Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three
Get insights from 125 questions on Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 12th Chapter Three
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Short Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans:No, the difference in potentials of the electrodes is measured. A reference electrode is to be taken while measuring the electrode potential of the electrode.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Ans: The relation between Gibbs free energy and the emf of the cell is as follows;
ΔG=−nFEcell
E cell s the cell potential
is the standard emf of the cell
Maximum work obtained from the galvanic cell is nFE .
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
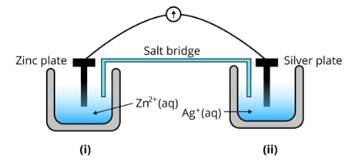
Ans: (i) The diagram is as follows;
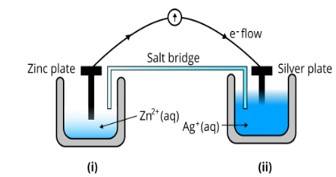
(ii) Agis cathode where the reduction process is taking place where Ag+ takes electrons and deposits them at the cathode
(iii) Potential is zero when the salt bridge is suddenly removed.
(iv) Cell will stop functioning at discharging position when the cell potential is zero
(v) The concentration of Zn2+ ions will increase and the concentration of Ag+ ions will decrease due to conversion in oxidized and reduced forms.
(vi) When the cell is dead, the potential is zero and at equilibrium condition. Thus, the concentration of Zn2+ and A
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a Long Answer Type Questions as classified in NCERT Exemplar
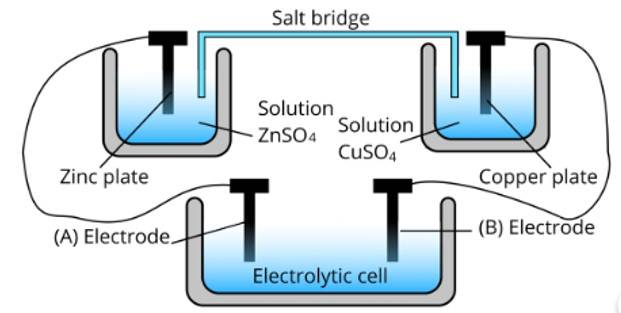
Ans: (i) Cell 'B' will act as an electrolytic cell because to less value of Ecell The reactions occurring in the cell are as follows;
At anode: Zn2+ + 2e− → Zn
At cathode: Cu (s) → Cu2+ + 2e−
(ii) Cell 'B' has a higher emf so it acts as a galvanic cell. The reactions are as follows;
At anode: Zn → Zn2+ + 2e−
At cathode: Cu2+ + 2e− → Cu
New question posted
6 months agoTaking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers