Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Eleven
Get insights from 89 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Eleven, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Eleven
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
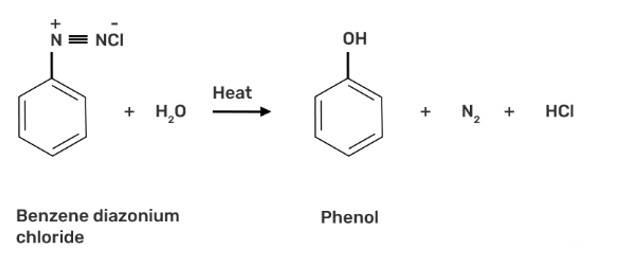
When benzene diazonium chloride is heated with water, it forms phenol along with nitrogen and hydrochloric acid as by-products as shown below:
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The decreasing order of reactivity of alcohol with sodium metal:
Tertiary Alcohols > Secondary Alcohols > Primary Alcohols
When alcohol reacts with active metals e.g. Na. K etc., the O-H bond of alcohols breaks to form the corresponding alkoxide. The alkyl group is electron donating and has +I effect due to which the O-H bond becomes strong and hence, the reactivity of alcohol decreases.
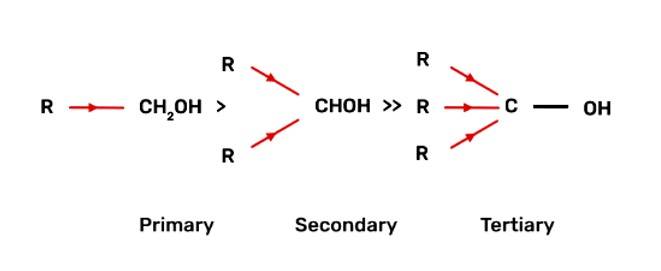
Fig: +I effect of alkyl group of alcohol
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The increasing order of acidity:
o-cresol < Phenol < o-nitrophenol
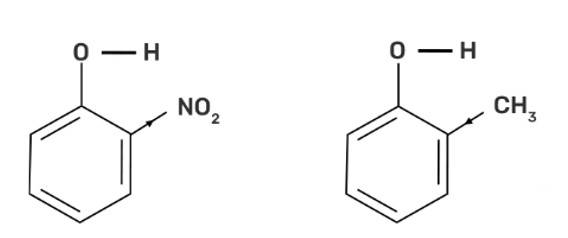
The electron-withdrawing group on the substituted phenol increases the acidity due to increasing the polarity of the O-H bond and thus, the acidity increases and vice versa. -NO2 is an electron-withdrawing group whereas the -CH3 group is an electron-donating group.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
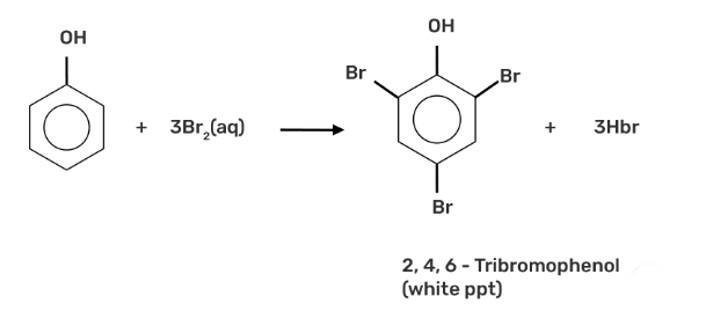
When phenol is treated with bromine water, it forms the white precipitate of 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol. In the bromination reaction of phenol, water is ionized. And also bromine gets ionized to produce bromonium ions to a larger extent. Phenol gets ionized to produce an ortho-para directing phenoxide ion. Bromine water is mostly used as a test for C=C double bond. During this reaction white precipitates form at the end and bromine water is decolourised.
Hence, the formation of bromonium ions and strong ortho-para directing species indicates that the product formation is
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Out of o-nitrophenol and o-cresol, o-nitrophenol is more acidic due to the -I effect and -R effect of -NO2 group as the -NO2 group is an electron withdrawing group whereas the -CH3 group is electron releasing group and has +I effect on the conjugate base which increases the electron density and decreases the polarity of O-H bond and hence less acidic.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
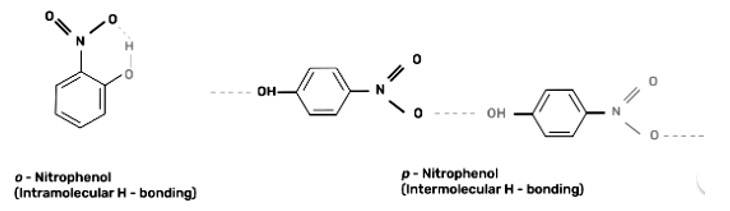
Out of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol, o-nitrophenol is more volatile due to presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding in o-nitrophenol whereas p-nitrophenol has intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The strong oxidising agents such as acidified KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7 reagents are used for the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid. These reagents are so strong that they convert the alcohols to carboxylic acids.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reagent used for the conversion of ethanol to ethanal is pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) which is a complex formed by CrO3, pyridine and HCl which converts the primary alcohols to aldehydes.
CH3—CH2—OH ![]() CH3—CHO
CH3—CHO
Ethanol Ethanal
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
2-chloroethanol is more acidic than ethanol because the conjugate base of 2-chloroethanol is more stable than that of ethanol due to the -I effect of chlorine atom.
Stability: Cl—CH2—CH2—OΘ > CH3—CH2—OΘ
Acidity: Cl—CH2—CH2—OH > CH3—CH2—OH
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
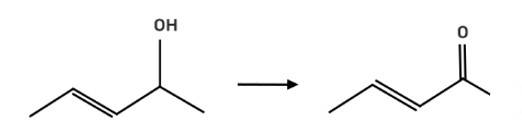
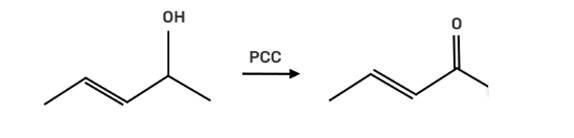
The reagent pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a complex formed by CrO3, pyridine and HCl converts the secondary alcohol to ketone without oxidising the double bond.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers