- Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Multiple Choice Questions
- Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Question and Aanswers
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Multiple Choice Questions
| 1. Monochlorination of toluene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis with aq. NaOH yields. I. o-Cresol II. m-Cresol III. 2, 4-Dihydroxytoluene IV. Benzyl alcohol |
| Ans: IV Benzyl alcohol The chlorine atom is substituted by the hydrogen atom of methyl hydrocarbon present in toluene to form benzyl chloride on monochlorination of toluene in presence of sunlight by free radical pathway C6H5CH3 + Cl2 Toluene Benzyl Chloride
Benzyl chloride (monochlorinated toluene product) on hydrolysis with aq. NaOH yields benzyl alcohol by substituting the chloride ion by OH- ion by nucleophilic substitution reaction. C6H5CH2Cl Benzyl Benzyl Chloride Alcohol |
| 2. How many alcohols with molecular formula C4H10O are chiral in nature? I. 1 II. 2 III. 3 IV. 4 |
| Ans: 1 The alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O is butanol has 4 isomers, these are:
| OH
| CH3 CH3 |
| OH
Butane-2-ol has chiral carbon which has all different substituted groups attached, so butane-2-ol alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O is chiral in nature. |
| 3. What is the correct order of reactivity of alcohols in the following reaction? R - OH + HCl I. 1° > 2° > 3° II. 1° < 2° > 3° III. 3° > 2° > 1° IV. 3° > 1° > 2° |
| Ans: III 3° > 2° > 1° Alcohols are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary by lucas reagent which is a mixture of concentrated HCl and dry anhydrous ZnCl2. The carbocation is formed as the intermediate during the lucas test of alcohol.More the stability of intermediate carbocation, more will be the reactivity of alcohol.
Tertiary carbocation is most stable then the secondary alcohol is stable due to hyperconjugation and the primary alcohol is the least stable.
Stability of intermediate carbocation: 3° > 2° > 1°
Reactivity of alcohol: 3° > 2° > 1° |
| 4. CH3CH2OH can be converted into CH3CHO by ________________ . I. catalytic hydrogenation II. treatment with LiA1H4 III. treatment with pyridinium chlorochromate IV. treatment with KMnO4 |
| Ans: III. treatment with pyridinium chlorochromate
The pyridinium chlorochromate is a complex of chromium trioxide with pyridine. This reagent is preferred for mild oxidation to form aldehydes and hence the oxidation to carboxylic acid is prevented.
Primary alcohols are oxidized to form aldehyde, whereas secondary and tertiary alcohols are oxidized to form ketones. The conversion of a hydroxyl group to aldehyde can be done by the removal of hydrogen atoms (Oxidation), looking at the following options; pyridinium chlorochromate and potassium dichromate are both oxidizing agents. However, when pyridinium chlorochromate is used, it is a weaker oxidizing agent compared to potassium permanganate; hence, it reduces ethanol to acetaldehyde (ethanal). CH3CH2OH |
| 5. The process of converting alkyl halides into alcohols I. addition reaction II. substitution reaction III. dehydrohalogenation reaction IV. rearrangement reaction |
| Ans: II. substitution reaction
Alkyl halides undergo substitution reactions to form corresponding alcohol.The halide ion, X- is substituted by OH- ion to form alcohol by nucleophilic substitution reaction.
R-X → R-OH |
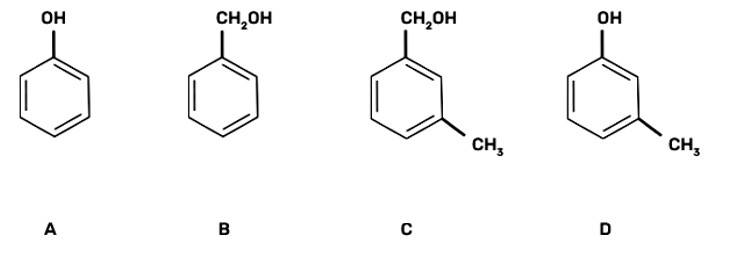
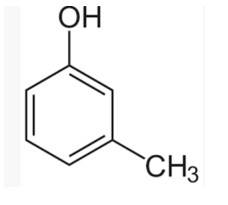
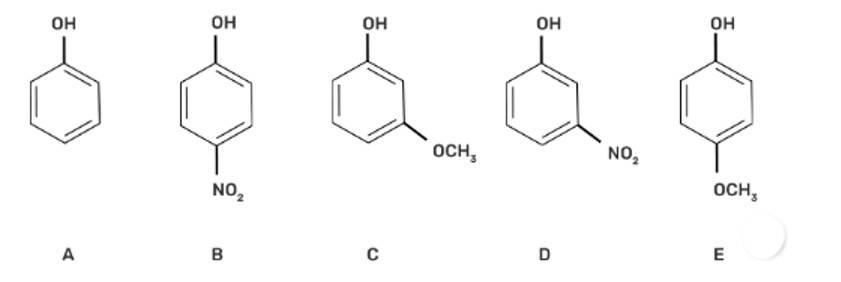
| 6. Which of the following compounds is aromatic alcohol? |
| Ans: III. B, C
The aromatic alcohols or aryl-alcohols are a class of chemical compounds containing a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group.
In the given question, the aromatic alcohols are those compounds in which the hydroxyl group is not directly attached to the benzene ring but is linked to a carbon atom situated in a side-chain. In short, we will search for that figure in which the hydroxyl group is linked to sp3 hybridised carbon. So, compound B and C have -OH groups attached to sp3 hybridized -CH3 groups and hence are aromatic alcohols and compounds A and D have -OH groups attached to sp2 benzene rings, hence are non-aromatic compounds |
| 7. Give IUPAC name of the compound given below. CH3—CH—CH2--CH2--CH—CH3 | | Cl OH I. 2-Chloro-5-hydroxyhexane II. 2-Hydroxy-5-chlorohexane III. 5-Chlorohexan-2-ol IV. 2-Chlorohexan-5-ol |
| Ans: III. 5-Chlorohexan-2-ol The IUPAC naming of the given compound are as follows: Word root: It depends upon the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain selected, called the parent chain. Depending upon the number of carbons in the chain the compound is assigned a word. The given compound contain 6 carbon attached in the continuous longest chain and word root for 6 carbon atoms is ‘hex’.
The suffix- A suffix is added after the word root to indicate the nature of the carbon-carbon bond. The given carbon chain contains a single bond then a suffix will be added as “ane”.
Prefix- The groups which are not regarded as functional but present in the carbon chain as substituents are written before the word root as a prefix. Such groups are fluorine, chlorine, nitro, etc.
According to the IUPAC rule, the prefix (Chlorine) will be written first followed by the word root and primary suffix and secondary suffix. As the compound contains chlorine which will be regarded as substituents and will be written as a prefix. The compound contains six carbon atoms due to which it will be considered as hexane and the word root will be “hex”. Since it is an alkane compound, the primary suffix will be “ane” and the secondary suffix will be “ol”. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is 5-Chlorohexan-2-ol. |
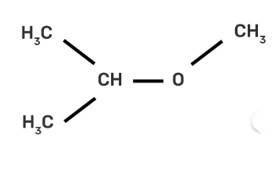
| 8. IUPAC name of m-cresol is I. 3-methylphenol II. 3-chlorophenol III. 3-methoxyphenol IV. benzene- 1.3-diol |
| Ans: I. 3-methylphenol
The m-cresol is an organic compound which contains a benzene ring, a -OH group and a methyl group. It has a methyl group substituted to meta position in the phenol ring. According to the IUPAC system, the -OH group is given more priority than the methyl group.
The cresols are also called hydroxytoluene or the methylphenols. These contain a benzene ring with one methyl and one phenol group substituted. There are three forms of cresols which are o-cresol, m-cresol and p-cresol. m- cresol is a colourless liquid and is viscous in nature. In case of m-cresol, the methyl group and the hydroxyl group at 1st and 3rd position. The structure of m-cresol can be written as-
|
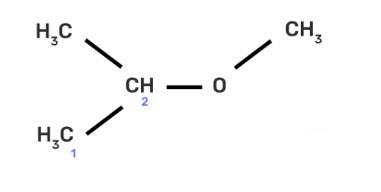
| 9. IUPAC name of the compound CH3—CH—OCH3 is _______________ . | CH3 I. 1-methoxy-1-methylethane II. 2-methoxy-2-methylethane III. 2-methoxypropane IV. isopropylmethyl ether |
| Ans: II. 2-methoxy-2-methylethane
IUPAC provides consistency to the names of organic compounds. It enables every compound to possess a unique name, which otherwise is not plausible with the common names. The chemical structure of the given compound is shown below: |
| 10. Which of the following species can act as the strongest base? I. ΘOH II. ΘOR III. ΘOC6H5 IV.
|
| Ans: II. ΘOR
The species which is the weakest acid has the strongest conjugate base. The ROH is the weakest acid among the given compounds due to the inductive effect of the alkyl group. Therefore, the strongest conjugate base is ΘOR. |
| 11. Which of the following compounds will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water? I. C6H5OH II. C6H5CH2OH III. (CH3)3COH IV. C2H5OH |
| Ans: I. C6H5OH
C6H5OH, phenol is a strong acid (due to resonance) which will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water to form sodium phenoxide and water. Phenol is more acidic than sp3 hybridized attached alcohols. |
| 12. Phenol is less acidic than I. ethanol II. o-nitrophenol III. o- IV. o-methoxyphenol |
| Ans: IV. o-methoxy phenol
The stability of the conjugate base determines the acidic character of the compound. Higher the stability of the conjugate base, the higher is the acidic character.
Phenol, O-nitrophenol, O-methyl phenol, and O-methoxy phenol all are aromatic compounds. In aromatic compounds, the negative charge of the conjugate base charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge gives additional stability to the compound.
Ethanol is not aromatic and it cannot delocalise the negative charge formed after the H+ ion leaves the c. So, it is the least acidic among the given options. Thus, we can eliminate it. There are two types of groups, the electron-withdrawing, and the electron releasing group. The methyl group and the methoxy group are electron releasing groups. They release the electrons and hence decreases the stability of the negatively charged conjugate base..
On the other hand, a nitro group is an electron-withdrawing group. They withdraw the electrons from the aromatic ring. Withdrawing the negative charge from the ring will increase the stability of the compound in this case.
Phenoxide is stabilised by resonance effect only and it does not have any electron releasing group. So, it is more acidic than o-methyl phenol and o-methoxy phenol. But the absence of an electron-withdrawing group makes it less acidic than o-nitrophenol. |
| 13. Which of the following is most acidic? I. Benzyl alcohol II. Cyclohexanol III. Phenol IV. m-Chlorophenol |
| Ans: IV. m-Chlorophenol
Phenols are more acidic than sp3 and sp2 hybridized alcohol. The m-Chlorophenol is more acidic than phenol due to the -I effect (dominated by the + R effect) of chlorine atom increasing the acidity of phenol. |
| 14. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds. III. d > e > c > b > a IV. e > d > c > b > a |
| Ans: II. b > d > a > c > e
The acidic strength decreases with increasing stability of the conjugate base of the given alcohol. -NO2 group at the para position in compound (b) is the most acidic due to the -M effect of the -NO2 group.
Compound (d) has -I effect on the conjugate base, whereas the -OCH3 group has + M effect on the conjugate base and hence decreases the acidity of compounds (c) and (e). |
| 15. Mark the correct increasing order of reactivity of the following compounds with HBr/HC1.
|
| Ans: III. b < c < a
The reaction will proceed by SN1 mechanism to form the carbocation intermediate, more the stability of carbocation more will be the reactivity of the given compound with HBr/HC1.
-NO2 group is an electron withdrawing group and due to the -M effect, increases the stability of carbocation. Cl group at para position shows + M effect due to it, carbocation is least stable and hence, the compound (c) is the least reactive. |
| 16. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of boiling point. Propan- 1-ol. butan-l-ol. butan-2-ol. pentan- 1-ol I. Propan- 1-ol. butan-2-ol. butan- 1-ol. pentan- 1-ol II. Propan- 1 -ol. butan- 1 -ol. butan-2-ol. pentan- 1 -ol III. Pentan-l-ol. butan-2-ol. butan- 1 -ol. propan- 1-ol IV. Pentan-l-ol. butan- 1-ol. butan-2-ol. propan- 1-ol |
| Ans: I. Propan- 1-ol. butan-2-ol. butan- 1-ol. pentan- 1-ol
The compounds Propan-l-ol, butan-2-ol, butan-1-ol ,pentan-1-ol belong to the alcohol family. The structure of the given alcohols are as shown below:
|
| 17. Which of the following are used to convert RCHO into RCH2OH? I. H2/Pd II. LiA1H4 III. NaBH4 IV. Reaction with RMgX followed by hydrolysis |
| Ans: I. H2/Pd II. LiA1H4 III. NaBH4
Aldehydes and ketones are converted to alcohols by catalytic hydrogenation.The reagents used to convert the aldehydes to alcohol are by H2/Pd , lithium aluminium hydride (LiA1H4), and sodium borohydride (NaBH4). |
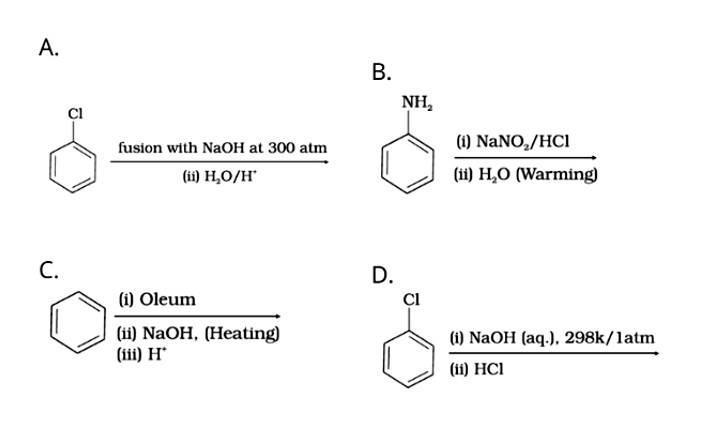
| 18. Which of the following reactions will yield phenol?
|
| Phenol is prepared by:
|
| 19. Which of the following reagents can be used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes? I. CrO3 in anhydrous medium. II. KMnO4 in an acidic medium. III. Pyridinium chlorochromate. IV. Heat in the presence of Cu at 573K. |
| Ans: I. CrO3 in anhydrous medium. II. Pyridinium chlorochromate. III. Heat in the presence of Cu at 573K.
KMnO4 is a strong oxidising agent and oxidises the primary alcohol to ketone. Hence cannot be used as a reagent to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes. |
| 20. Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reactions with I. Br2/water II. Na III. Neutral FeCl3 IV. All the above |
| Ans: I. Br2/water III. Neutral FeCl3
Phenol does not give the bromine water (Br2/water ) test whereas ethanol gives the bromine water.
Phenol on reaction with neutral FeCl3 forms a colored complex with Fe3+ ion whereas ethanol does not form the colored complex with neutral FeCl3. |
| 21. Which of the following arc benzylic alcohols? I. C6H5—CH2—CH2—OH II. C6H5—CH2—OH III. C6H5—CH—OH | CH3 IV. C6H5—CH—CH—OH | CH3 |
|
Ans: I. C6H5—CH2—OH III. C6H5—CH—OH | CH3
Benzylic alcohol are those alcohols which have phenyl group attached to the alpha carbon of alcohol.
R—CαH2—OH : Benzylic Alcohol
The compound II and III have phenyl group attached at the Cα of the alcohol and thence they are benzylic alcohols |
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Question and Aanswers
| 1. Write the mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxybenzene. |
| Ans: In case of anisole, methylphenyl oxonium ion,
|
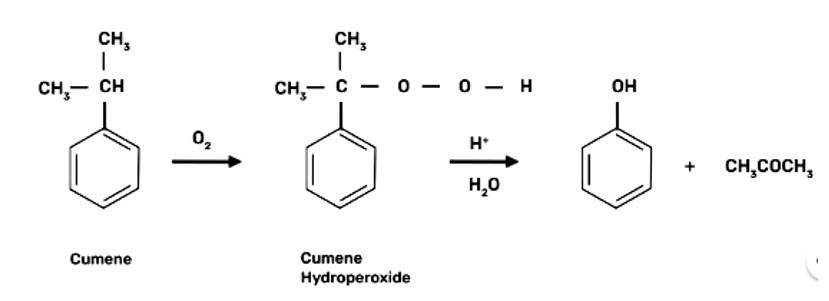
| 2. (a) Name the starting material used in the industrial preparation of phenol. |
| Ans: Cumene is the beginning element for the industrial production of phenol.
|
| (b) Write complete reaction for the bromination of phenol in aqueous and non-aqueous medium. |
| Ans:
|
| (c) Explain why Lewis acid is not required in bromination of phenol? |
| Ans: Benzene is normally halogenated in the presence of a Lewis acid, such as FeBr3, which polarises the halogen molecule. Even in the absence of Lewis acid, the polarisation of the bromine molecule occurs in the case of phenol. It's because the benzene ring's —OH group has a strong activating impact. |
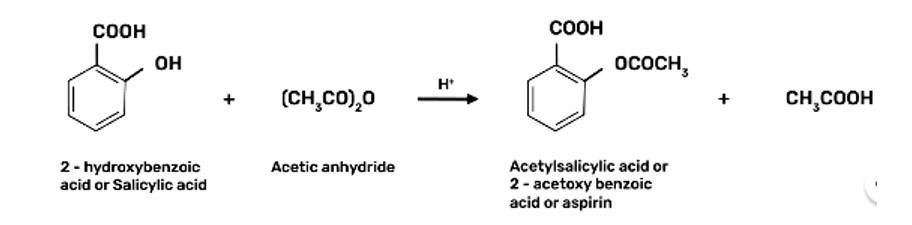
| 3. How can phenol be converted to aspirin? |
| Ans:
|
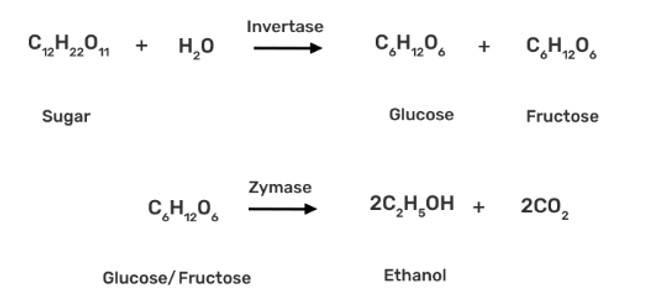
| 4. Explain a process in which a biocatalyst is used in industrial preparation of a compound known to you. |
| Ans: Commercially, ethanol (C2H5OH) is made by fermenting carbohydrates, which is the earliest process. In the presence of an enzyme called invertase, sugar in molasses, sugarcane, or fruits like grapes is transformed to glucose and fructose (both of which have the formula C6H12O6).
In the presence of another enzyme, zymase, present in yeast, glucose and fructose are fermented. |
Commonly asked questions
Write the mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxybenzene.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In case of anisole, methylphenyl oxonium ion, 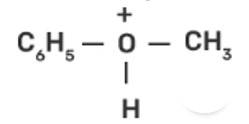
(a) Name the starting material used in the industrial preparation of phenol.
(b) Write complete reaction for the bromination of phenol in aqueous and non-aqueous medium.
(c) Explain why Lewis acid is not required in bromination of phenol?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Cumene is the beginning element for the industrial production of phenol.
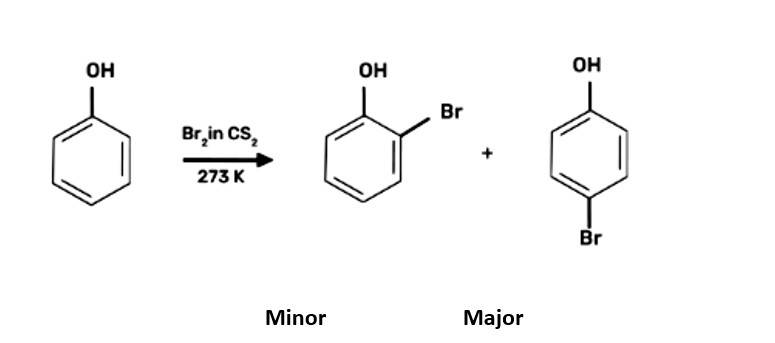
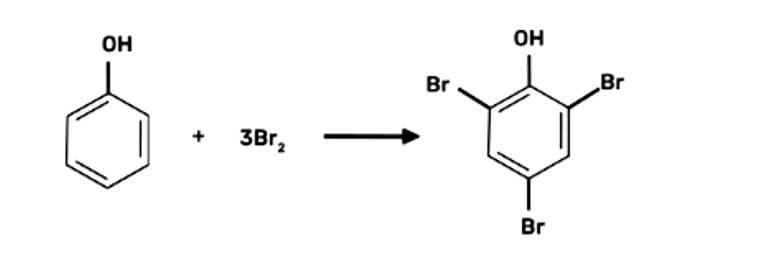
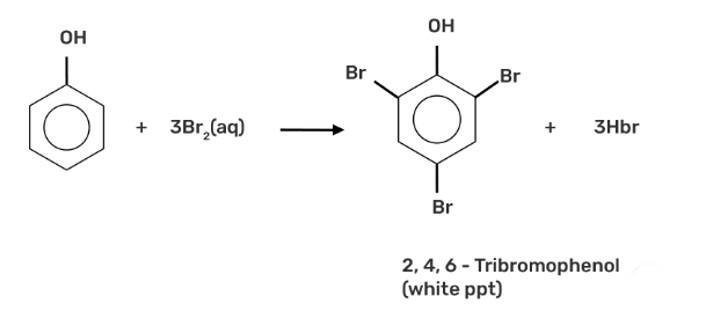
When bromine water is used to treat phenol. As a whitish precipitate, 2,4,6-tribromophenol is formed
How can phenol be converted to aspirin?
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
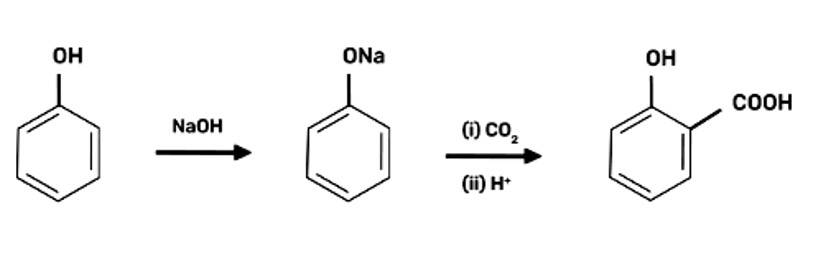

2-Hydroxybenzoic acid
(Salicylic Acid)
2-hydoxybenzoic acid on treatment with acetic anhydride will give aspirin.
Explain a process in which a biocatalyst is used in industrial preparation of a compound known to you.
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Commercially, ethanol (C2H5OH) is made by fermenting carbohydrates, which is the earliest process. In the presence of an enzyme called invertase, sugar in molasses, sugarcane, or fruits like grapes is transformed to glucose and fructose (both of which have the formula C6H12O6).
In the presence of another enzyme, zymase, present in yeast, glucose and fructose are fermented.
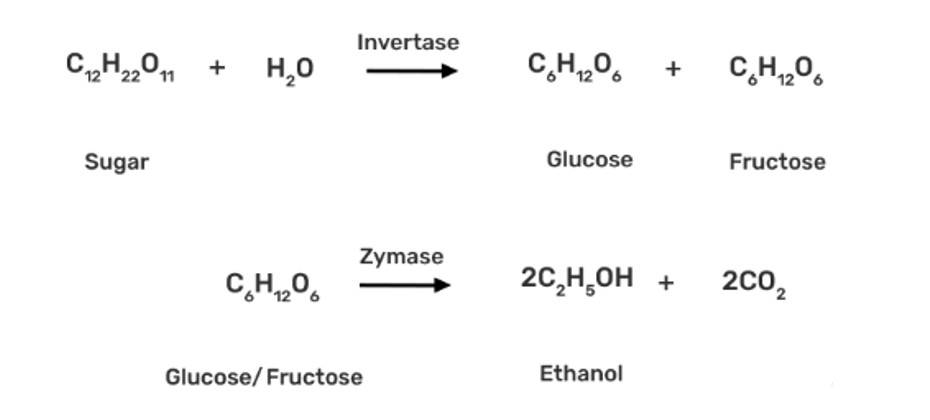
Grapes are used to make wine because they contain sugars and yeast. The amount of sugar in grapes increases as they ripen, and yeast forms on the outer peel. When grapes are crushed, sugar and enzymes collide, causing fermentation to begin. Fermentation takes place in the absence of oxygen in anaerobic circumstances. During fermentation, carbon dioxide is emitted.
What is the structure and IUPAC name of glycerol?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The structure of glycerol is:
CH2—CH—CH2
| | |
OH OH OH
The IUPAC of glycerol is Propane-1,2,3-triol.
Write the IUPAC name of the following compounds.
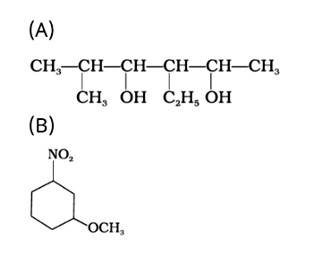
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The IUPAC name of the given compound is:
(A) 3-Ethyl-5-methylhexane-2,4-diol
(B) 1-Methoxy-3-nitrocyclohexane
Write the IUPAC name of the compound given below.
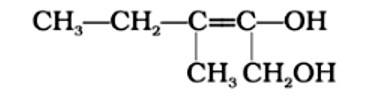
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
3-Methylpent-2-ene-1,2-diol
Name the factors responsible for the solubility of alcohols in water.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The solubility of alcohol in water depends upon the following factors:
(a) Hydrogen bonding: Alcohols form hydrogen bonding with water due to the presence of -OH group in alcohol and hence alcohols are soluble in water.
(b) Size of alkyl or aryl group: The alkyl and aryl group are hydrophobic in nature and larger the size of alkyl or aryl group of alcohol lesser will be the solubility of alcohol in water.
What is denatured alcohol?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Alcohols such as ethanol are made unfit for consumption by adding some additives like copper sulphate and pyridine which gives a foul smell, and bad taste to alcohol, it is known as denatured alcohol.
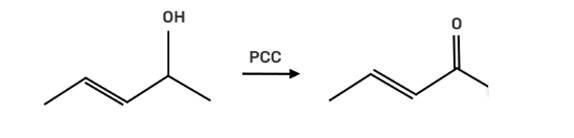
Suggest a reagent for the following conversion.
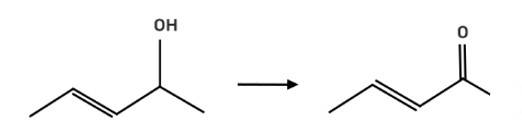
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reagent pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) is a complex formed by CrO3, pyridine and HCl converts the secondary alcohol to ketone without oxidising the double bond.
Out of 2-chloroethanol and ethanol which is more acidic and why?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
2-chloroethanol is more acidic than ethanol because the conjugate base of 2-chloroethanol is more stable than that of ethanol due to the -I effect of chlorine atom.
Stability: Cl—CH2—CH2—OΘ > CH3—CH2—OΘ
Acidity: Cl—CH2—CH2—OH > CH3—CH2—OH
Suggest a reagent for conversion of ethanol to ethanal.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reagent used for the conversion of ethanol to ethanal is pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) which is a complex formed by CrO3, pyridine and HCl which converts the primary alcohols to aldehydes.
CH3—CH2—OH ![]() CH3—CHO
CH3—CHO
Ethanol Ethanal
Suggest a reagent for conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The strong oxidising agents such as acidified KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7 reagents are used for the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid. These reagents are so strong that they convert the alcohols to carboxylic acids.
Out of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol which is more volatile? Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Out of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol, o-nitrophenol is more volatile due to presence of intramolecular hydrogen bonding in o-nitrophenol whereas p-nitrophenol has intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
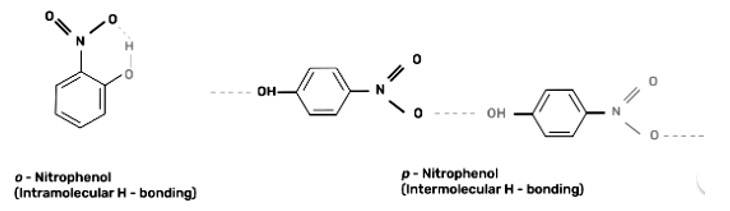
Out of o-nitrophenol and o-cresol which is more acidic?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Out of o-nitrophenol and o-cresol, o-nitrophenol is more acidic due to the -I effect and -R effect of -NO2 group as the -NO2 group is an electron withdrawing group whereas the -CH3 group is electron releasing group and has +I effect on the conjugate base which increases the electron density and decreases the polarity of O-H bond and hence less acidic.
When phenol is treated with bromine water, white precipitate is obtained. Give the structure and the name of the compound formed.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When phenol is treated with bromine water, it forms the white precipitate of 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol. In the bromination reaction of phenol, water is ionized. And also bromine gets ionized to produce bromonium ions to a larger extent. Phenol gets ionized to produce an ortho-para directing phenoxide ion. Bromine water is mostly used as a test for C=C double bond. During this reaction white precipitates form at the end and bromine water is decolourised.
Hence, the formation of bromonium ions and strong ortho-para directing species indicates that the product formation is 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol.
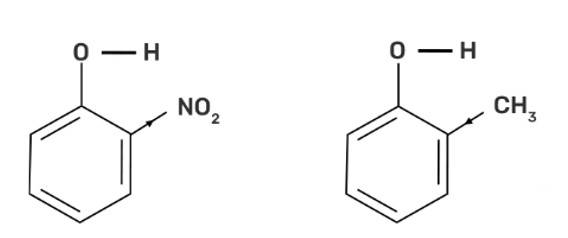
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of acidity and give a suitable explanation. Phenol, o-nitrophenol. o-cresol
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The increasing order of acidity:
o-cresol < Phenol < o-nitrophenol
The electron-withdrawing group on the substituted phenol increases the acidity due to increasing the polarity of the O-H bond and thus, the acidity increases and vice versa. -NO2 is an electron-withdrawing group whereas the -CH3 group is an electron-donating group.
Alcohols react with active metals e.g. Na. K etc. to give corresponding alkoxides. Write down the decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal towards primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The decreasing order of reactivity of alcohol with sodium metal:
Tertiary Alcohols > Secondary Alcohols > Primary Alcohols
When alcohol reacts with active metals e.g. Na. K etc., the O-H bond of alcohols breaks to form the corresponding alkoxide. The alkyl group is electron donating and has +I effect due to which the O-H bond becomes strong and hence, the reactivity of alcohol decreases.
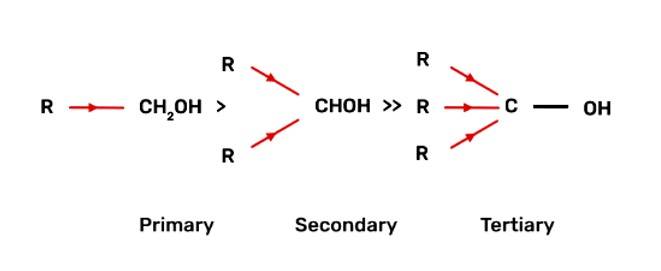
Fig: +I effect of alkyl group of alcohol
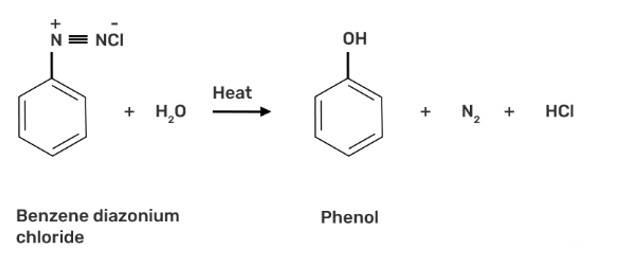
What happens when benzene diazonium chloride is heated with water?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
When benzene diazonium chloride is heated with water, it forms phenol along with nitrogen and hydrochloric acid as by-products as shown below:
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of acidity.
H2O, ROH, HC ≡ CH
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The decreasing order of acidity:
H2O > ROH > HC ≡ CH
The more the stability of the conjugate base of the given compounds, the more acidity will be.
? OH > ? O-R > ? C ≡ CH
The negative charge on the electronegative oxygen atom is more stable than carbon atom. The + I effect of the alkyl group does not stabilize the negative charge on the electronegative oxygen atom, hence less stable than ? OH.
Name the enzymes and write the reactions involved in the preparation of ethanol from sucrose by fermentation.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The enzyme invertase, which is present in yeast, is used to convert sucrose to glucose and fructose. The glucose and fructose are further converted to ethanol by zymase enzyme (also present in yeast).
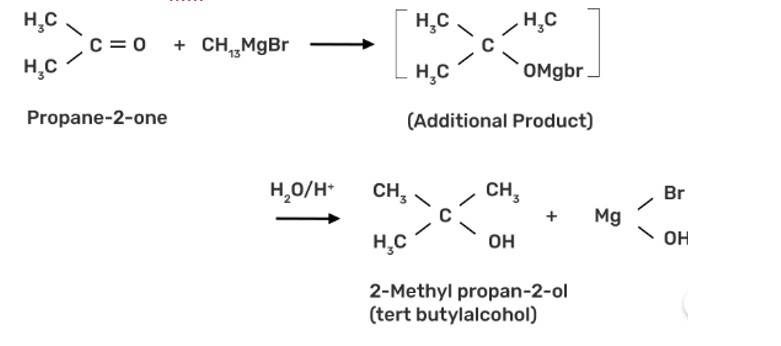
How can propan-2-one be converted into tert- butyl alcohol?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The propan-2-one can be converted into tert-butyl alcohol by using CH3MgBr grignard reagent to form the additional product tert-butyl alcohol.
Write the structures of the isomers of alcohols with molecular formula C4H10O. Which of these exhibits optical activity?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O is butanol has 4 isomers, these are:
(a) CH3-CH2CH2-CH2OH (Butane-1-ol)
(b) CH3-C*H-CH2-CH3 (Butane-2-ol)
|
OH
(c) CH3-CH-CH2-OH (2-methylpropane-1-ol)
|
CH3
CH3
|
(d) CH3- C-CH3 (2-methylpropan-2-ol)
|
OH
Only butane-2-ol has chiral carbon due to it being the alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O exhibits optical activity.
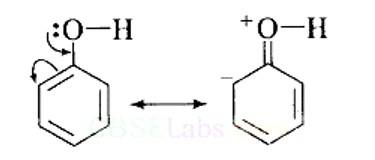
Explain why is OH group in phenols more strongly held as compared to OH group in alcohols.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The electron pairs of oxygen atom of hydroxyl (-OH) group in phenols are in conjugation with the pi electrons of phenyl ring and hence, the bond C-OH bond has double bond character due to which OH group in phenols more strongly held as compared to OH group in alcohols.
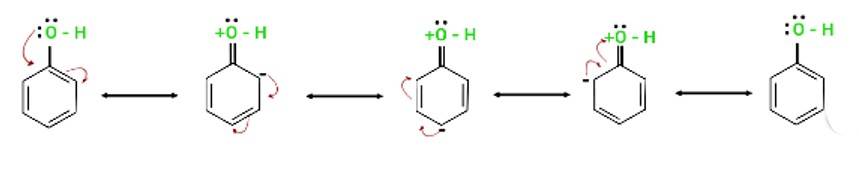
Resonance in phenol
Explain why nucleophilic substitution reactions are not very common in phenols.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The C-OH bond in phenols has double bond character due to resonance of electron pairs of oxygen atom with the pi electrons of phenyl ring, which makes the C-OH bond strong and hence, the nucleophilic substitution of a nucleophile with the -OH group of alcohol is not possible as the C-OH does not break easily.
Preparation of alcohols from alkenes involves the electrophilic attack on alkene carbon atom. Explain its mechanism.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
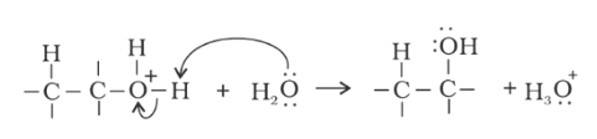
Step 1: Protonation of alkene due to the presence of double bond which attacks the H3O+ ion and forms carbocation.
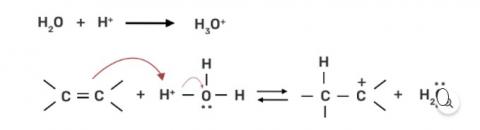
Step 2: Water molecule act as nucleophile and attack the carbocation.

Step 3: Deprotonation occur to get the alcohol and hydronium ion forms
Explain why is O=C=O nonpolar while R—O—R is polar.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In O? C? O, the dipole moment is zero, hence non-polar while in R—O—R the dipole moment is non-zero due to which it is polar.
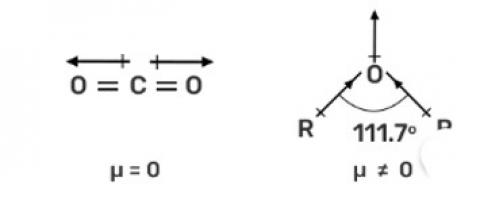
The CO2 is a linear molecule and the dipole moment is equal and in the opposite direction due to which the dipole moment is zero. While in R—O—R, has bent structure and lone pair of electrons due to which the net dipole moment is nonzero and hence, it is a polar molecule.
The CO2 is a linear molecule and the dipole moment is equal and in the opposite direction due to which the dipole moment is zero. While in R—O—R, has bent structure and lone pair of electrons due to which the net dipole moment is nonzero and hence, it is a polar molecule.
Why is the reactivity of all the three classes of alcohols with conc. HCl and ZnCl2 (Lucas reagent) different?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The reaction of alcohol with the conc. HCl and ZnCl2 (Lucas reagent) leads to the formation of a carbocation through SN1 mechanism. The more stable the carbocation, the faster the reaction will be.
Tertiary carbocation is the most stable due to hyperconjugation and inductive effect then is the secondary alcohol and the primary alcohol is the least stable.
Stability of carbocation:
Tertiary carbocation > Secondary carbocation > Primary carbocation
According to stability of carbocation, the reactivity order of the alcohol is:
Tertiary alcohol > Secondary alcohol > Primary alcohol
Tertiary alcohol reacts immediately with Lucas reagent and shows turbidity, secondary alcohol does not show turbidity with Lucas reagent at room temperature but on heating turbidity appears and primary alcohol do not react with lucas reagent even on heating.
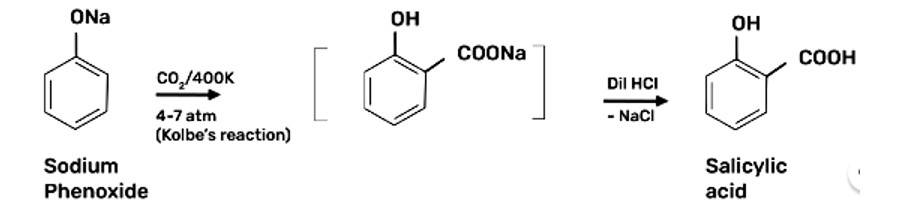
Write steps to carry out the conversion of phenol to aspirin.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Step 1: Addition of NaOH to obtain sodium phenoxide
Step 2: Sodium Phenoxide undergoes Kolbe’s reaction at high temperature and pressure in presence of carbon dioxide (CO2) gas. The product is further hydrolysed to obtain salicylic acid.
Step 3: Acetylation of salicylic acid occur when it is treated with acetic anhydride

Nitration is an example of aromatic electrophilic substitution and its rate depends upon the group already present in the benzene ring. Out of benzene and phenol which one is more easily nitrated and why?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The nitration of aromatic compounds occurs by using HSO4 and HNO3 which leads to the formation of NO2+ (nitronium ion) electrophile.
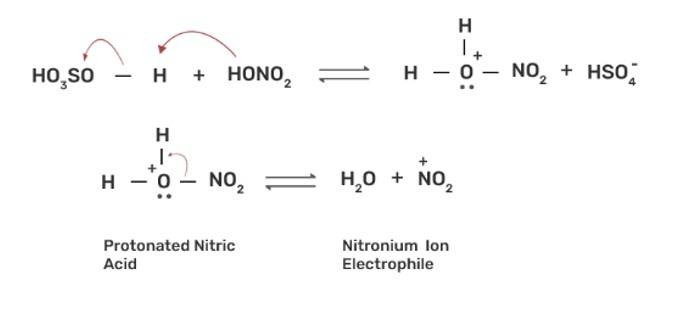
Due to the formation of NO2+ electrophile, we can say that nitration is an example of aromatic electrophilic substitution. The electron releasing group on the benzene ring increases the rate of nitration and vice-versa.
Phenol is more easily nitrated than benzene as the hydroxyl (-OH) group on the benzene ring is an electron releasing group which increases the electron density at the ortho and para position due to +R effect of -OH group. The nitration occurs at these electron rich sites by the attack of NO2+ electrophile.
In Kolbe's reaction, instead of phenol, phenoxide ion is treated with carbon dioxide. Why?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Phenoxide ion is more reactive than phenol to electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction due to the more in electron density of phenoxide ion and hence, phenoxide ion easily undergoes the electrophilic substitution reaction than phenol by the weak CO2 electrophile.
Dipole moment of phenol is smaller than that of methanol. Why?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
In phenol, the electron pairs on oxygen atom of -OH group are in conjugation (or resonance) with phenyl ring which decreases the polarity of the C-OH bond whereas in methanol the polarity of C-OH bond is more due to electron releasing group of -CH3.
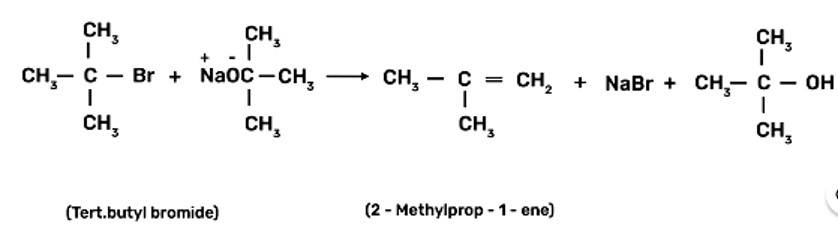
Ethers can be prepared by Williamson synthesis in which an alkyl halide is reacted with sodium alkoxide. Di-tert-butyl ether can't be prepared by this method. Explain.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ethers are prepared by Williamson synthesis by the reaction of alkyl halide with the stadium alkoxide. But this is not possible in case of di-tert-butyl ether. In case of preparation of di-tert-butyl ether, tert-butyl halide must react with sodium tert-butoxide. Alkoxides are nucleophiles but they are strong bases as well, due to which elimination is favoured instead of substitution and leads to the formation of 2-methylprop-1-ene.
Why is the C—O—H bond angle in alcohols slightly less than the tetrahedral angle whereas the C—O—C bond angle in ether is slightly greater?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The bond angle C—O—H in alcohols is less than tetrahedral angle because of the repulsion between the lone pairs present on the oxygen atom, which pushes the bond C—O—H closer. Therefore, C—O—H bond angle in alcohols is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle.
In ethers, the lone pairs on oxygen atoms are also present but the two bulky alkyl groups also have repulsive force which increases the C—O—C bond angle. Therefore, the C—O—C bond angle in ether is slightly greater than tetrahedral angle .
Explain why low molecular mass alcohols are soluble in water.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The occurrence of intermolecular hydrogen bonds due to the H- bonds in alcohol compounds play a major role . With the increasing number of alkyl groups the molecular mass increases due to which the polar nature of these compounds get suppressed . Hence, the solubility factor of alcohols is indirectly proportional to the molecular mass.
Explain why p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
The electron withdrawing group (-NO2), withdraws electrons and disperses the negative charge. Therefore, -NO2 group stabilizes the phenoxide ion. Hence p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol.
Explain why alcohols and ethers of comparable molecular mass have different boiling points.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Due to the presence of intermolecular H- bonds in alcohol the energy required to break H – bonds is more than the energy required to break simple dipole bonds present in ethers . Thus, the boiling point of alcohol is higher than the boiling point of ethers.
The carbon-oxygen bond in phenol is slightly stronger than that in methanol. Why?
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
This can be explained as under:
(i) In phenol, the conjugation of unshared electron pairs over oxygen with aromatic ring results in partial double bond character in C – O bond.
In methanol, no such conjugation (resonance) is possible.
(ii) In phenol, oxygen is attached to sp2 hybridised carbon while in methanol, oxygen attached to sp2 hybridised carbon. An sp2 hybridised carbon is more electronegative (because of greater 5-character) than sp3 hybridised carbon atom. Therefore, the bond between oxygen and sp2 hybridised carbon is more stable than the bond between oxygen and sp2, hybridised orbital.
Arrange water, ethanol and, phenol in increasing order of acidity and give reason for your answer.
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Increasing order of acidity is: ethanol < water < phenol.
This is because the phenoxide ion obtained after the removal of H+ is resonance stabilised, while the ethoxide ion obtained after the removal of H+ is destabilised by +1 effect of ethyl group. Thus phenol is a stronger acid than ethanol.
Now, ethanol is a weaker acid than water because the electron releasing ethyl group increases the ethanol density on oxygen and consequently the proton will not be released easily. There is no such effect is water.
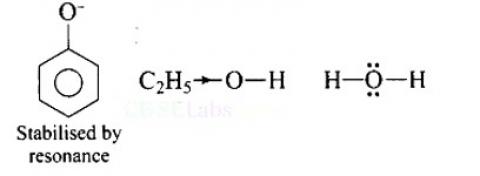
Monochlorination of toluene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis with aq. NaOH yields.
I. o-Cresol
II. m-Cresol
III. 2, 4-Dihydroxytoluene
IV. Benzyl alcohol
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(IV) Benzyl alcohol
The chlorine atom is substituted by the hydrogen atom of methyl hydrocarbon present in toluene to form benzyl chloride on monochlorination of toluene in presence of sunlight by free radical pathway.
C6H5CH3 + Cl2 ![]() C6H5CH2Cl
C6H5CH2Cl
Toluene Benzyl Chloride
Benzyl chloride (monochlorinated toluene product) on hydrolysis with aq. NaOH yields benzyl alcohol by substituting the chloride ion by OH- ion by nucleophilic substitution reaction.
C6H5CH2Cl ![]() C6H5CH2OH
C6H5CH2OH
Benzyl Benzyl
Chloride Alcohol
How many alcohols with molecular formula C4H10O are chiral in nature?
I. 1
II. 2
III. 3
IV. 4
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(I) The alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O is butanol has 4 isomers, these are:
(a) CH3-CH2CH2-CH2OH (Butane-1-ol)
(b) CH3-C*H-CH2-CH3 (Butane-2-ol)
|
OH
(c) CH3-CH-CH2-OH (2-methylpropane-1-ol)
|
CH3
CH3
|
(d) CH3- C-CH3 (2-methylpropan-2-ol)
|
OH
Butane-2-ol has chiral carbon which has all different substituted groups attached, so butane-2-ol alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O is chiral in nature.
What is the correct order of reactivity of alcohols in the following reaction?
R - OH + HCl ![]() R - Cl + H2O
R - Cl + H2O
I. 1° > 2° > 3°
II. 1° < 2° > 3°
III. 3° > 2° > 1°
IV. 3° > 1° > 2°
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(III) 3° > 2° > 1°
Alcohols are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary by lucas reagent which is a mixture of concentrated HCl and dry anhydrous ZnCl2. The carbocation is formed as the intermediate during the lucas test of alcohol.More the stability of intermediate carbocation, more will be the reactivity of alcohol.
Tertiary carbocation is most stable then the secondary alcohol is stable due to hyperconjugation and the primary alcohol is the least stable.
Stability of intermediate carbocation:
3° > 2° > 1°
Reactivity of alcohol:
3° > 2° > 1°
CH3CH2OH can be converted into CH3CHO by ________________ .
I. Catalytic hydrogenation
II. Treatment with LiA1H4
III. Treatment with pyridinium chlorochromate
IV. Treatment with KMnO4
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(III) Treatment with pyridinium chlorochromate
The pyridinium chlorochromate is a complex of chromium trioxide with pyridine. This reagent is preferred for mild oxidation to form aldehydes and hence the oxidation to carboxylic acid is prevented.
Primary alcohols are oxidized to form aldehyde, whereas secondary and tertiary alcohols are oxidized to form ketones. The conversion of a hydroxyl group to aldehyde can be done by the removal of hydrogen atoms (Oxidation), looking at the following options; pyridinium chlorochromate and potassium dichromate are both oxidizing agents. However, when pyridinium chlorochromate is used, it is a weaker oxidizing agent compared to potassium permanganate; hence, it reduces ethanol to acetaldehyde (ethanal).
CH3CH2OH ![]() CH3CHO
CH3CHO
The process of converting alkyl halides into alcohols involves
I. Addition reaction
II. Substitution reaction
III. Dehydrohalogenation reaction
IV. Rearrangement reaction
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(II) Substitution reaction
Alkyl halides undergo substitution reactions to form corresponding alcohol.The halide ion, X- is substituted by OH- ion to form alcohol by nucleophilic substitution reaction.
R-X → R-OH
Which of the following compounds is aromatic alcohol?
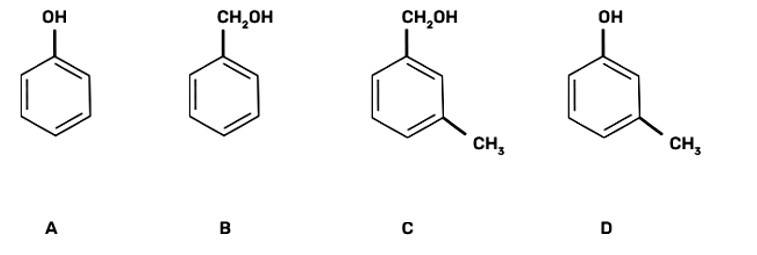
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(III) B, C
The aromatic alcohols or aryl-alcohols are a class of chemical compounds containing a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group.
In the given question, the aromatic alcohols are those compounds in which the hydroxyl group is not directly attached to the benzene ring but is linked to a carbon atom situated in a side-chain. In short, we will search for that figure in which the hydroxyl group is linked to sp3 hybridised carbon.
So, compound B and C have -OH groups attached to sp3 hybridized -CH3 groups and hence are aromatic alcohols and compounds A and D have -OH groups attached to sp2 benzene rings, hence are non-aromatic compounds.
Give IUPAC name of the compound given below.
CH3—CH—CH2--CH2--CH—CH3
| |
Cl OH
I. 2-Chloro-5-hydroxyhexane
II. 2-Hydroxy-5-chlorohexane
III. 5-Chlorohexan-2-ol
IV. 2-Chlorohexan-5-ol
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(III) 5-Chlorohexan-2-ol
The IUPAC naming of the given compound are as follows:
Word root: It depends upon the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain selected, called the parent chain. Depending upon the number of carbons in the chain the compound is assigned a word. The given compound contain 6 carbon attached in the continuous the longest chain and word root for 6 carbon atoms is ‘hex’.
The suffix- A suffix is added after the word root to indicate the nature of the carbon-carbon bond. The given carbon chain contains a single bond then a suffix will be added as “ane”.
Prefix- The groups which are not regarded as functional but present in the carbon chain as substituents are written before the word root as a prefix. Such groups are fluorine, chlorine, nitro, etc.
According to the IUPAC rule, the prefix (Chlorine) will be written first followed by the word root and primary suffix and secondary suffix. As the compound contains chlorine which will be regarded as substituents and will be written as a prefix. The compound contains six carbon atoms due to which it will be considered as hexane and the word root will be “hex”.
Since it is an alkane compound, the primary suffix will be “ane” and the secondary suffix will be “ol”. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the given compound is 5-Chlorohexan-2-ol.
IUPAC name of m-cresol is
I. 3-methylphenol
II. 3-chlorophenol
III. 3-methoxyphenol
IV. benzene- 1.3-diol
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(I) 3-methylphenol
The m-cresol is an organic compound which contains a benzene ring, a -OH group and a methyl group. It has a methyl group substituted to meta position in the phenol ring. According to the IUPAC system, the -OH group is given more priority than the methyl group.
The cresols are also called hydroxytoluene or the methylphenols. These contain a benzene ring with one methyl and one phenol group substituted. There are three forms of cresols which are o-cresol, m-cresol and p-cresol. m- cresol is a colourless liquid and is viscous in nature.
In case of m-cresol, the methyl group and the hydroxyl group at 1st and 3rd position. The structure of m-cresol can be written as-
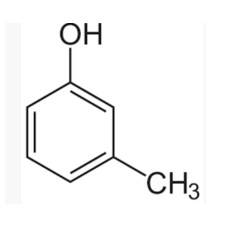
Now, if we see the IUPAC nomenclature then the -OH group should be given 1st place because it has more priority and the methyl group should be at 3rd position i.e. at meta to OH group.
Thus, the IUPAC name is- 3-Methylphenol
IUPAC name of the compound CH3—CH—OCH3 is _______________ .
|
CH3
I. 1-methoxy-1-methylethane
II. 2-methoxy-2-methylethane
III. 2-methoxypropane
IV. isopropylmethyl ether
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(II) 2-methoxy-2-methylethane
IUPAC provides consistency to the names of organic compounds. It enables every compound to possess a unique name, which otherwise is not plausible with the common names. The chemical structure of the given compound is shown below:
The given compound is an alkane so suffix in our case will be –ane. An ether functional group is also present so prefix will be Alkoxy-.
To determine the name of a compound, identify the longest and continuous chain of carbon containing the functional group and count the number of carbon atoms in the chain as shown in the table below.
In the given compound, the number of carbon atoms in the longest chain is 2. That means the prefix of alkane in our case is eth-.
Numbering of the carbons in the longest chain of carbon (Remember that If the organic molecule is not an alkane (and has a functional group) you have to initiate numbering such that the functional group is placed on the carbon having the lowest possible number).
In the given compound, we can number as shown below:
In the given compound, either the group and methyl group present on the second carbon will be treated like a branched group. It will be written as 2-methyl methoxy before the main chain name.
Finally, combine the elements of the compound name in the specified order as: branched groups, prefix, suffix according to the functional group and its location along the longest carbon chain.
Therefore, the given compound will have IUPAC name as: 2-methyl methoxy ethane.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (B), the IUPAC name of the given compound is 2-Methyl methoxy ethane.
Which of the following species can act as the strongest base?
I. ΘOH
II. ΘOR
III. ΘOC6H5
IV. 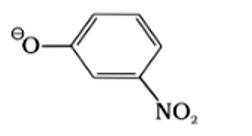
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(II) ΘOR
The species which is the weakest acid has the strongest conjugate base. The ROH is the weakest acid among the given compounds due to the inductive effect of the alkyl group. Therefore, the strongest conjugate base is ΘOR.
Which of the following compounds will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water?
I. C6H5OH
II. C6H5CH2OH
III. (CH3)3COH
IV. C2H5OH
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(I) C6H5OH
C6H5OH, phenol is a strong acid (due to resonance) which will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water to form sodium phenoxide and water. Phenol is more acidic than sp3 hybridized attached alcohols.
Phenol is less acidic than
I. Ethanol
II. o-nitrophenol
III. o-methylphenol
IV. o-methoxyphenol
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(IV) o-methoxy phenol
The stability of the conjugate base determines the acidic character of the compound. Higher the stability of the conjugate base, the higher is the acidic character.
Phenol, O-nitrophenol, O-methyl phenol, and O-methoxy phenol all are aromatic compounds. In aromatic compounds, the negative charge of the conjugate base charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge gives additional stability to the compound.
Ethanol is not aromatic and it cannot delocalise the negative charge formed after the H+ ion leaves the c. So, it is the least acidic among the given options. Thus, we can eliminate it.
There are two types of groups, the electron-withdrawing, and the electron releasing group. The methyl group and the methoxy group are electron releasing groups. They release the electrons and hence decreases the stability of the negatively charged conjugate base.
On the other hand, a nitro group is an electron-withdrawing group. They withdraw the electrons from the aromatic ring. Withdrawing the negative charge from the ring will increase the stability of the compound in this case.
Phenoxide is stabilised by resonance effect only and it does not have any electron releasing group. So, it is more acidic than o-methyl phenol and o-methoxy phenol. But the absence of an electron-withdrawing group makes it less acidic than o-nitrophenol.
Which of the following is most acidic?
I. Benzyl alcohol
II. Cyclohexanol
III. Phenol
IV. m-Chlorophenol
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(IV) m-Chlorophenol
Phenols are more acidic than sp3 and sp2 hybridized alcohol. The m-Chlorophenol is more acidic than phenol due to the -I effect (dominated by the + R effect) of chlorine atom increasing the acidity of phenol.
Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(II) b > d > a > c > e
The acidic strength decreases with increasing stability of the conjugate base of the given alcohol. -NO2 group at the para position in compound (b) is the most acidic due to the -M effect of the -NO2 group.
Compound (d) has -I effect on the conjugate base, whereas the -OCH3 group has + M effect on the conjugate base and hence decreases the acidity of compounds (c) and (e).
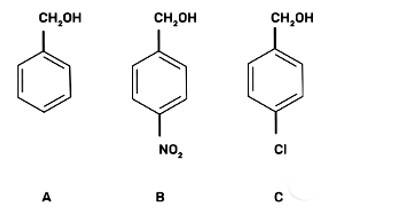
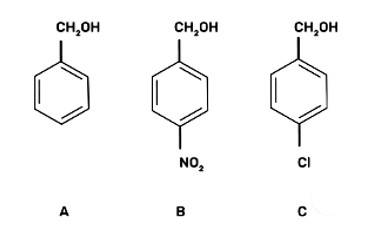
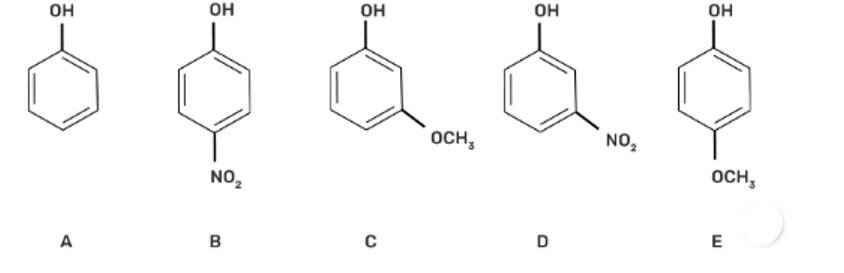
Mark the correct increasing order of reactivity of the following compounds with HBr/HCl.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(III) b < c < a
The reaction will proceed by SN1 mechanism to form the carbocation intermediate, more the stability of carbocation more will be the reactivity of the given compound with HBr/HC1.
-NO2 group is an electron withdrawing group and due to the -M effect, increases the stability of carbocation. Cl group at para position shows + M effect due to it, carbocation is least stable and hence, the compound (c) is the least reactive.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of boiling point. Propan- 1-ol. butan-l-ol. butan-2-ol. pentan- 1-ol
I. Propan- 1-ol. butan-2-ol. butan- 1-ol. pentan- 1-ol
II. Propan- 1 -ol. butan- 1 -ol. butan-2-ol. pentan- 1 -ol
III. Pentan-l-ol. butan-2-ol. butan- 1 -ol. propan- 1-ol
IV. Pentan-l-ol. butan- 1-ol. butan-2-ol. propan- 1-ol
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(I) Propan- 1-ol. butan-2-ol. butan- 1-ol. pentan- 1-ol
The compounds Propan-l-ol, butan-2-ol, butan-1-ol, pentan-1-ol belong to the alcohol family. The structure of the given alcohols are as shown below:
With increase in the molecular weight, the boiling points of alcohols increase. Hence, butan-1-ol has higher boiling point than propan-1-ol. Similarly, pentan-1-ol has higher boiling point than butan-1-ol.
Hence, the increasing order of the boiling points of alcohols is propan-1-ol < butan-1-ol < pentan-1-ol.
With increase in the branching of alkyl groups, the boiling point of alcohols decreases. Thus, butan-2-ol has lower boiling point than butan-1-ol. The increasing order of the boiling points of given alcohols is
Note : In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
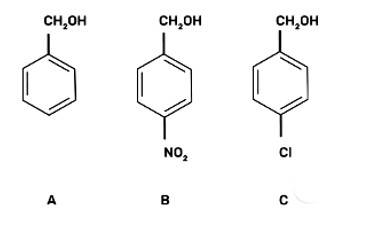
Which of the following are used to convert RCHO into RCH2OH?
I. H2/Pd
II. LiA1H4
III. NaBH4
IV. Reaction with RMgX followed by hydrolysis
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
I. H2/Pd
II. LiA1H4
III. NaBH4
Aldehydes and ketones are converted to alcohols by catalytic hydrogenation.The reagents used to convert the aldehydes to alcohol are by H2/Pd, lithium aluminium hydride (LiA1H4), and sodium borohydride (NaBH4).
Which of the following reactions will yield phenol?
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
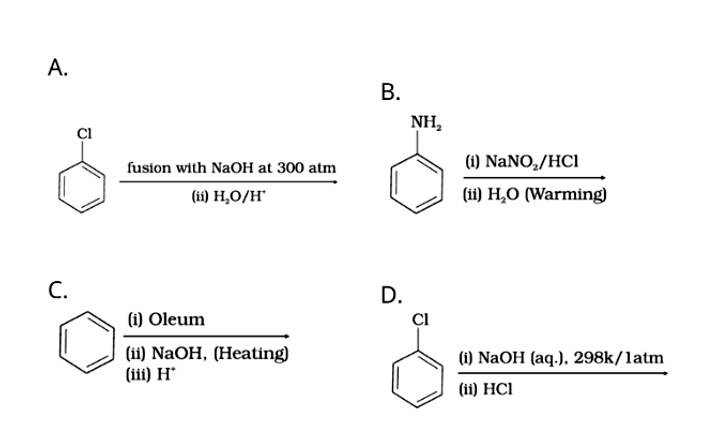
Phenol is prepared by:
Dow’s process: The chlorobenzene on heating with NaOH, form sodium phenoxide which on hydrolysis with water of acid from phenol.
Diazotization of aniline: Aniline on reacting with nitrous acid at 0-5o C followed by hydrolysis with water form phenol.
Benzene undergoes sulphonation on reacting with oleum to form benzene sulphonic acid which on heating with sodium hydroxide forms sodium phenoxide and then phenol on hydrolysis.
The nucleophilic substitution of haloarenes such as chlorobenzene requires drastic conditions for conversion to phenol so chlorobenzene will not be converted to phenol on heating with NaOH at 298K / 1atm.
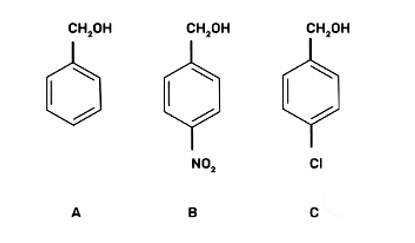
Which of the following reagents can be used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes?
I. CrO3 in anhydrous medium.
II. KMnO4 in an acidic medium.
III. Pyridinium chlorochromate.
IV. Heat in the presence of Cu at 573K.
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
I. CrO3 in anhydrous medium.
II. Pyridinium chlorochromate.
III. Heat in the presence of Cu at 573K.
KMnO4 is a strong oxidising agent and oxidises the primary alcohol to ketone. Hence cannot be used as a reagent to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes.
Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reactions with
I. Br2/water
II. Na
III. Neutral FeCl3
IV. All the above
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
I. Br2/water
III. Neutral FeCl3
Phenol does not give the bromine water (Br2/water ) test whereas ethanol gives the bromine water.
Phenol on reaction with neutral FeCl3 forms a colored complex with Fe3+ ion whereas ethanol does not form the colored complex with neutral FeCl3.
Which of the following arc benzylic alcohols?
I. C6H5—CH2—CH2—OH
II. C6H5—CH2—OH
III. C6H5—CH—OH
|
CH3
IV. C6H5—CH—CH—OH
|
CH3
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
II. C6H5—CH2—OH
III. C6H5—CH—OH
|
CH3
Benzylic alcohol are those alcohols which have phenyl group attached to the alpha carbon of alcohol.
R—CαH2—OH : Benzylic Alcohol
The compound II and III have phenyl group attached at the Cα of the alcohol and thence they are benzylic alcohols
Match the items of Column I and Column II in the following questions.
Match the structures of the compounds given in Column I with the name of the compounds given in Column II.
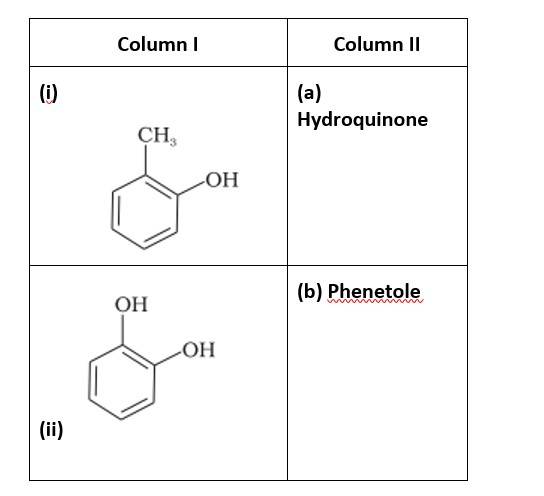
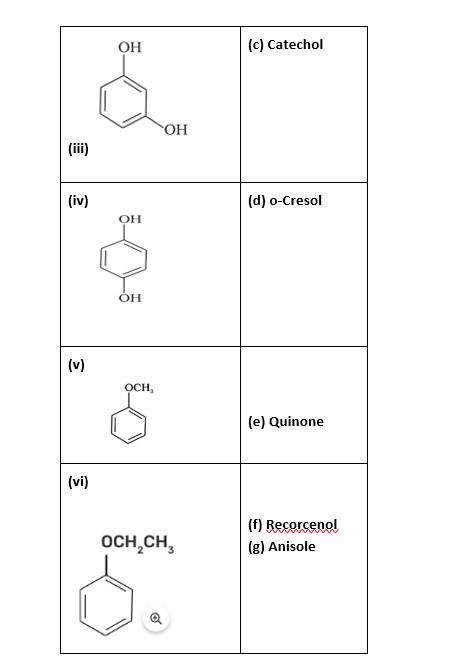
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)- (d); (ii)- (c); (iii)- (f); (iv)- (a); (v)- (g); (vi)- (b)
Match the starting materials given in column I with the products formed by these (Column II) in the reaction with HI.
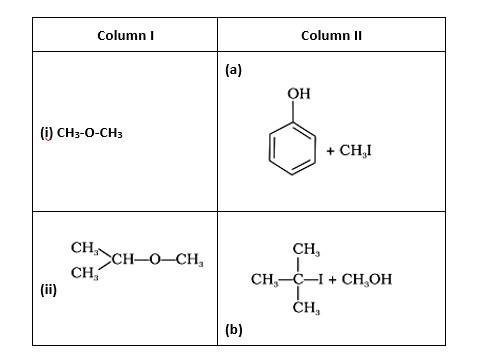
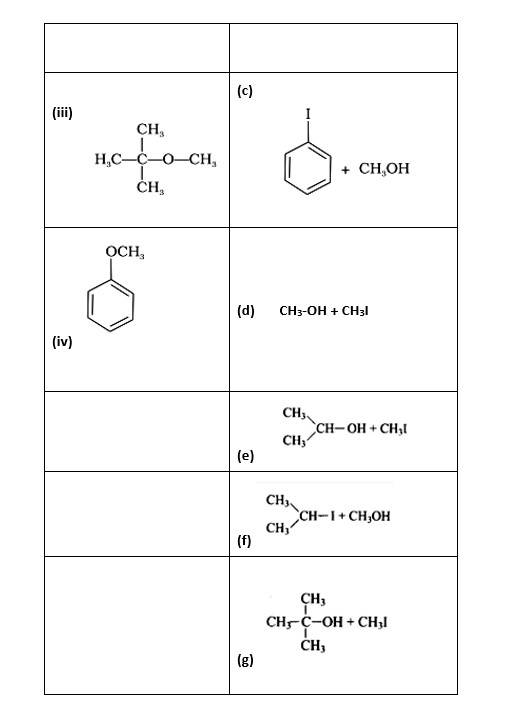
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)- (d) (ii)- (e); (iii)- (b); (iv)- (a)
Match the items of column I with items of column II.
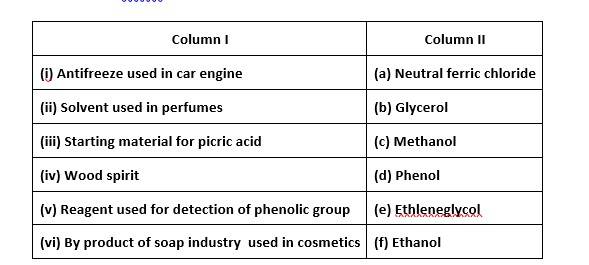
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)- (e) ; (ii)- (f) ; (iii)- (d) ; (iv)- (c); (v)- (a); (vi)- (b)
Match the items of column I with items of column II.
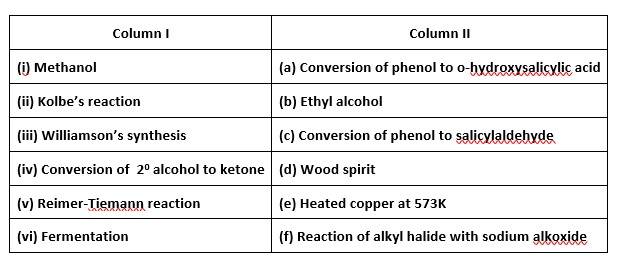
This is a matching answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i)- (d); (ii)- (a); (iii)- (f); (iv)- (e); (v)- (c); (vi)- (b)
In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
(iii) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
(iv) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
(v) Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
1. Assertion: Addition reaction of water to but-1-ene in acidic medium yields butan-1-ol.
Reason: Addition of water in acidic medium proceeds through the formation of primary carbocation.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Correct assertion: Addition reaction of water to but-1-ene in acidic medium yields butan-2-o1.
Correct reason: Addition of water in acidic medium proceeds through the formation of secondary carbocation.
Assertion: p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol.
Reason: Nitro group helps in the stabilisation of the phenoxide ion by dispersal of negative charge due to resonance.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(i) Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation: P-nitrophenol is more acidic as nitro group helps in the stabilization of the phenoxide ion by dispersal of negative charge due to resonance.
Assertion: IUPAC name of the compound CH3—CH-O =CH2-CH2—CH3 is 2 - Ethoxy - 2 - methylethane. |
CH3
Reason: In IUPAC nomenclature, ether is regarded as hydrocarbon derivative in which a hydrogen atom is replaced by —OR or —OAr group [where R= alkyl group and Ar= aryl group]
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iv) Assertion is a wrong statement but reason is correct.
Explanation: Correct assertion is the IUPAC name of the compound is 1- (2-propoxy) propane.
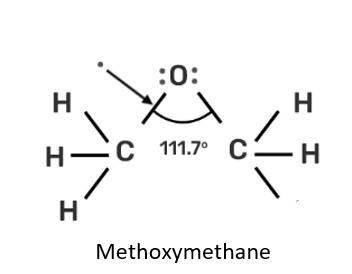
Assertion: Bond angle in ethers is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle.
Reason: There is a repulsion between the two bulky (—R) groups.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iv) Assertion is a wrong statement but reason is correct.
Explanation: 141 pm
Assertion: Boiling points of alcohols and ethers are high.
Reason: They can form intermolecular hydrogen-bonding.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Explanation: Correct assertion: Boiling points of alcohol are higher than that of ethers of comparable molecular mass.
Correct reason: Alcohols can form intermolecular hydrogen bonding while ethers cannot.
Assertion: Like bromination of benzene, bromination of phenol is also carried out in the presence of Lewis acid.
Reason: Lewis acid polarises the bromine molecule.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iv) Assertion is a wrong statement but reason is correct.
Explanation: Bromination of phenol cannot be carried out in presence of Lewis acid.
Assertion: o-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than the m- and p-isomers.
Reason: m- and p- Nitrophenols exist as associated molecules.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(v) Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Explanation: Due to intramolecular hydrogen bonding o-Nitrophenol does not form hydrogen bond with water
Assertion: Ethanol is a weaker acid than phenol.
Reason: Sodium ethoxide may be prepared by the reaction of ethanol with aqueous NaOH.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iii) Assertion is a correct statement but reason is wrong.
Explanation: Phenoxide ion is stabilized by resonance which is not possible in alkoxide ion.
Assertion: Phenol forms 2,4,6– tribromophenol on treatment with Br2 in carbon disulphide at 273K.
Reason: Bromine polarises in carbon disulphide.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(ii) Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Explanation: Correct assertion: Phenol on treatment with bromine water can form 2,4,6- tribromophenol
Correct reason: In water, phenol gives phenoxide ions which activate the ring towards electrophilic substitution reaction.
Assertion: Phenols give o- and p-nitrophenol on nitration with conc. HNO3 and H2SO4 mixture.
Reason: —OH group in phenol is o–, p– directing.
This is a assertion and reason answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(iv) Assertion is a wrong statement but reason is correct.
Explanation: Phenol on treatment with dil. HNO3 form o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol.
Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Eleven Exam

 C6H5CH2Cl
C6H5CH2Cl