.

New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.12
i. Ribose, 2-deoxyribose, galactose, and fructose are
Monosaccharides are the simplest units of carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler compounds.
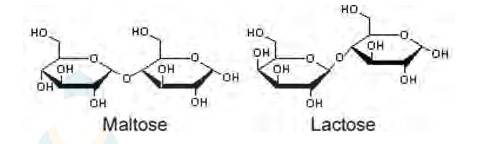
ii. Maltose and lactose are
A disaccharide is a carbohydrate that is formed when two monosaccharides are joined together and a molecule of water is removed from the structure. Lactose is a disaccharide formed from the combination of galactose and glucose.

New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.11
Carbohydrates are an essential compound for the organic life It is used as primary source of energy by plants and animals. It also fulfill other needs like synthesizing of other chemicals and provide the structure for cells within the body.
Energy is stored in it in the form of starch which, provide either complex or simple type of sugars. Complex sugars i.e., polysaccharides, give a constant supply of energy while simpler sugars, like monosaccharides, supplies a quicker jolt before dissolving.
Animals receive these starches through foods, especially those made from plant life such as grains and bread.
Plants manufacture their own ca
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.10
All those carbohydrates which reduce Fehling's solution to red precipitate of Cu2O or Tollen's reagent to metallic Ag is called reducing sugars. All monosaccharides (both aldoses and ketoses) and disaccharides except Sucrose are reducing sugars.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.9
Monosaccharides are the only the simplest units of carbohydrates and they are the simplest form of sugar. In other words, It is the most basic form of carbohydrates. They are made up of hydrogen, carbon and oxygen atoms. They are the building blocks of more complex carbohydrates i.e., they can join together and form complex carbohydrates.
For example:
i. Monosaccharides form
ii. 3-10 of them form
iii. 11 or more of them form
Monosaccharides are used to produce and store energy. Most organisms create energy by breaking down the monosaccharide glucose and harvesting the energy released from the bonds. Other Monosaccharides are
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers

