Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
As per Galileo's Law of Inertia, objects in motion have a natural tendency to stay in motion. This property is called inertia. But, they stop moving as there are external forces. Now, we should know that friction is a type of force. It acts in parallel and opposes motion when two surfaces are in contact. Then we have air resistance, which is a type of friction that acts on objects as they move through the air.
In an ideal scenario, as Galileo and Newton would have proved through their observations and mathematical enquiries, there will be no friction or air resistance. Then an object in motion would continue to move indefinitely in
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
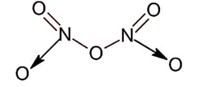
All given oxide have nitrogen – nitrogen bond except N2O5 as ;
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
w = 20 g
Mole of Na2O=
1 mole of Na2O gives 2 mole of NaOH
mole of Na2O gives moles of NaOH
Molarity of NaOH solution
= 1.29 M
=
Ans. = 13
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
50 ml of 1 (M) HCl + 30 ml of 1 (M) NaOH
NaOH + HCl -> NaCl + H2O
30 * 1 mmol 50 * 1 mmol
0 mmol 20 mmol
x = 6021
Ans. = 6021
New answer posted
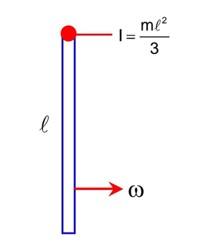
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
By work energy theorem
Work done = change in K.E.
Work done by friction work done by spring
As 90% of K.E. is losed by friction so that
-K -> -16 * 105
K = 16 * 105
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers