Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three
Get insights from 125 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Electrolysis of brine solution is as follows
NaCl (aq)→Na+ (aq)+Cl− (aq)
At the cathode, the reaction goes this way,
H2O (l) + e−→12H2 (g)+OH− (aq)
At the anode, the reaction goes this way,
Cl− (aq)→12Cl2 (g) + e−
The pH of the solution will increase as sodium hydroxide is being formed.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: When the opposing potential becomes equal to the electrical potential there is no current flowing in the cell and the cell reaction stops and there is no chemical reaction in the cell
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Alternating current is used to stop electrolysis so that the concentration of the ions in the solution remains constant.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
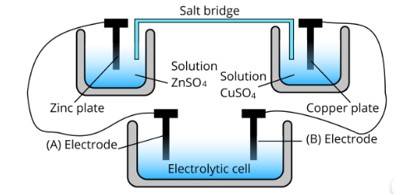
Ans: The cell represented above shows an electrochemical cell in which two different electrodes are present and the cell at the bottom represents the electrolytic cell.
In this zinc is losing electrons moving towards electrode A and copper is accepting an electron from electrode B. Therefore, the polarity of electrode A is positive and electrode B is negative.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The potential difference between the metal and its solution is termed electrode potential.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: In the electrolysis process of sodium chloride, oxidation of water at anode requires more potential. So Cl− is oxidized at anode instead of water.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: Galvanic cell consists of two electrodes in which anode and cathode are present as electrodes. The anode is present on the left side at which oxidation occurs. The cathode is present on the right side at which reduction occurs and in the middle, there is a salt bridge which is depicted by parallel lines. Therefore, the galvanic cell is Cu|Cu2+ |Ag+ |Ag.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: According to Faraday's second law of electrolysis, the amount of different substances liberated keeping the electricity flow same through the electrolytic solution is directly proportional to the equivalent weight.
=
E1and E2 have different values. Therefore, the mass of copper and silver deposited will be different
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: At the stage of equilibrium E? Cell =0. So according to the relation,
ΔrG =−nFEcell
ΔrG =−n*F*0
ΔrG =0
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: E? Cell can never be zero. For a feasible reaction E? Cell should be positive or ΔrGshould be negative and at the stage of equilibrium, both of these parameters are zero.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers