Biomolecules
Get insights from 151 questions on Biomolecules, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Biomolecules
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
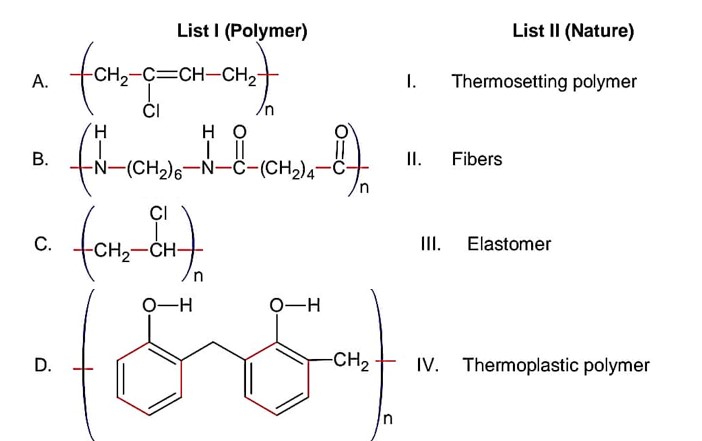
(A) Neoprene is Elastomer
(B) Nylon- (6, 6) is fibre
(C) PVC is thermoplastic
(D) Novolac is thermosetiting plastic.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Helix (2°) structure of protein is stabilized by intermolecular H-bonding.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
In maltose, two units of a-D-glucose are linked by glycosidic linkage at C1 and C4 as shown.
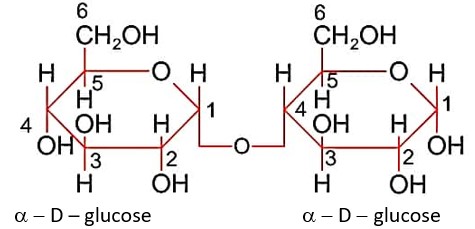
a - D – glucose a - D - glucose
Maltose has hemiacetal link so it is reducing sugar.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.33
The different types of RNA found in the cell are listed below:-
(i) Messenger RNA (m-RNA)
It carries the genetic message code from the DNA to ribosomes. It is produced by the DNA; m-RNA is also single stranded and constitutes about 15% of total RNA.
(ii) Ribosomal RNA (r-RNA)
It is found in the ribosomes and it is usually associated with protein to form the ribosomes. It is synthesised in the nucleus by DNA. It is single stranded, comprising about 80% of total RNA. It is metabolically stable.
(iii) Transfer RNA (t-RNA)
It is synthesised in nucleus by DNA. It is also called soluble RNA. It is single stranded. There are 20
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.32
The structural difference between DNA and RNA are as follows:-
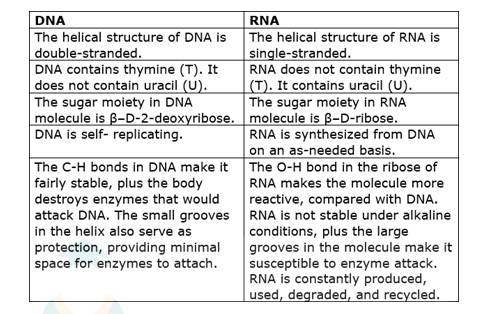
The functional difference between DNA and RNA are as follows:-

New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.31
In the helical structure of DNA, the two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between specific pairs of bases.
Cytosine from hydrogen bond with guanine, while adenine forms hydrogen bond with thymine. As a result, the two strands are complementary to each other.
DNA consists of two strands of nucleic acid chains coiled around each other in the form of a double helix. The base of one strand of DNA is paired with bases on other strand by means of hydrogen bonding.
This hydrogen bonding is very specific as the bases can only base pair in a complementary manner.
Adenine pairs with only thymine via 2 hydrogen bonds and guanine pairs
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.30
A nucleoside is formed when l-position of a pyrimidine (cytosine, thymine or uracil) or 9- position of a purine (guanine or adenine) base is attached to C-l of sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) by a linkage. Thus in general, nucleosides may be represented as: Sugar-Base.
Nucleoside = sugar + base
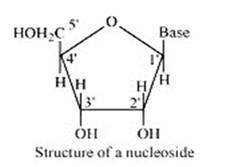
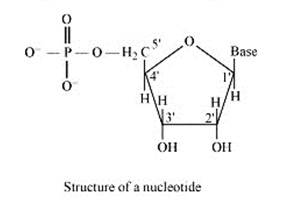
On the other hand, all the three basic components of nucleic acids (i.e., pentose sugar, phosphoric acid and base) are present in a nucleotide.These are obtained by esterification of C5' –OH group of the pentose sugar by phosphoric acid. Thus, in general, a nucleotide is represented as:-
Nucleotide= sugar + base + phosphoric acid
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
14.29
Nucleic acids are Biomolecules which are found in the nuclei of all living cells, inform of nucleoproteins or chromosomes (proteins containing nucleic acids as the prosthetic group). Nucleic acids are of two types: – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). Nucleic acids are also known as Polynucleotide as they are long- chain polymers of nucleotides.
The two important functions of nucleic acids are listed below:-
(i) DNA which is responsible for the transference of hereditary effects from one generation to another, which is due to their property of replication during cell division as a result of which two identica
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers