Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Four
Get insights from 99 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Four, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Four
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii)
The molecular orbital diagram of O22-, π∗2Px and π∗2Py molecular orbitals are completely filled, which are partially filled in O2. These are no unpaired electrons. So, O22-does not contain unpaired electrons.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii)
A double bond has one s bond and one π bond. In the above given structure 5π bonds are present. The s bonds are the additions of all the single bonds in the structure. There are 19s bonds in the above given structure.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i)
(i) The molecule of BH4 - has four bond pairs and zero lone pair of electrons, so it will be a tetrahedral molecule.
(ii) NH2 - has two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom. So, it will have a bent geometry.
(iii) CO3 2- has three bond pairs and no lone pairs of electrons on carbon atoms. So, it will have a trigonal planar geometry.
(iv) H3O+ has three bond pairs and one lone pair of electrons on oxygen atoms. So, it has a pyramidal geometry.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iv)
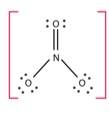
The number of bond pairs on the nitrogen atom of NO3- are 4 and the structure of - NO3 does not have any lone pairs of electrons. The structure of NO3- molecule is:
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
In a polyatomic molecule or an ion, the formal charge of an atom is defined as the difference between the valence electrons present in that atom and the number of electrons assigned to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Formal charge = No. of valence electrons - (No. of lone pair
Formal Charge = 6 -
Formal Charge = -1
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
The size and the electronegativity are the main factors on which the strength of a compound depends on. As the size of the atom decreases, the electronegativity increases and thus the hydrogen-bonding becomes stronger. Thus, the strength of hydrogen-bonding in the given compounds is: H2O > HF > NH3
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
The hybrid orbitals of nitrogen in the given species will be confirmed by knowing the hybridization. In NO2+ the central nitrogen atom is sp hybridized as it has a linear shape. The molecule NO3- is sp2 due to the presence of one lone pair of electrons on a nitrogen atom and hence having a bent geometry. The molecule NH4+ is sp3 hybridized having a tetrahedral geometry.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii)
The dipole moment of the molecule depends on the difference in the electronegativity of the atoms present in the structure. The dipole moment of CO2 is 0, HI is 0.38, H2O is 1.84 and SO2 is 1.62.
As the oxygen atom is highly electronegative and hydrogen is least electronegative, the difference in electronegativity will be the highest for water molecules. Therefore, water molecules will have the highest dipole moment.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
In a molecular structure if a central atom has the same hybridization as the central atom of another molecular species, then the two structures are known as isostructural species.
(i) In NF3 the central nitrogen atom is sp3 hybridized and in BF3 the central boron atom is sp2 . So, these two molecules are not isostructural pairs.
(ii) In BF4 the central boron atom is sp3 hybridized and in NH4 + the central nitrogen atom is also sp3 So, these two molecules are identified as isostructural pairs.
(iii) In BCl3 the central boron atom is sp2 hybridized and in
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The average bond enthalpy is defined as the ratio of total bond dissociation enthalpy to the number of bonds broken in the structure.
The identical O- H bonds in water molecule does not have the same bond enthalpies. According to the structure of a water molecule, there are two O- H bonds, but there is a change in the breaking of the first O- H bond than the second because of the different charge.
Hence in water molecule the average bond enthalpy will be:
The average O-H bond enthalpy = = 464 mol-1
In ethanol C2H5OH the bond enthalpy of O-H is different becaus
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers