Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Four Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure offers comprehensive practice material for how atoms combine to form molecules. The chapter is crucial in chemistry and it explains the types, nature, and geometry of chemical bonds. The solutions are given in a step-by-step format that helps students solve the numerical, theoretical, and conceptual problems with ease.
Students can also download the Chemical Bonding NCERT PDF for practicing the solutions of MCQs, Shorty type questions, Long Type Questions, Matching Type and Assertion and Reason questions. The PDF is prepared by Shiksha's subject matter experts. The students can rely on these solutions, and practice them offline or they can also take a printout and practice on paper.
The students should also read the Class 11th Chapter Four Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NCERT Solutions.
- Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter Four Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 Short Answer Type Questions
- Chemistry Class 11 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Long Answer Type Questions
- Class 11 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Matching Type Questions
- NCERT Exemplar Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 Assertion and Reason Type
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Objective Type Questions
- Common Mistakes and Tips for NCERT Chemistry Exemplar Chapter Four
- JEE Mains 2020
- 01 Oct 2025
Download PDF of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter Four Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
The students can download the Chemical Bonding PDF NCERT from this page. There are numerous benefits of this PDF for exam preparation and improving learning efficiency. Once the students download the PDF, they can use it for quick revision and practice on the go, even when they do not have any internet connectivity. Practicing the exemplar questions helps student in deepening their concept clarity. The chapter deals with critical topics like hybridization, bond formation, bond parameters, and molecular geometry.
Also read:
NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 Short Answer Type Questions
SA questions involve small derivations, brief explanations, or the application of basic theories like the octet rule, Lewis structures, bond parameters, VSEPR theory, and electronegativity. It requires students to give answers in a concise format. Practicing short-answer type questions helps students to build accuracy in presenting precise chemical reasoning, and also in clarifying the concepts. Students can also read NCERT Class 11 Notes here.
SA Questions
Explain the non linear shape of H2S and non planar shape of PCl3 using valence shell electron pair repulsion theory.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In the Lewis structure of PCl3, the phosphorus atom is surrounded by three bond pairs (chlorine atoms) and one lone pair. These four electron pairs are arranged in a tetrahedral geometry around the central phosphorus atom. Due to the presence of lone pair of electron on the phosphorus atom, PCl3 will have a distorted tetrahedral geometry. Thus, it will form a pyramidal shape and is non-linear in structure.
In H2S, the central sulphur atom is surrounded by two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons. It can be said that these four electron pairs are arranged in a tetrahedral geometry. Due to the presence of two lone pairs on the central sulphur atom, the lone pair-bond pair repulsion happens and due to this the molecule H2S has a V-shaped geometry and is non-linear in structure.
Using molecular orbital theory, compare the bond energy and magnetic character of O2+ and O2 – species
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The electronic configurations of O2+ and O2 - according to molecular orbital theory is:
O2+: σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2, π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p1x
O2- : σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2, π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p2y π*2p1x
The bond order of O2+
Bond order = ( Nb- Na)
Bond order = (10-5)=2.5
The bond order of O2-
(10-7)= = 1.5
As the bond order of O2+ is higher, it is more stable than O2 -, because higher the bond order more stable is the bond. Both the molecular species have the presence of unpaired electrons. So, they both are paramagnetic in nature.
Commonly asked questions
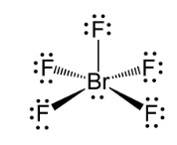
Explain the shape of BrF5.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In BrF5 the central bromine atom has 7 valence electrons. It makes five bonds with the fluorine atom and one lone pair of electron is left. Due to the lone pair-bond pair repulsions, BrF5 makes a structure of square pyramidal geometry. Due to the distortion of fluorine ions, each fluorine ion makes an angle of 90° . The square pyramidal shape of BrF5 is
Structures of molecules of two compounds are given below :
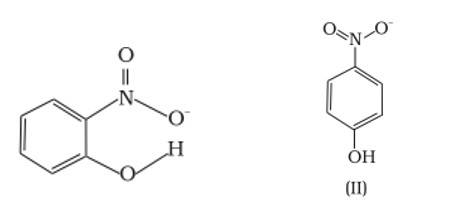
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (a) Which of the two compounds will have intermolecular hydrogen bonding and which compound is expected to show intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
Ans: The intramolecular hydrogen bonding is shown by compound (I) and the intermolecular hydrogen bonding is shown by compound (II) . In compound (I) the NO2 and OH group are close together in comparison to that in compound (II) . So, that is why compound (I) shows intramolecular hydrogen bonding. The intermolecular hydrogen bonding in compound (II) is shown as:
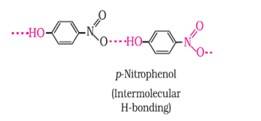
(b) The melting point of a compound depends on, among other things, the extent of hydrogen bonding. On this basis explain which of the above two compounds will show higher melting point.
Ans: Due to the formation of intermolecular hydrogen bonds, compound (II) will have a higher melting point. Thus, due to hydrogen bond formation more molecules are joined together.
(c) Solubility of compounds in water depends on power to form hydrogen bonds with water. Which of the above compounds will form hydrogen bond with water easily and be more soluble in it?
Ans: Compound (I) will be less soluble in water due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding; it will not be able to form hydrogen bonds with water. Whereas, compound (II) can form hydrogen bonds with water more easily and is thus more soluble in water.
Why does type of overlap given in the following figure not result in bond formation?
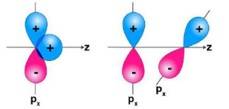
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In the first figure given above, the area which is under + overlapping is equal to the area under +- overlap. Both the overlaps cancel out with each other as they are oppositely charged. Due to cancelling out of the overlaps the net overlap will be zero. In the second figure given above, both the p-orbitals are perpendicular to each other. Due to the, px py orbitals being perpendicular with each other, no overlap will be possible.
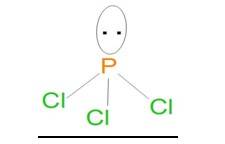
Explain why PCl5 is trigonal bipyramidal whereas IF5 is square pyramidal.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In PCl5, P has 5 valence electrons in orbitals and make 5 bonds with 5 Cl atoms, it will share one of its electrons from 3s to 3d orbital, therefore the hybridization will be sp3d and the geometry will be trigonal bipyramidal. IF5, the Iodine atom has 7 valence electrons in molecular orbitals it will form 5 bonds with 5 Cl atoms using 5 electrons from its molecular orbital, two electrons will form one lone pair on Iodine atom, which gives the square pyramidal geometry.
In both water and dimethyl ether (CH3 —Ο — CH3 ), oxygen atom is central atom, and has the same hybridisation, yet they have different bond angles. Which one has greater bond angle? Give reason.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Although the hybridisation of the central atom oxygen in both the molecules is 3 sp but dimethyl ether will have a higher bond angle than water molecule.
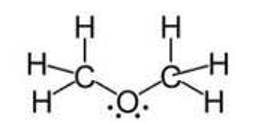
Due to the presence of two bulky methyl groups in dimethyl ether, the repulsive forces will be greater in them than the two hydrogens in water molecules. In dimethyl ether the -CH3 is a group attached to three hydrogen atom through s bonds. Thus, the C- H bond pairs increase the electron density on the carbon atom which results in lone pair-bond pair repulsions. Due to this lone pair-bond pair repulsions, the bond angle of dimethyl ether is greater than that of water molecules.
Write Lewis structure of the following compounds and show formal charge on each atom.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The Lewis structures of the compounds are:
Lewis structure for nitric acid:
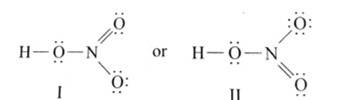
Lewis structure of nitrogen dioxide:
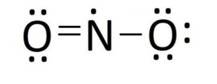
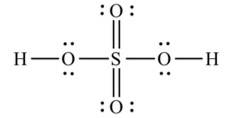
Lewis structure of sulphuric acid:
The energy of σ2pz molecular orbital is greater than π2px and π2py molecular orbitals in nitrogen molecule. Write the complete sequence of energy levels in the increasing order of energy in the molecule. Compare the relative stability and the magnetic behaviour of the following species : N2, N2+ , N2– , N2
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The general sequence of the energy level of the molecular orbital is σ1s < σ*1s < σ2s< σ*2s < π2px = π2py < σ2pz
N2 = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2p2x = π2p2y σ2p2z
N2+ = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2p2x = π2p2y σ2p1z
N2- = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2p2x= π2p2y σ2p2z σ2p2x
N22+ = σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2p2x = π2p2y
The formula for finding the bond order (B. O) for any molecular species is:
Bond order = ( Nb- Na)
Hence, the bond orders of the given molecular species are:
N2= ( 10-4)= 3
N2+= ( 9-4)= 2.5
N2-= ( 10-5)= 2.5
N22+= (8-4)= 2
The order for the stability of the given molecular species thus will be:
N2.> N2-> N2+> N22+
What is the effect of the following processes on the bond order in N2 and O2?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) N2 → N2+ + e-
The electronic configuration of N2 is:
σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2p2x = π2p2y σ2p2z
So, its bond order will be 3
The electronic configuration of N2+ is:
σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2p2x = π2p2y σ2p1z
Its bond order will be 2.5
Hence the bond order decreases in this reaction N2 → N2+ + e-
(ii) O2→ O2+ + e-
The electronic configuration of O2 is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2 π2p2y π2p2x π*2p1y π*2p1x
Its bond order will be 2
The electronic configuration of O2+ will be:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2, π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p1x
Its bond order will be 2.5 .
Hence, the bond order in this reaction increases O2→ O2+ + e-
Give reasons for the following :
(i) Covalent bonds are directional bonds while ionic bonds are nondirectional.
(ii) Water molecule has bent structure whereas carbon dioxide molecule is linear.
(iii) Ethyne molecule is linear.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) Due to the electrostatic forces between the two opposite charges, ionic bonds are non-directional. The bonding direction does not matter as the electrostatic field of an ion is non-directional. Whereas, the formation of covalent bonds happens with the overlap of the atomic orbitals. The direction of the bonds is given by the direction of overlapping.
(ii) The hybridization of the oxygen atom in water molecules is 3 sp due to the presence of two lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom. Tetrahedral geometry is acquired by these four 3 sp hybridized orbitals with two bonds of hydrogen atoms and two lone pairs of electrons. Due to the presence of lone pairs of electron the bond angle gets reduced as there is a repulsion between the LP-LP and thus the molecule acquires a bent shape. The hybridization of carbon atoms in the carbon dioxide molecule is sp. The two sp are arranged in such a way that it makes an angle of 180° . That is why carbon dioxide has a linear shape.
What is an ionic bond? With two suitable examples explain the difference between an ionic and a covalent bond?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Ionic bonds are such bonds in which complete transfer of electrons from one atom to another atom. Due to complete transfer positive and negative ions are formed in this bond. The ions in this bond are held together by electrostatic force of attraction. The formation of calcium fluoride CaF2 leads to the formation of an ionic bond.
Ca→ Ca2+ + e - The electronic configuration of Ca= [Ar] 4s2 and Ca2+= [Ar]
F +e -→F- The electronic configuration of F= [He] 2p5 and F = [He ]2p6
Thus Ca2+ +2F- → CaF2
A covalent bond is formed due to mutual sharing of electrons between two atoms of a non-metal. This mutual sharing of electrons between the two non-metal species leads to the formation of a covalent bond. The making of Cl2 leads to a formation of a covalent bond between two chloride ions.
Arrange the following bonds in order of increasing ionic character giving reason.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
N—H, F—H, C—H and O—H
Ans: The ionic character in a molecular species is decided by the electronegativity difference between the two bonded atoms. Greater the electronegativity difference between two bonded pairs, the greater will be the ionic character. The electronegativity difference of the given species is
C - F = (2.5 - 2.1) = 0.4
N -H = (3.0 - 2.1) = 0.9
O - H = (3.5 - 2.1) = 1.4
F - H = (4.0 - 2.1) = 1.9
According to the above given difference in the electronegativities, the order of increasing ionic character is:
C – H< N - H
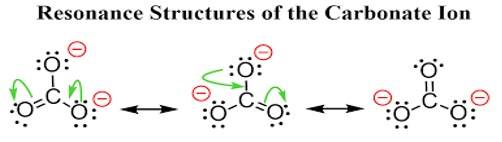
Explain why CO32– ion cannot be represented by a single Lewis structure. How can it be best represented?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The carbonate ion CO32- can be best represented by its resonating structures. The carbonate ion cannot be represented by a single Lewis structure because the three carbon oxygen bond lengths are the same. This cannot be shown by a single Lewis structure. For showing the similar lengths of all the carbon to oxygen bonds three hybrid structures are constructed which are in resonance with each other.
Predict the hybridisation of each carbon in the molecule of organic compound given below. Also indicate the total number of sigma and pi bonds in this molecule.
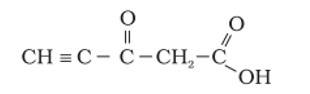
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The hybridization of Carbon 1 is sp, carbon 2 is sp, carbon 3 sp2, carbon 4 is sp3 and carbon 5 is sp2. The triple bond has 2 pie bonds and one sigma bond. Each double bond has one sigma and one pie bond. Every single bond is a sigma bond. Thus, the total number of sigma bonds is 11 and pie bonds are 4.
Group the following as linear and non-linear molecules :
H2O, HOCl, BeCl2, Cl2O
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: BeCl2 has a linear structure
HOCl is also non-linear in structure.
H2O has a V-shaped structure.
Cl2O has a V-shaped structure.
Elements X, Y and Z have 4, 5 and 7 valence electrons respectively.
(i) Write the molecular formula of the compounds formed by these elements individually with hydrogen.
(ii) Which of these compounds will have the highest dipole moment?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) According to the electronic configuration, a total of 8 electrons must be present in the valence shell of an element. Element X has 4 valence electrons, so it will share the remaining 4 electrons for the formation of the bond, the molecular formula will be XH4 . The element Y has 5 valence shell electrons, so it will form 3 bonds and the formula will be YH3 . The element Z has 7 valence shell electrons, so it will form one bond with hydrogen and has the molecular formula H-Z .
(ii) Elements X, Y and Z having, 5 and 4 7 valence electrons respectively belongs to the second period and group 14th ,15th and 17th . The electronegativity of the elements increases on moving across the period and the dipole moment is calculated by the difference in the electronegativity of the atoms in a molecular structure. Higher the difference in the electronegativity will be the dipole moment. So, the dipole moment of H - Z will be the highest.
Draw the resonating structure of
(i) Ozone molecule
(ii) Nitrate ion
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i)

(ii) 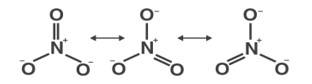
Predict the shapes of the following molecules on the basis of hybridisation.
BCl3, CH4 , CO2, NH3
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In compound BCl3, Boron has sp2-hybridisation and the shape is Triangular Planar.
In methane CH4, Carbon has sp3 -hybridization and shape are Tetrahedral.
In carbon dioxide CO2, carbon has sp-hybridisation and shape is Linear.
In ammonia NH3, nitrogen has sp3-hybridisation and shape is Pyramidal.
All the C—O bonds in carbonate ion (CO32– ) are equal in length. Explain.
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: All the C-Obonds in carbonate ion (CO32-) are equal in length due to the equivalent resonance of all the three carbon-oxygen bonds gets a double bond character atleast once. This type of double bond character happened throughout 3C- O skeleton, and hence all the bonds acquired equal bond length.
What is meant by the term average bond enthalpy? Why is there difference in bond enthalpy of O—H bond in ethanol (C2H5OH) and water?
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The average bond enthalpy is defined as the ratio of total bond dissociation enthalpy to the number of bonds broken in the structure.
The identical O- H bonds in water molecule does not have the same bond enthalpies. According to the structure of a water molecule, there are two O- H bonds, but there is a change in the breaking of the first O- H bond than the second because of the different charge.
Hence in water molecule the average bond enthalpy will be:
The average O-H bond enthalpy = = 464 mol-1
In ethanol C2H5OH the bond enthalpy of O-H is different because the electronic environment around oxygen atom is different. In ethanol the O-H is attached to the carbon atom and in water molecule the O-H is attached to the hydrogen atom.
A wire of length 314cm carrying current of 14A is bent to form a circle. The magnetic moment of the coil is_________ A -m2. [Given π = 3.14]
In bromination of Propyne, with Bromine 1, 1, 2, 2-tetrabromopropane is obtained in 27% yield. The amount of 1, 1, 2, 2- tetrabromopropane obtained from 1g of Bromine in this reaction is_______________× 10-1g. (Nearest integer) (Molar mass: Bromine = 80g / mol)
Reaction is
Mass of product, 1, 2, 2- tetrobromopropane obtained
=
= 3.30375
= 3.0375 × 10-1
Chemistry Class 11 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Long Answer Type Questions
LA questions require an in-depth understanding of the concepts. Students need to provide detailed explanations. These solutions help students to prepare for the descriptive questions in board exams and other entrance exams. LA questions for the Chemical Bonding may include comparing ionic vs. covalent bonds, predicting molecular geometry using VSEPR theory, deriving or explaining hybridization in molecules, drawing and analyzing molecular orbital diagrams, and explaining bond polarity and dipole moment.
LA Questions
| 1. (i) Discuss the significance/ applications of dipole moment. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: The significance of dipole moment is as follows: (a) Dipole moment is used to predict the nature of the molecules. A molecule having zero dipole moment is considered as a nonpolar molecule and a molecule having a specific dipole moment is considered as polar in nature. (b) Dipole moment is important in determining the shape of a molecule. The shape of a molecule will not be symmetrical if it has a specific dipole moment, it may be bent or angular. A linear molecular which is symmetrical has a zero dipole moment. (c) Dipole moment is helpful in the comparison of the polarities of the molecules. If the value of the dipole moment is higher, more will be the polarity of the molecule and vice-versa. (d) Dipole moment also determines if a molecule is in cis- or trans- position, because cis-isomers have higher dipole moment than trans-isomers. (e) Dipole moment measurements help in differentiating in the ortho-, meta-, and para-isomers. The dipole moment of para-isomers is zero and the dipole moment of ortho-isomers is more than meta-isomers. |
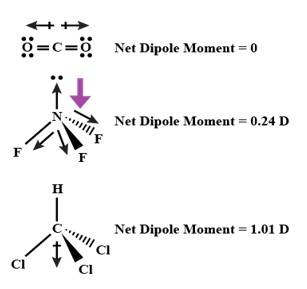
| 1. (ii) Represent diagrammatically the bond moments and the resultant dipole moment in CO2 , NF3 and CHCl3. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: According to the below shown diagrams, the bond moments and dipole moment of the following molecules is: For CO2 molecule: Carbon dioxide has a linear geometry, hence in the above structure the dipole of one C-Ois cancelled by another C-O . So, the dipole moment of CO2 is zero. For NF3 molecule: In nitrogen trifluoride, fluorine is more electronegative than hydrogen. The lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atoms also influences the dipole moment of the structure. The dipole moment of NF3 was found out to be 0.23D. In the above molecule, the dipole in F-N weakens the dipole induced by the lone pair of electrons. Thus the vector sum of the four dipole moments is low. For CHCl3 molecule: The two terminal chlorine atoms are cancelled with each other, the net dipole moment for chloroform was found out to be 1.04D. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: Introduced by Hietler and London in 1927, valence bond theory was further develop dy Pauling. Valence bond theory (VBT) describes the information about the atomic orbitals, it tells about the electronic configuration of elements, the overlap criteria of atomic orbitals and also the hybridization of atomic orbitals is depicted by the valence bond theory. A and B are two hydrogen atoms which are approaching each other and these hydrogen atoms have the nuclei , NA NB respectively, the electrons in the two hydrogen atoms are represented as , eA eB respectively. When the distance between these two hydrogen atoms is large, then there will be no interaction between them. New attractive and repulsive forces begin to generate as these two hydrogen atoms approach each other. Attractive forces arise between these two hydrogen atoms. As a result of these attractive forces, the two atoms come closer to each other. It has been found experimentally that the magnitude of new attractive forces was more than the new repulsive forces. Due to this when the two atoms approach each other the potential energy decreases. Therefore, a stage occurs, where the net force of attraction balances the net repulsive forces and a state of minimum energy is acquired by the system. At this stage the two hydrogen atoms form a bond together, thus forming a stable bond. When the two hydrogen atoms form a bond, the energy is released, the hydrogen molecule formed is more stable than the individual hydrogen atom. The energy released during the formation of the hydrogen molecule is called bond enthalpy. |
| 4. Describe hybridisation in the case of PCl5 and SF6. The axial bonds are longer as compared to equatorial bonds in PCl5 whereas in SF6 both axial bonds and equatorial bonds have the same bond length. Explain. |
| This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar Ans: Hybridisation in the case of PCl5 : The hybridisation of phosphorus PCl5 is sp3d and it has a trigonal bipyramidal geometry. The axial bonds in PCl5 are slightly longer as compared to the equatorial bonds because axial bonds experience greater repulsive forces from other bonds as compared to the equatorial bonds. Hybridisation in the case of SF6: The hybridisation of sulphur in SF6 is sp3d2 and the molecule has an octahedral geometry. The bond length of axial as well as the equatorial bonds are similar because all the bonds in octahedral geometry experience similar repulsive forces from other bonds. |
Commonly asked questions
Use the molecular orbital energy level diagram to show that N2 would be expected to have a triple bond, F2, a single bond and Ne2, no bond.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Formation of N2 molecule: Electronic Configuration
σ1s2 σ* < 1s2 < σ2s2 < σ*2s2 < [ π2p2x = π2p2y] < σ2p2z
The bond order will be:
( 10-4)= 3.0
Bond order indicates the number of bonds in a diatomic molecule. Triple bond N=N.
Formation of F2 molecule: Electronic Configuration
σ1s2 < σ*1s2< σ2s2 < σ*2s2 < σ2p2z < [ π2p2x = π2p2y] < [ π*2p2x = π*2p2y] σ*2p2z
The bond order will be:
( 10-10)= 0
Hence there will be no bond formation in between the neon atoms.
Describe hybridisation in the case of PCl5 and SF6. The axial bonds are longer as compared to equatorial bonds in PCl5 whereas in SF6 both axial bonds and equatorial bonds have the same bond length. Explain.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Hybridisation in the case of PCl5 :
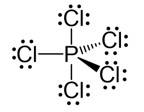
The hybridisation of phosphorus PCl5 is sp3d and it has a trigonal bipyramidal geometry. The axial bonds in PCl5 are slightly longer as compared to the equatorial bonds because axial bonds experience greater repulsive forces from other bonds as compared to the equatorial bonds.
Hybridisation in the case of SF6:
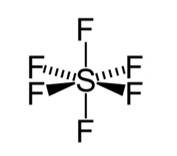
The hybridisation of sulphur in SF6 is sp3d2 and the molecule has an octahedral geometry. The bond length of axial as well as the equatorial bonds are similar because all the bonds in octahedral geometry experience similar repulsive forces from other bonds.
(i) Discuss the concept of hybridisation. What are its different types in a carbon atom.
(ii) What is the type of hybridisation of carbon atoms marked with star.
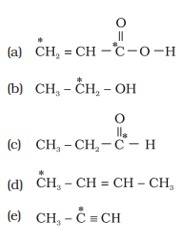
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) Different types of hybridization in a carbon atom are:
(a) sp hybridization: The carbon atoms forming triple bonds with each other determines hybridized carbon. ( Cº C ).
(b) sp2 hybridization: The carbon atoms forming double bonds with each other determine sp2 hybridized carbon. (C=C). (c) sp3 hybridization: The carbon atoms forming single bonds with each other determine sp3 hybridized carbon. ( C-C).
(ii)The starred C atom is sp2 hybridised.
B] The starred C atom is sp3 hybridised.
C] The starred C atom is sp2 hybridised.
D] The starred C atom is sp3 hybridised.
E] The starred C atom is sp2 hybridised.
Comprehension given below is followed by some multiple choice questions. Each question has one correct option. Choose the correct option.
Molecular orbitals are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals. Two atomic orbitals combine to form two molecular orbitals called bonding molecular orbital (BMO) and anti bonding molecular orbital (ABMO). Energy of anti bonding orbital is raised above the parent atomic orbitals that have combined and the energy of the bonding orbital is lowered than the parent atomic orbitals. Energies of various molecular orbitals for elements hydrogen to nitrogen increase in the order :
σ1s σ*1s< σ2s < σ*2s< [ π2px = π2py] < σ2pz< [ π*2px = π*2py] σ*2pz
for oxygen and fluorine order of energy of molecular orbitals is given below :
σ1s σ*1s< σ2s < σ*2s< σ2pz< [ π2px = π2py] < [ π*2px = π*2py] σ*2pz
Different atomic orbitals of one atom combine with those atomic orbitals of the second atom which have comparable energies and proper orientation. Further, if the overlapping is head on, the molecular orbital is called ‘Sigma’, (σ) and if the overlap is lateral, the molecular orbital is called ‘pi’, (π). The molecular orbitals are filled with electrons according to the same rules as followed for filling of atomic orbitals. However, the order for filling is not the same for all molecules or their ions. Bond order is one of the most important parameters to compare the strength of bonds.
Which of the following statements is correct?
(i) In the formation of dioxygen from oxygen atoms 10 molecular orbitals will be formed.
(ii) All the molecular orbitals in the dioxygen will be completely filled.
(iii) Total number of bonding molecular orbitals will not be same as total number of anti bonding orbitals in dioxygen. (iv) Number of filled bonding orbitals will be same as number of filled anti bonding orbitals.
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: (i) The electronic configuration of dioxygen is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2 π2p2y π2p2x π*2p1y π*2p1x
(ii) As it can be seen from the electronic configuration of oxygen atom π*2p1X π*2p1Y the are partially. So, the statement given is incorrect.
(iii) The statement given is correct because there are five bonding molecular orbitals and four antibonding molecular orbital in oxygen molecules. Hence, the bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals are no equal.
(iv) The filled bonding orbitals are not the same as the number of filled antibonding orbitals. The filled bonding orbitals are five and only two filled antibonding orbitals are present in dioxygen molecules.
Which of the following molecular orbitals has maximum number of nodal planes?
(i) σ∗1
(ii) σ*2px
(iii) π2px
(iv) π*2py
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
Nodal plane is a plane which passes through the nucleus and the probability of finding an electron on a nodal plane is zero. Amongst the above given molecular orbital, only π*2px contains two nodal planes. Rest of the molecular orbitals, σ∗1, π2px, π*2py contains one nodal plane.
Which of the following pair is expected to have the same bond order?
(i) O2 , N2
(ii) O2+, N2-
(iii) O2-, N2+
(iv) O2-,N2-
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
(i) The electronic configuration of O2 is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2 π2p2y π2p2x π*2p1y π*2p1x
Bond order = ( Nb- Na)
Bond order = (10-6)=2.0
The electronic configuration of N2 :
σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2p2x, π2p2y σ2p2z
Bond order = (10-4)=3.0
So, the bond order of O2 , N2 will not be equal.
(ii) The electronic configuration of O2+ is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2,π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p1x
Bond order = (10-5)=2.5
The electronic configuration of N2-
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 ,π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2 π*2p1x
Bond order = (10-5)=2.5
Hence, the bond order of O2+,N2- will be equal.
(iii) The electronic configuration of O2 - is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2,π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p2y π*2p1x
Bond order = (10-7)=1.5
The electronic configuration of N2+ is:
σ1s2 σ*1s2 σ2s2 σ*2s2 π2p2x , π2p2y σ2p1z
Bond order = (9-4)=2.5
Hence, the bond order of O2-, N2+ will not be equal.
(iv) The electronic configuration of O2 - is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2,π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p2y π*2p1x
Bond order = (10-7)=1.5
The electronic configuration of N2-
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 ,π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2 π*2p1x
Bond order = (10-5)=2.5
Hence, the bond order of O2 - , N2- will not be equal.
In which of the following molecules, σ2pz molecular orbital is filled after π2px and π2py molecular orbitals?
(i) O2
(ii) Ne2
(iii) N2
(iv) F2
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii)
Molecules from hydrogen to nitrogen shows this type of electronic configuration:
σ1s σ*1s< σ2s < σ*2s< [ π2px = π2py] < σ2pz< [ π*2px = π*2py] σ*2pz in which σ2pz is filled after π2px and π2py
So, amongst the given elements only nitrogen will show this type of electronic configuration in which σ2pz molecular orbital is filled after π2py and π2px
The electronic configuration of N2 is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2 π*2p1x
Class 11 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Matching Type Questions
These questions are to test students' ability to link the related concepts and chemical terms, such as bond types with examples, hybridizations with molecular geometries, molecules with their shapes, and bond angles with specific molecular shapes. These questions help in reinforcing the inter-conceptual understanding, clarity, and memory.
Matching Type Questions
Match the species in Column I with the type of hybrid orbitals in Column II.
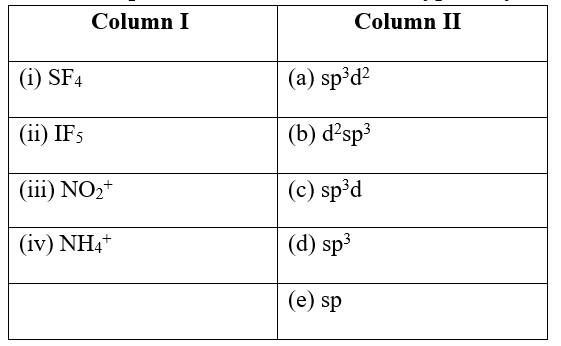
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
(i) SF4 (c) sp3d
(ii) IF5 (a) sp3d2
(iii) NO2+ (e) sp
(iv) NH4+ (d) sp3
Explanation :-
(i) SF4 has a total of 34 valence electrons. Sulphur has 6 valence electrons and each fluoride has 7 valence electrons. The central atom sulphur will thus share one electron with all the four fluoride ions and thus make four bonds. A lone pair of electrons (two electrons) is left on the sulphur atom. Thus, the sulphur atom is surrounded by five electron pairs, four bond pairs and one lone pair. Having five electron pairs surrounding sulphur, it will have a trigonal bipyramidal geometry with sp3d hybridization
(ii) IF5 has the total of 42 valence shell electrons, 7 valence electrons in iodine and 7 in each of the fluoride ions. The central iodine atom will thus make five sigma bonds with chlorine and a lone pair of electrons will be left on the iodine atom. The six electron pairs thus will have a hybridization of sp3d2 and octahedral geometry.
(iii) In NO2+, nitrogen forms two sigma bonds and two pi-bonds with the oxygen atom. The oxygen atoms are arranged in an angle of 180° with the nitrogen atoms. The s-orbital of the nitrogen forms a hybrid with the p-orbital of the nitrogen atom, thereby forming two sp hybridized hybrid orbitals, having a linear geometry.
(iv) NH4+ has the total of 8 valence electrons. Due to the presence of positive charge, nitrogen has 4 valence electrons and hydrogen has one in every four hydrogen atoms. The four valence electrons in nitrogen make sigma bonds with the four hydrogen atoms, thereby making a tetrahedral geometry and having 3 sp hybridized orbitals.
Match the species in Column I with the geometry/shape in Column II.
| Column I |
Column II |
| (i) H3O+ |
(a) Linear |
| (ii) HC ≡ CH |
(b) Angular |
| (iii) ClO2- |
(c) Tetrahedral |
| (iv) NH4+ |
(d) Trigonal bipyramidal |
|
|
(e) Pyramidal |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
(i) H3O+ (e) Pyramidal
(ii) HC? CH (a) Linear
(iii) ClO2- (b) Angular
(iv) NH4+ (c) Tetrahedral
Explanation :-
(i) The shape of H3O+ is pyramidal this structure has the total 8 valence electrons, six in oxygen atom, three in each hydrogen atoms and one electron is lost due to positive charge. Out of five valence electrons in oxygen three form a sigma bond with the hydrogen atom and a lone pair is left on the oxygen atom. Although the four electron pairs make a tetrahedral geometry but to the lone pair of electrons, lone-pair bond-pair repulsion occurs which distorts the shape and makes it pyramidal.
(ii) The ethyne molecule has a linear geometry, because the two carbon atoms make two pi bonds with each other and one sigma bond with the hydrogen atom. The carbon and hydrogen atoms are sp hybridized.
(iii) ClO2 - has 20 valence electrons in its structure. Chlorine atoms make one pibond and two sigma bonds with the oxygen atoms. The pi-bond is in resonance and hence ClO2 - has two resonating structures. Two lone pairs of electrons are left on the oxygen at om and hence, due to lone pair-lone pair repulsion the bond angle reduces and the shape becomes linear.
(iv) NH4+ has the total of 8 valence electrons. Due to the presence of positive charge, nitrogen has 4 valence electrons and hydrogen has one in every four hydrogen atoms. The four valence electrons in nitrogen make sigma bonds with the four hydrogen atoms, thereby making a tetrahedral geometry and having sp3 hybridized orbitals.
Commonly asked questions
Match the species in Column I with the bond order in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) NO |
1.5 |
|
(ii) CO |
2.0 |
|
(iii) O22- |
2.5 |
|
(iv) O2 |
3.0 |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
(i) NO (c) 2.5
(ii) CO (d) 3.0
(iii) O22- (a) 1.5
(iv) O2 (b) 2.0
Explanation :-
(i) The electronic configuration of NO is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2 π*2p1x
The bond order will be:
( 10-5)= 2.5
(ii) The electronic configuration of CO is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2
The bond order will be:
( 10-4)= 3.0
(iii) The electronic configuration of O2 - is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2, π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p2y π*2p1x
The bond order will be:
( 10-7)= 1.5
(iv) The electronic configuration of O2 is:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2 π2p2y π2p2x π*2p1y π*2p1x
The bond order will be:
( 10-6)= 2.0
Match the items given in Column I with examples given in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) Hydrogen bond |
(a) C |
|
(ii) Resonance |
(b) LiF |
|
(iii) Ionic solid |
(c) H2 |
|
(iv) Covalent solid |
(d) HF |
|
|
(e) O3 |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
(i) Hydrogen bond (d) HF
(ii) Resonance (e) O3
(iii) Ionic bond (b) LiF
(iv) Covalent solid (a) C
Explanation :-
(i) In hydrogen fluoride HF, hydrogen forms strong hydrogen bonds with fluorine because of the electronegativity of fluorine. Fluorine is more electronegative than hydrogen and thus the electrons in fluorine are more stabilized and they cannot be easily donated to an acceptor.
(ii) Ozone is a neutral molecule which is stabilized through resonance. The negative charge created by an extra electron is delocalized by resonance through terminal oxygen atoms.
(iii) In lithium fluoride LiF, the lithium metal has a positive charge ( 1) + and is a cation. The fluoride ion has a negative charge ( 1) - and is an anion. These two oppositely charged ions are held together by an ionic bond.
(iv) Carbon is a known covalent solid. The two allotropes of carbon, diamond and graphite are covalent network solids with different geometries. Due to the presence of covalent bonds in graphite and diamond, they have very high melting points and are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
Match the shape of molecules in Column I with the type of hybridisation in Column II.
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
(i) Tetrahedral |
(a) sp2 |
|
(ii) Trigonal |
(b) sp |
|
(iii) Linear |
(c) sp3 |
This is a Matching Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:
(i) Tetrahedral (c) sp3
(ii) Trigonal (a) sp2
(iii) Linear (b)sp
Explanation :-
(i) A tetrahedral molecule has four electron pairs and these make sigma bonds with each other. The s and p orbitals overlap with each other thus forming a sp3 hybridized molecule.
(ii) There are two possibilities for the central atom to have sp2 Either all the bonds are in place i.e, the bond pairs are all sigma bonds or pi bonds or there are only two bonds and one lone pair of electrons.
(iii) The sp hybridization involves the mixing of the valence electrons in s orbital with another valence electron in the p orbital which yields two sp orbitals which are oriented in a linear geometry.
NCERT Exemplar Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 Assertion and Reason Type
These evaluate the student's ability to see the logical relationship between two statements. Assertion and Reason Type Questions cover areas like factors affecting bond angles, the cause-and-effect relation in molecular shape, exceptions to the octet rule, and stability of molecules based on bond formation. The students need to analyze whether the reason correctly explains the assertion and whether both the assertion and the reason are true. Practicing these types of questions helps in building conceptual accuracy and logical thinking.
Assertion and Reason Type
Assertion (A) : Sodium chloride formed by the action of chlorine gas on sodium metal is a stable compound.
Reason (R) : This is because sodium and chloride ions acquire octet in sodium chloride formation.
(i) A and R both are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) A and R both are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) A is true but R is false.
(iv) A and R both are false
This is a Assertion Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i)
Both the statements given in assertion and reason are correct and the reason given is the correct explanation for the assertion. The sodium chloride formed by the action of chlorine gas on the sodium metal has a complete octet. The valence shells of both the atoms are fulfilled, that is why attains an octet.
Assertion (A) : Though the central atom of both NH3 and H2O molecules are sp3 hybridised, yet H–N–H bond angle is greater than that of H–O–H.
Reason (R) : This is because nitrogen atom has one lone pair and oxygen atom has two lone pairs.
(i) A and R both are correct, and R is the correct explanation of A.
(ii) A and R both are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) A is true but R is false.
(iv) A and R both are false.
This is a Assertion Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i)
The statements given in the assertion and reason, both are correct and the reason given is the correct explanation for the assertion. In NH3 only one lone pair of electron is present and due to that lone pair-bond pair repulsion occurs which forms a distorted tetrahedral geometry (pyramidal) .
In H2O two lone pairs of electrons are present on the oxygen atom and due to this lone pairlone pair repulsion occurs which shifts the bonds and forms a bent geometry. The lone pair-lone pair repulsion is more than the lone pair-bond pair repulsion. Thus, bond angle in H-N-H is more than that of H-O-H.
Commonly asked questions
Assertion (A): Among the two O–H bonds in H2O molecule, the energy required to break the first O–H bond and the other O–H bond is the same.
Reason (R) : This is because the electronic environment around oxygen is the same even after breakage of one O–H bond.
(i) A and R both are correct, and R is correct explanation of A.
(ii) A and R both are correct, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(iii) A is true but R is false.
(iv) A and R both are false.
This is a Assertion Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iv)
Both the statements given in the assertion and reason are false.
The energy required to break the first O-H bond is not same than that of the second O-H bond in water molecule, that means the bond enthalpies of the two O-Hare different. This is because the electronic environment around the oxygen atom in water molecules is not the same even after the O-H bond breaks.
Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Objective Type Questions
These mostly include multiple-choice questions. MCQs test the quick recall, concept understanding, and application of theories. They cover theories like VSEPR, Lewis theory, and MOT, bond characteristics (length, angle, energy), shape and hybridization of molecules, and fundamental definitions. Practicing the MCQs is especially beneficial for the NEET and JEE exams, where speed and accuracy matter.
Objective Type Questions
(i) [NF3 and BF3 ]
(ii) [BF4 and NH4+ ]
(iii) [BCl3 and BrCl3]
(iv) [NH3 and NO3– ]
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
In a molecular structure if a central atom has the same hybridization as the central atom of another molecular species, then the two structures are known as isostructural species.
(i) In NF3 the central nitrogen atom is sp3 hybridized and in BF3 the central boron atom is sp2 . So, these two molecules are not isostructural pairs.
(ii) In BF4 the central boron atom is sp3 hybridized and in NH4 + the central nitrogen atom is also sp3 So, these two molecules are identified as isostructural pairs.
(iii) In BCl3 the central boron atom is sp2 hybridized and in BrCl3 the central bromine atom is sp3d hybridized. So, these two molecules are not isostructural pairs.
(iv) In NH3 the central nitrogen atom is sp3 and in NO3 the central nitrogen atom is sp2 So, these two molecules are not isostructural pairs.
Polarity in a molecule and hence the dipole moment depends primarily on electronegativity of the constituent atoms and shape of a molecule. Which of the following has the highest dipole moment?
(i) CO2
(ii) HI
(iii) H2O
(iv) SO2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii)
The dipole moment of the molecule depends on the difference in the electronegativity of the atoms present in the structure. The dipole moment of CO2 is 0, HI is 0.38, H2O is 1.84 and SO2 is 1.62.
As the oxygen atom is highly electronegative and hydrogen is least electronegative, the difference in electronegativity will be the highest for water molecules. Therefore, water molecules will have the highest dipole moment.
Commonly asked questions
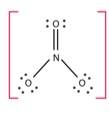
In NO3 – ion, the number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons on nitrogen atom are
(i) 2, 2
(ii) 3, 1
(iii) 1, 3
(iv) 4, 0
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iv)
The number of bond pairs on the nitrogen atom of NO3- are 4 and the structure of - NO3 does not have any lone pairs of electrons. The structure of NO3- molecule is:
Which molecule/ion out of the following does not contain unpaired electrons?
(i) N2+
(ii) O2
(iii) O22–
(iv) B2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii)
The molecular orbital diagram of O22-, π∗2Px and π∗2Py molecular orbitals are completely filled, which are partially filled in O2. These are no unpaired electrons. So, O22-does not contain unpaired electrons.
If the electronic configuration of an element is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d2 4s2, the four electrons involved in chemical bond formation will be_____.
(i) 3p6
(ii) 3p6, 4s2
(iii) 3p6, 3d2
(iv) 3d2, 4s2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iv)
The electrons involved in the formation of any chemical bond are the valence shell electrons. In the given electronic configuration,1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3d2 4s2 the valence shell electrons are in d-orbital and s-orbital. So, the four electrons involved in the chemical bond formation will be 3d2 4s2.
The electronic configurations of three elements, A, B and C are given below. Answer the questions 14 to 17 on the basis of these configurations.
|
A |
1S2 2S2 2P6 |
|
B |
1S2 2S2 2P6 3S2 3P3 |
|
C |
1S2 2S2 2P6 3S2 3P5 |
table form of A may be represented by the formula :
(i) A
(ii) A2
(iii) A3
(iv) A4
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i)
The electronic configuration of A 1S2 2S2 2P6 is having no unpaired electrons in the outer most shells. So, an atom having no unpaired electron in its valence shell is said to be stable.
The molecular formula of the compound formed from B and C will be:
(i) BC
(ii) B2C
(iii) BC2
(iv) BC3
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iv)
The electronic configuration of B given as 1S2 2S2 2P6 3S2 3P3 which represents phosphorous atom. The electronic configuration of C is given as 1S2 2S2 2P6 3S2 3P5 which represents chlorine molecule.
So, the molecular formula representing B and C will be phosphorous trichloride ( PCl3 ) which corresponds to BC3 .
Which of the following order of energies of molecular orbitals of N2 is correct?
(i) (π2py ) < (σ2pz ) < (π* 2px) ≈ (π*2py)
(ii) (π2py ) > (σ2pz ) > (π* 2px ) ≈ (π*2py )
(iii) (π2py ) < (σ2pz ) > (π* 2px) ≈ (π*2py )
(iv) (π2py ) > (σ2pz ) < (π* 2px ) ≈ (π*2py )
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iv)
In the molecules of boron ( B2 ), carbon ( C2 ) and nitrogen ( N2 ) the energy of s2pz molecular orbital is greater than the energy of P2px and P2py molecular orbital.
So, the correct order of energies of molecular orbital of N2 is
(π2py ) > (σ2pz ) < (π* 2px ) ≈ (π*2py )
Which of the following options represents the correct bond order :
(i) O2– > O2 > O2+
(ii) O2 – < O2 < O2 +
(iii) O2 – > O2 < O2+
(iv) O2– < O2 > O2+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
The electronic configurations and the bond orders of the given species are given below:
Bond order of O2 - : σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 σ2p2z (π2p2x = π2p2y) (π∗2p1x= π∗2p1y)
Bond order = ( Nb- Na)
BO= (10-7)= = 1.5
Bond order of O2 + : σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 σ2p2z (π2p2x = π2p2y) (π∗2p1x= π∗2p0y)
Bond order = (10-5)= =2.5
Bond order of O2 : σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 σ2p2z (π2p2x = π2p2y) (π∗2p1x= π∗2p1y)
BO= (10-6) = =2
So, the correct order of bond order is (ii) O2 – < O2 < O2 +
Amongst the following elements whose electronic configurations are given below, the one having the highest ionisation enthalpy is
(i) [Ne]3s2 3p1
(ii) [Ne]3s2 3p3
(iii) [Ne]3s2 3p2
(iv) [Ar]3d104s24p3
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
Aluminium has [Ne]3s2 3p1 electronic configuration. Phosphorus has [Ne]3s2 3p3. The electronic configuration of silicon is [Ne]3s2 3p2 and the electronic configuration of arsenic is [Ar]3d104s24p3.
Ionisation energy increases as the atomic number in a period increases and decreases on moving down the group. It is also known that the ionisation enthalpy of group 15 elements is more than group 16 elements as group 15 has half-filled p-subshells which gives extra stability.Thus, the electronic configuration having the highest ionization enthalpy is [Ne]3s2 3p3
Which of the following statements are correct about CO32– ?
(i) The hybridisation of central atom is sp3.
(ii) Its resonance structure has one C–O single bond and two C=O double bonds.
(iii) The average formal charge on each oxygen atom is 0.67 units.
(iv) All C–O bond lengths are equal.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii) and (iv)
(i) The hybridization of the central carbon atom in CO3 2- is 2 sp as the carbon is bonded with three oxygen atoms. So, the given statement is incorrect.
(ii) The resonance structure of CO32- has one C= O double bonds and two C- O single bonds. So, the statement is incorrect.
(iii) The net charge on three oxygen atoms is -2, hence the average formal charge on each oxygen atom is 0.67 units. So, the given statement is correct.
(iv) As it can be seen from the resonating structures that the structures of the bonds are not fixed. Hence, all the C- O bond lengths are equal. So, the given statement is correct.
Which of the following statements are not correct?
(i) NaCl being an ionic compound is a good conductor of electricity in the solid state.
(ii) In canonical structures there is a difference in the arrangement of atoms.
(iii) Hybrid orbitals form stronger bonds than pure orbitals.
(iv) VSEPR Theory can explain the square planar geometry of XeF4.
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i) and option (ii)
(i) NaCl being an ionic compound is a good conductor of electricity in the molten state. It is not a bad conductor of electricity in solid state. So, the statement mentioned in the question is not correct. Hence, this is the correct answer.
(ii) There is no difference in the arrangement of atoms in the canonical structures. The difference is in the arrangement of electron pairs in the canonical structures. So, the statement mentioned in the question is not correct. Hence, this is the correct answer.
(iii) The hybrid orbitals have the same energy and shape and hence they are more effective in the formation of stable bonds than the pure atomic orbitals. So, the statement given is correct. Hence, this is not the correct answer.
(iv) XeF4 acquires a square planar geometry, this can very well be explained by the VSEPR theory. The hybridisation of the central xenon atom will be sp3d2 due to the presence of two lone pairs of electrons on the central xenon atom. So, the statement given is correct. Hence, this is not the correct answer.
The types of hybrid orbitals of nitrogen in NO2 + , NO3 – and NH4 + respectively are expected to be
(i) sp, sp3 and sp2
(ii) sp, sp2 and sp3
(iii) sp2, sp and sp3
(iv) sp2, sp3 and sp
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
The hybrid orbitals of nitrogen in the given species will be confirmed by knowing the hybridization. In NO2+ the central nitrogen atom is sp hybridized as it has a linear shape. The molecule NO3- is sp2 due to the presence of one lone pair of electrons on a nitrogen atom and hence having a bent geometry. The molecule NH4+ is sp3 hybridized having a tetrahedral geometry.
Hydrogen bonds are formed in many compounds e.g., H2O, HF, NH3 . The boiling point of such compounds depends to a large extent on the strength of hydrogen bond and the number of hydrogen bonds. The correct decreasing order of the boiling points of above compounds is :
(i) HF > H2O > NH3
(ii) H2O > HF > NH3
(iii) NH3 > HF > H2O
(iv) NH3 > H2O > HF
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
The size and the electronegativity are the main factors on which the strength of a compound depends on. As the size of the atom decreases, the electronegativity increases and thus the hydrogen-bonding becomes stronger. Thus, the strength of hydrogen-bonding in the given compounds is: H2O > HF > NH3
In PO43– ion the formal charge on the oxygen atom of P–O bond is
(i) + 1
(ii) – 1
(iii) – 0.75
(iv) + 0.75
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
In a polyatomic molecule or an ion, the formal charge of an atom is defined as the difference between the valence electrons present in that atom and the number of electrons assigned to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Formal charge = No. of valence electrons - (No. of lone pair
Formal Charge = 6 -
Formal Charge = -1
Which of the following species has tetrahedral geometry?
(i) BH4 –
(ii) NH2–
(iii) CO32–
(iv) H3O+
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i)
(i) The molecule of BH4 - has four bond pairs and zero lone pair of electrons, so it will be a tetrahedral molecule.
(ii) NH2 - has two bond pairs and two lone pairs of electrons on the nitrogen atom. So, it will have a bent geometry.
(iii) CO3 2- has three bond pairs and no lone pairs of electrons on carbon atoms. So, it will have a trigonal planar geometry.
(iv) H3O+ has three bond pairs and one lone pair of electrons on oxygen atoms. So, it has a pyramidal geometry.
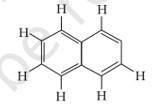
Number of π bonds and σ bonds in the following structure is–
(i) 6, 19
(ii) 4, 20
(iii) 5, 19
(iv) 5, 20
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii)
A double bond has one s bond and one π bond. In the above given structure 5π bonds are present. The s bonds are the additions of all the single bonds in the structure. There are 19s bonds in the above given structure.
In which of the following molecule/ion all the bonds are not equal?
(i) XeF4
(ii) BF4–
(iii) C2H4
(iv) SiF4
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii)
(i) The molecule XeF4 has a square planar geometry and the bond lengths of all the fluoride atoms attached to xenon atoms are equal.
(ii) The molecule BF4 - has a tetrahedral geometry and the bond lengths of all the fluoride bonds attached to boron are equal.
(iii) In the molecule C2H4 all the bonds are not equal. The bond length of the double bond between the carbon atoms is 134 pm and the bond length of CH- is 110 pm.
(iv) The molecule SiF4 has a tetrahedral geometry and the bond lengths of all the fluoride atoms attached to silicon atoms are equal.
In which of the following substances will hydrogen bond be strongest?
(i) HCl
(ii) H2O
(iii) HI
(iv) H2S
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
Hydrogen bond is the strongest in that molecules have a higher difference in electronegativity. Due to the small size of the oxygen atom, it has the highest electronegative character. So, H2O molecules will have the strongest hydrogen bonding
HCl, HI and H2Sdo not have hydrogen bonding between their atoms. So, H2O will have the strongest hydrogen bonding.
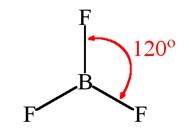
Which of the following angle corresponds to sp2 hybridisation?
(i) 90°
(ii) 120°
(iii) 180°
(iv) 109°
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
For a molecule having a hybridization of sp2, its geometry in plane is trigonal planar. For a molecule having a trigonal planar geometry, its bond angle will be 120°
Stable form of C may be represented by the formula :
(i) C
(ii) C2
(iii) C3
(iv) C4
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
The electronic configuration of C is given 1S2 2S2 2P6 3S2 3P5 which the electronic configuration of chlorine atom ( Cl ). It is unstable due to one unpaired electron in the p-subshell. Hence, the C2 will be the stable form of C as it will form a dichloride molecule ( Cl2 ).
The bond between B and C will be
(i) Ionic
(ii) Covalent
(iii) Hydrogen
(iv) Coordinate
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (ii)
The element B represents the electronic configuration of phosphorus atom and element C represents the electronic configuration of chlorine atom. Both phosphorus and chlorine are non-metals hence the bonding forming between them will be a covalent bond.
Which of the following statement is not correct from the view point of molecular orbital theory?
(i) Be2 is not a stable molecule.
(ii) He2 is not stable but He2 + is expected to exist.
(iii) Bond strength of N2 is maximum amongst the homonuclear diatomic molecules belonging to the second period.
(iv) The order of energies of molecular orbitals in N2 molecule is
σ2s < σ* 2s < σ2pz < (π2px = π2py ) < (π*2px = π* 2py) < σ* 2pz
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iv)
(a) A molecule which has a zero bond order never exists and a molecule having a non-zero bond order either exists or is expected to exist.
(b) If the value of bond order is high then the bond strength will also be higher. Electrons present in the bonding molecular orbital are known as the bonding molecular orbital ( Nb ) and the electrons present in the anti-bonding molecular orbital are known as anti-bonding electrons ( Na ). The half of the difference of bonding and anti-bonding electrons is known as the bond order.
The bond order of Be2 : Be2=s 1s2, s *1s2, s 2s2, s*2s2
The bonding and anti-bonding electrons are both 4 . Then the bond order (BO) will be:
BO= (4-4)
BO= 0
Bond order of Be2 is zero. So, it does not exist.
The electronic configuration of the outer most shell of the most electronegative element is
(i) 2s22p5
(ii) 3s23p5
(iii) 4s24p5
(iv) 5s25p5
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i)
The most electronegative element in the periodic table is fluorine having an atomic number 9 . The electronic configuration of fluorine is 1s2 2s2 2p5. Hence, the electronic configuration of the outermost shell of fluorine is 2s2 2p5 .
In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
Which of the following have identical bond order?
(i) CN–
(ii) NO+
(iii) O2–
(iv) O22–
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i) and option (ii)
Bond order depends on the electronic configuration of the molecular species, and the electronic configuration depends on the number of electrons a particular atom is contributing in its molecular structure.
The CN- species has a total of 14 electrons; 6 electrons from carbon atom, 7 electrons from nitrogen atom and 1 electron for the negative charge.
The NO+ species has a total of 14 electrons; 8 from oxygen atoms, 7 from nitrogen atom and 1 electron will be subtracted due to the positive charge on the species.
The O2 - species has a total of 17 electrons; 8 from each oxygen atom and 1 for the negative charge on the species.
The O22- species has a total of 18 electrons; 8 from each oxygen atom and 2 for the negative charge on the species. Hence, the molecular species / ion having the same bond order will be CN- and NO+ .
Which of the following attain the linear structure:
(i) BeCl2
(ii) NCO+
(iii) NO2
(iv) CS2
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i) and (iv)
The structures of NO2 and NCO+ has a lone pair of electron on nitrogen atom thus it will form a bent shape rather than a linear shape.
CO is isoelectronic with
(i) NO+
(ii) N2
(iii) SnCl2
(iv) NO2-
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i) and (ii)
The species having the same number of electrons are known as isoelectronic species.
The number of electrons in CO species is 14; 8 electrons from oxygen atom and 6 electrons from carbon atom.
The number of electrons in NO+ is 14; 8 electrons from oxygen atom, 7 electrons from nitrogen atom and 1 electron will be subtracted due to the positive charge on the species.
The number of electrons in N2 is 14 ; 7 from each nitrogen atom.
The number of electrons in SnCl2 is 84 ;50 from the tin atom and 17 from each chlorine atom.
The number of electrons in NO2 - is 24 ; 7 from nitrogen atom, 8 from each oxygen atom and 1 from the negative charge on the species.
Hence, NO+ and N2 are the isoelectronic species of CO.
Which of the following species have the same shape?
(i) CO2
(ii) CCl4
(iii) O3
(iv) NO2-
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii) and (iv)
(i) The number of valence electrons in CO2 is 14. The oxygen atom attached to the carbon atom forms a double bond. Therefore, the hybridization of the structure is sp2. Thus, carbon dioxide is linear in shape.
(ii) The number of valence electrons in CCl4 is 32. The structure of CCl4 is arranged in a tetrahedral manner. The chlorine atoms are arranged such that the hybridization is sp3.
(iii) The number of valence electrons in O3 is 24. The hybridization of the molecule is sp2 and due to the presence of lone pair of electrons on the central oxygen atom and due to the effect of resonance, ozone molecule has a bent shape.
(iv) The number of valence electrons in NO2- is 24. The hybridization of the molecule is sp2 and due to the presence of lone pair on the nitrogen atom it attains a bent shape.
Dimagnetic species are those which contain no unpaired electrons. Which among the following are dimagnetic?
(i) N2
(ii) N22–
(iii) O2
(iv) O22-
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (i) and (iv)
(i) N2 will have 14 electrons in its structure. So, its electronic configuration will be:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2
According to the molecular electronic configuration of N2 it does not contain any unpaired electrons, it will be diamagnetic in nature.
(ii) N22– will have 16 electrons in its structure. So, its molecular electronic configuration will be:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2, , π*2p1y
According to the molecular electronic configuration of 2 N2 -, it has two unpaired electrons in π*2p1x , π*2p1y sub- shell. Hence, it will be paramagnetic in nature.
(iii) O2 will have 16 electrons in its structure. So, its molecular electronic configuration will be:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2 π2p2y π2p2x π*2p1y π*2p1x
According to the molecular electronic configuration of O2, it has two unpaired electrons in π2p1y π*2p1x sub-shell. Hence, it will be paramagnetic in nature.
(iv) O22- will have 18 electrons in its structure. So, its molecular electronic configuration will be:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2 π2p2y π2p2x π*2p2y π*2p2x
According to the molecular electronic configuration of O22- it does not contain any unpaired electrons, it will be diamagnetic in nature.
Species having same bond order are :
(i) N2
(ii) N2–
(iii) F2+
(iv) O2–
This is a Multiple Choice Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Option (iii) and (iv)
The formula of bond order is:
Bond order = ( Nb- Na)
Number of bonding and antibonding electrons can be found from the molecular electronic configuration of the species.
(i) Total number of electrons in N2 is 14. So, its molecular electronic configuration will be
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2
The bond order will be:
( 10-4)= 3
(ii) The total number of electrons in N2 - is 15. So, its molecular electronic configuration will be:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2, π2p2x , π2p2y, s2pz2 π*2p1x
The bond order will be:
( 10-5)= 2.5
(iii) The total electrons in F2+ is 17. So, its electronic configuration will be:
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2, π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p2y π*2p1x
The bond order will be:
( 10-7)= 1.5
(iv) The total electrons in O2- is 17 So, its electronic configuration will be
σ1s2 σ∗1s2 σ2s2 σ∗2s2 s2pz2, π2p2y , π2p2x, π*2p2y π*2p1x
( 10-7)= 1.5
Common Mistakes and Tips for NCERT Chemistry Exemplar Chapter Four
These are the common mistakes that students make in Chapter Four Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure:
- Students make mistakes in the Octet rule by assuming that all atoms must strictly follow the octet rule. They overlook the exceptions like molecules with incomplete octets (e.g., BF₃) or expanded octets (e.g., SF₆, PCl₅).
- Many students mix up the molecular shapes (like tetrahedral, and trigonal planar) with hybridization types (like sp³, sp²) leading to incorrect predictions of geometry.
- They make errors in the Lewis Dot Structures such as misplaced lone pairs, incorrect counting of valence electrons, or forming invalid bonds—especially for resonance structures or polyatomic ions.
- In VSEPR Theory, they may fail to correctly count bonding and lone pairs or may also ignore lone pair repulsion effects.
- They get confused between the bond length and bond order by incorrectly assuming that the bond order increases bond length. The fact is higher bond order = shorter and stronger bonds.
- They make mistakes in the Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) by misplacing the electrons in the MO diagrams.
The following are the tips to avoid common mistakes:
- Read and understand the Lewis structures, valence electrons, bonding theories, and hybridization.
- Use tables and flowcharts to apply concepts correctly as they make the concepts easier to remember. The students should create a quick reference table for bond angles, hybridizations, shapes, and examples.
- Visual practice is important for improving spatial understanding and reducing errors. Hence, students should draw the Lewis structures, MO diagrams, and VSEPR models.
- Before memorizing the concepts, try to understand them first.
- Practice the NCERT exemplar to gain more accuracy and confidence for the exam.
Related Links
| NCERT Solutions | NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry | NCERT Notes |
JEE Mains 2020
Commonly asked questions
The number of chiral carbons present in sucrose is
9.00
α - D - Glucose sucrose β – D - Fructose
Considering that ∆₀ > P, the magnetic moment (in BM) of [Ru(H₂O)₆]²⁺ would be
Δ? > P
Pairing of electron will take place
Number of unpaired electron = 0
µ = 0.00
For a dimerization reaction, 2A(g) → A₂(g), at 298 K, ∆Uᶱ = -20 kJmol⁻¹, ∆Sᶱ = -30 JK⁻¹mol⁻¹, then the ∆Gᶱ will be J.
13.49
2 A (g) → A? (g)
Δn_g = 1 - 2
Δn_g = 1
ΔH = ΔU + Δn_gRT
ΔH = -20 × 10³ + (-1)8.31 × 298
ΔH = -22477.572 J mol? ¹
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
ΔG = -22477.572 - (-30)298 = -22477.572 + 8940
ΔG = -13537.57 J mol? ¹
The volume, in mL, of 0.02M K₂Cr₂O₇ solution required to react with 0.288 g of ferrous oxalate in acidic medium is (Molar mass of Fe = 56 mol⁻¹)
50.00
K? Cr? O? + FeC? O? → Fe³? + CO? + Cr³? + K? + H? O
n_f=6 n_f=3
Now apply equivalent concept
0.02 × 6 × V = (0.288 / (144/3) × 10³
Normality
V = (0.288 × 10³)/ (48 × 6 × 0.02) = 50.00 mL
For a reaction X + Y = 2Z, 1.0 mol of X, 1.5 mol of Y and 0.5 mol of Z were taken in a 1 L vessel and allowed to react. At equilibrium, the concentration of Z was 1.0 mol L⁻¹. The equilibrium constant of the reaction is x/15. The value of x is
16.00
X + Y? 2Z
Initial 1.0 1.5 0.5
At equ m 1-x 1.5-x 0.5+2x
equ m conc 0.75 1.25 1.0
0.5 + 2x = 1
x = 0.25
K = 1 / (0.75 × 1.25)
K = 16/15
x = 16.00
The number of N atoms in 681 g of C7H5N3O6 is x × 1021. The value of x is___________.
(NA = 6.02 × 1023 mol1) (Nearest Integer)
Molar mass of C7H5N3O6 = 12 × 7 + 1 × 5 + 14 × 3 + 16 × 6 = 84 + 42 + 96 = 227 g/mol
Number of moles = = 3 mol
The distance between Na+ and Cl ions in solid NaCl of density 43.1g cm3 is ________×1010m. (Nearest Integer)
m
The longest wavelength of light that can be used for the ionization of lithium atom (Li) in its ground state is x × 108m. The value of x is_________. (Nearest Integer)
m
The standard entropy change for the reaction
[Given: The standard enthalpy change for the reaction is -165 kJ mol1]. The temperature in K at which the reaction attains equilibrium is__________.
[Nearest Integer)
T =?
At equilibrium
1L aqueous solution of H2SO4 contains 0.02m mol H2SO4. 50% of this solution is dilutd with deionized water to give 1L solution (A). In solution (A), 0.01m mol of H2SO4 are added. Total m mols of H2SO4 in the final solution is ________× 103 m mols
1000 ml solution contains 0.02 milli mole (mm)
500 ml solution contains 0.02 m.m
Solution made 1000 ml with H2O
m.m in final solution = 0.01 mm
Solution (A) + 0.01 m. m H2SO4
= 0.01 + 0.01
= 0.02 m.m
= 0.00002 × 103 mm
The standard free energy change for 50% dissociation of N2O4 into NO2 at and 1 atm pressure is -xJ mol-1. The value of x is_________. (Nearest Integer)
[Given: R= 8.31 J k-1 mol-1, log 1.33 = 0.1239, In 10 = 2.3]
In a cell, the following reactions take place
Fe2+ ® Fe3+
2I- ® I2 + 2e-
The standard electrode potential for the spontaneous reaction in the cell is x × 10-2 V 298 K. The value of x is________(Nearest Integer)
Fe+2 undergoes reduction & I2 undergoes oxidation.
= (0.77 – 0.54) V = 0.23 V
= 23 × 10-2 V
x = 23
![]()
For a given chemical reaction Concentration of C charges form 10 mmol dm-3 to 20 mmol dm-3 in 10 second. Rate of appearance of D is 1.5 times the rate of disappearance of B which is twice the rate of disappearance A. The rate of appearance of D has been experimentally determined to be 9 mmol dm-3 s-1. Therefore the rate of reaction is_____________mmol dm-3 s-1 (Nearest Integer)
rate of reaction = = 1m.m dm-3 S-1
If absorbs a light of wavelength 600nm d-d transition, then the value of octahedral crystal field splitting energy for will be_________× 10-21J. (Nearest Integer)
(Given: h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js and c = 3.08 × 108 ms-1)
J
J
Number of grams of bromine that will completely react with 5.0g of pent-1-ene is_____________×10-2g. (Atomic mass of Br = 80 g/mol) (Nearest Integer)
01 Oct 2025
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Four Exam