Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Six
Get insights from 63 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Six, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Six
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
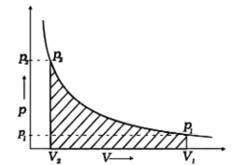
When a process can be reversed by bringing an extremely small change in it, we call it a reversible process. The pressure-volume graph can be used to calculate the work done. The pressure is not constant, and changes in infinitesimal amounts as compression happens from initial volume Vi to the final volume Vf. The below graph depicts the work done with the shaded area.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
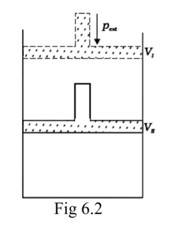
Assumption: Cylinder is filled with one mole gas, and the piston is frictionless. Let the pressure of gas inside be p and the volume of gas be V_ {I}.
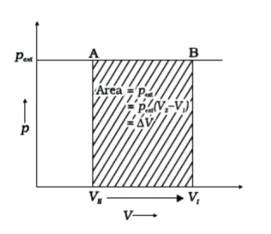
Piston is moved towards the inside to make the external pressure (P_ {ext}) equal to p. Now, let us assume that this change takes place in a single step, hence, V is the final volume. The work done by the piston is depicted in the graph shown below by shading the area.
PextΔV= AV1 (V1-V2)
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter six
Standard molar enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of a compound from its most stable states or reference states. As per the given information in the question, the standard enthalpy for the given equation is – 572 kJ mol–1
Now the enthalpy of formation for H2O will be half the enthalpy of the value in the given equation. So now we can calculate that
? fH? = = -286KJ/mol
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
As per the information provided in the question, for one mole of CCl4 (154 g), the heat of vaporisation required is 30.5 kJ/mol .
Hence for the vaporisation of 284 g of CCl4, we require:
= 56.2 kJ
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
ΔrH? =ΣB.E (reactant)-ΣB.E (product)
=B.E.H2 + BEBR2 -2 *B.E>HBr
= 435+192-2 (*368)
= 109KJmol-1
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Molar enthalpy change for graphite (ΔH)
= enthalpy change for 1 g x molar mass of C = -20.7*12 = -2.48 x 102 kJ mol-1
Since the sign of ΔH = -ve, it is an exothermic reaction.
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Given that, Cv = heat capacity at constant volume,
Cp = heat capacity at constant pressure
Difference between Cp and Cv is equal to gas constant (R).
.'. Cp – Cv = nR (where, n = no. of moles)
= 10 x 8.314 = 83.14J
New answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
For water, molar heat capacity = 18 x Specific heat or Cp = 18 x c
But, specific heat,
C = 4.18 J g-1 K-1 Heat capacity,
Cp = 18 x 4.18 JK-1 = 75.24 JK-1
New question posted
7 months agoNew answer posted
7 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
During free expansion, external pressure is zero, so Work done, w = -pextΔV
= -0(5 – 1) = 0
Since the gas is expanding isothermally, therefore, q = 0
ΔU = q + w =0+0=0
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers