We know an atom is the smallest unit of an element, but do we know the structure of an atom, what it is made of? In the structure of the atom, there is a nucleus in the center, with protons and neutrons, and electrons moving around the nucleus. In the structure of the atom class 11 NCERT notes, we’ll understand the atomic structure, and cover all the important topics mentioned below:
- What is Atomic Structure
- Discovery of Sub-atomic Particles
- Atomic Models
- Towards a Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
- Quantum Mechanical Model of an Atom
The “Structure of Atom” revision notes would be helpful to quickly go through the chapter and revise all the important topics.
- What is Atomic Structure?
- Discovery of Sub-Atomic Particles
- Atomic Models
- Towards a Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
- Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
- Revision Notes for Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
- About the Content Reviewer
- Structure of Atom FAQs
What is Atomic Structure?
Atomic structure refers to the different parts of an atom, with the nucleus at the center, where protons and neutrons are present, and electrons revolve around the nucleus.
Every atom has three main building blocks:
- Nucleus (The Center)- Contains protons and neutrons. The nucleus is very small but contains all the mass of an atom.
- Electrons- negative charge particles, move around the nucleus in orbitals. Much lighter than protons and neutrons.
- Empty Space- most of the atom is actually empty space. If an atom were the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would be like a marble in the center.
Discovery of Sub-Atomic Particles
To know what is contained in an atom, many experiments have been performed by many scientists in the past. You can imagine the discovery of sub-atomic particles is like having a closed box and you want to know what’s inside without opening it. You might shake it, listen to sounds, or feel its weight. Scientists did something similar with atoms to figure out what atoms contain.
Discovery of the Electron
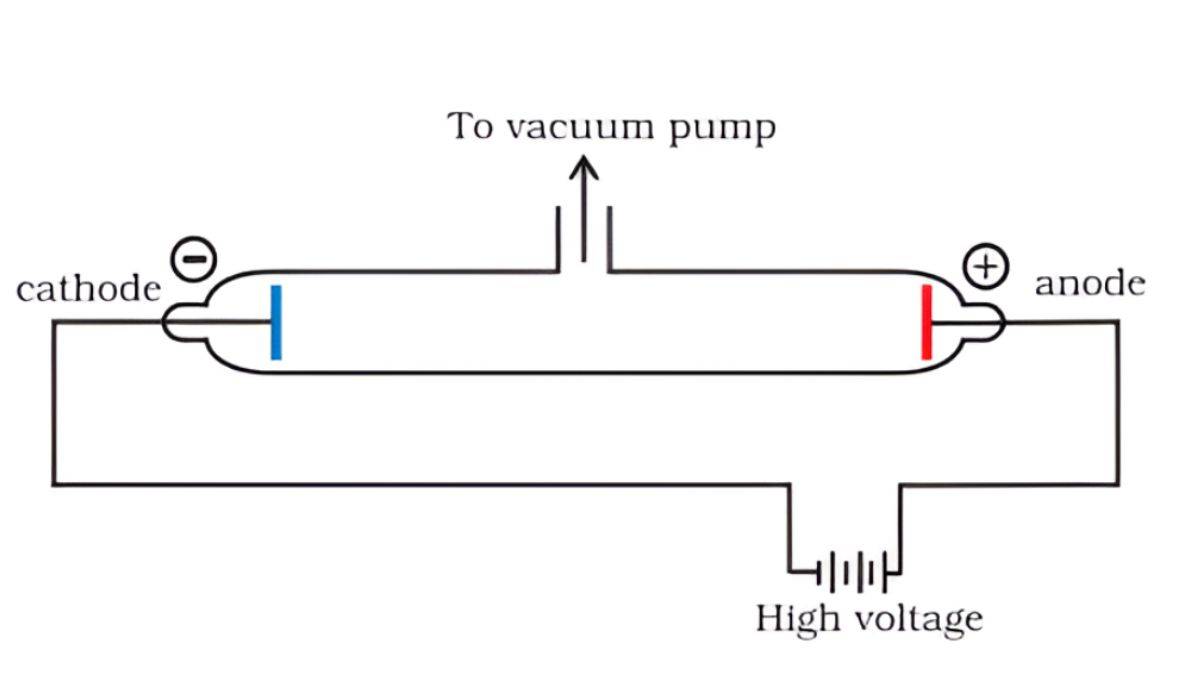
Cathode Ray Tube Experiments
In the 1890s, scientists passed electricity through the tubes (called cathode ray tubes), and they saw mysterious rays coming from the negative end (cathode).
J.J. Thomson’s Experiments (1897):
- These cathode rays were actually tiny particles
- They had a negative charge
- They were much lighter than atoms
- Thomson called them “electrons”
Properties of Electrons:
- Charge: -1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ coulombs (we just say -1 for simplicity)
- Mass: 9.109 × 10⁻³¹ kg (about 1/1837 times the mass of hydrogen)
- Symbol: e⁻
Thomson discovered that atoms are not solid balls - they contain smaller particles!
Discovery of Proton
Since atoms are neutral, and electrons are negative, there must be something positive inside atoms.
Goldstein’s Experiment (1886):
- Used a tube with holes in the cathode
- Found positive rays moving toward the negative end
- These rays were made of positive particles called protons
Properties of Protons:
- Charge: +1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ coulombs (we say +1)
- Mass: 1.673 × 10⁻²⁷ kg (about 1837 times heavier than an electron)
- Symbol: p⁺ or H⁺
Discovery of Neutron
For many years, scientists thought atoms only had protons and electrons. But the math does not make sense because atoms were heavier than expected.
James Chadwick (1932):
- Discovered neutral particles in the nucleus
- Called them neutrons
- They have no charge but have a mass similar to protons
Properties of Neutrons:
- Charge: 0 (neutral)
- Mass: 1.675 × 10⁻²⁷ kg (slightly heavier than proton)
- Symbol: n
Atomic Models
Many scientist prepared their own atomic models, but one after another, it gets better. Think of scientific models like different ways to explain how a car works. Each model gets better as we learn more. Some of the well-known Atomic models are those of John Dalton, J.J. Thomson, Ernest Rutherford, and Niels Bohr.
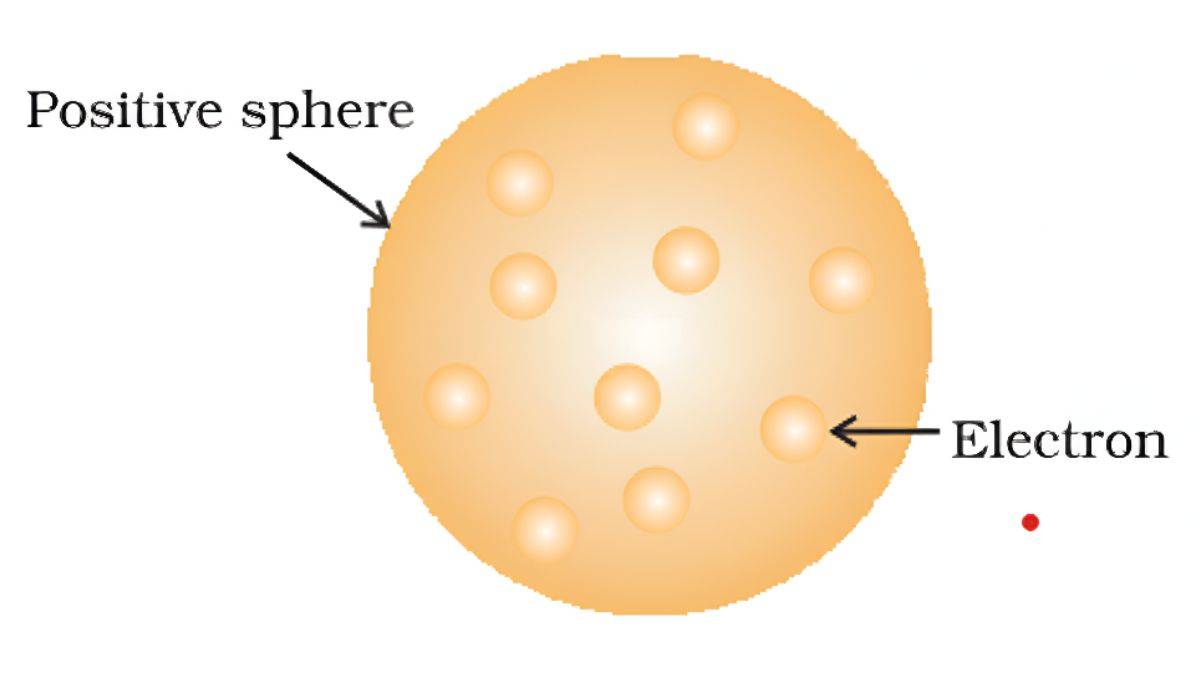
JJ Thomson’s Atomic Model (1904)
It is called The “Plum Pudding” Model.
Thomson thought atoms were like plum pudding or chocolate chip cookies:
- The atom is a ball of positive charge (the pudding)
- Electrons are stuck in it like plums or chocolate chips
- Overall, the atom is neutral
Limitations of Thomson’s Atomic model were:
It couldn’t explain the stability of an atom.
Rutherford’s Atomic Model (1911)
It is called The Nuclear Model.
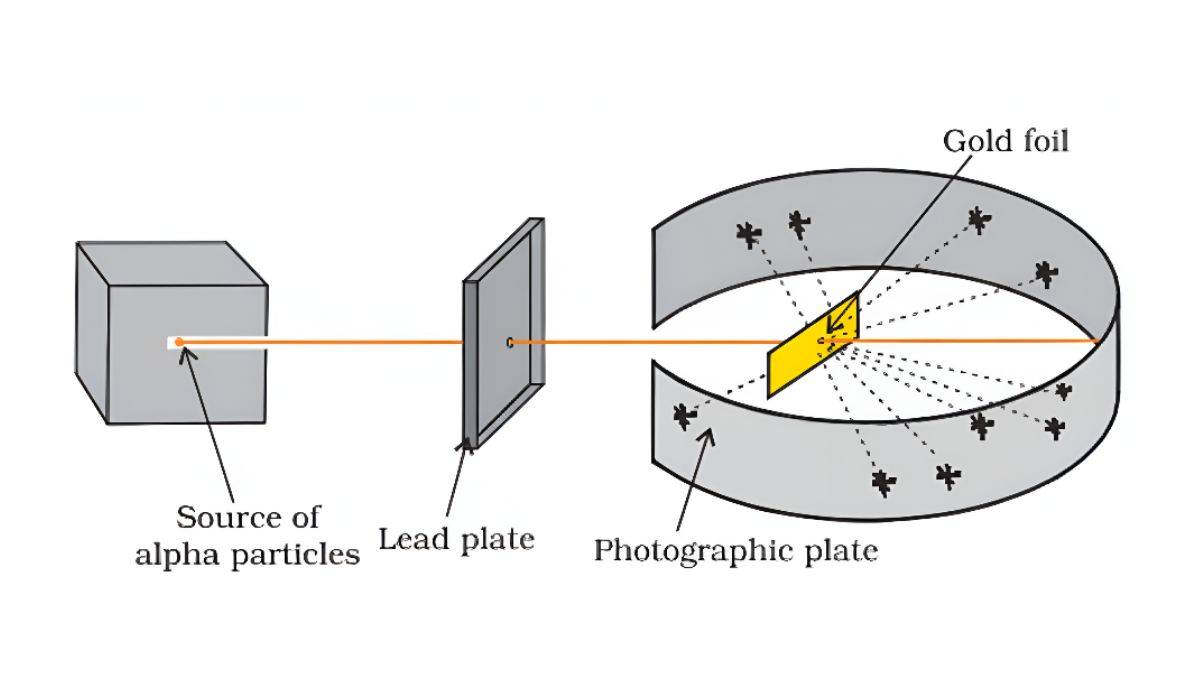
Rutherford did an experiment where he shot tiny particles at a thin gold sheet.
Gold Foil Experiment:
- Most particles went straight through
- Some bounced back at large angles
- A few bounced straight back
Rutherford’s Atomic Model Observation:
- Most of the atom is empty space
- All positive charge (protons) is concentrated in a tiny center (nucleus)
- Electrons move around this nucleus
Limitations of Rutherford’s Atomic Model:
Orbiting electrons should lose energy and collapse into the nucleus
Also Read: Developments Leading to Bohr’s Model of the Atom
Bohr’s Model (1913)
Niels Bohr fixed Rutherford’s model by adding special rules to it:
- Electrons move in fixed circular paths called orbits or energy levels
- Each orbit has a fixed energy - electrons don’t lose energy while in these orbits
- Electrons can jump from one orbit to another by absorbing or releasing energy
- Energy is released as light when electrons jump to lower orbits
Bohr’s Equation for Hydrogen:
Energy of electron in nth orbit: E = -13.6/n² eV
Successes of Bohr’s Model:
- Explained the hydrogen spectrum perfectly
- Introduced the concept of quantized energy levels
- Explained why atoms are stable
Limitations of Bohr’s Atomic Model:
- Only worked for hydrogen
- Assumed electrons move in perfect circles
Read more: Bohr’s Model of the Atom
Towards a Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
Ahead of Bohr’s atomic model, Werner Heisenberg and de Broglie first talked about a more stable atomic model and moved towards a quantum mechanical model of the atom, and developed:
- Wave Nature of Matter, and
- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Wave Nature of Matter
Louis de Broglie suggested that if light can behave like particles (photons), then particles like electrons might behave like waves.
de Broglie Equation:
λ = h/mv
Where:
- λ (lambda) = wavelength
- h = Planck’s constant
- m = mass of particle
- v = velocity of particle
This means electrons have wave-like properties!
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle (1927)
Werner Heisenberg discovered that you cannot know both the exact position and exact speed of an electron at the same time.
Uncertainty Principle:
Δx × Δp ≥ h/4π
For atoms, this means:
We can’t talk about electrons following exact paths. Instead, we talk about probability - where an electron is likely to be found.
Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
Based on Newton’s law of motion, we can identify the microscopic object, such as planetary movements, but it doesn’t work when we talk about electrons, atoms, and molecules. To identify such objects, the quantum mechanics model of the atom comes into play as it works on concepts like the dual wave nature and the uncertainty principle.
Principal Quantum Number (n)
The principal quantum number tells you which energy level or shell the electron is in
Values: n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7…
Also called: K, L, M, N, O, P, Q shells
- n = 1 is closest to the nucleus (lowest energy)
- Higher n means farther from the nucleus and higher energy
- Maximum electrons in shell = 2n²
Azimuthal Quantum Number (l)
The azimuthal quantum number tells the shape of the orbital and sublevel.
Values: l = 0, 1, 2, 3… up to (n-1)
Letters used: s, p, d, f for l = 0, 1, 2, 3
Orbital shapes:
- s orbitals (l = 0): Spherical (like a ball)
- p orbitals (l = 1): Dumbbell-shaped
- d orbitals (l = 2): More complex shapes
- f orbitals (l = 3): Very complex shapes
For each value of n:
n = 1: only s (l = 0)
n = 2: s and p (l = 0, 1)
n = 3: s, p, and d (l = 0, 1, 2)
n = 4: s, p, d, and f (l = 0, 1, 2, 3)
Shapes of Atomic Orbitals
s Orbitals
- Shape: Spherical (like a ball)
- Number: 1 in each shell
- Electrons: Maximum 2
- Examples: 1s, 2s, 3s, 4s…
Characteristics of s-orbital:
- 1s is smallest, 2s is bigger, 3s even bigger
- All are centered at the nucleus
- Higher s orbitals have more complex internal structure (nodes)
p Orbitals
- Shape: Dumbbell-shaped
- Number: 3 in each set (px, py, pz)
- Electrons: Maximum 6 (2 in each orbital)
- Start from: n = 2
Characteristics of p-orbital:
- Three p orbitals are perpendicular to each other
- px points along x-axis, py along y-axis, pz along z-axis
- All have the same energy in isolated atoms
d Orbitals
- Shape: More complex (cloverleaf and others)
- Number: 5 in each set
- Electrons: Maximum 10 (2 in each orbital)
- Start from: n = 3
Names: dxy, dxz, dyz, dx²-y², dz²
f Orbitals
- Shape: Very complex
- Number: 7 in each set
- Electrons: Maximum 14 (2 in each orbital)
- Start from: n = 4
Electronic Configuration of an Atom
Electronic configuration tells us how electrons are arranged in different orbitals of an atom.
Rules for Filling Orbitals
- Aufbau Principle (Building Up)
Electrons fill orbitals starting from the lowest energy level.
Energy order: 1s < 2s < 2p < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p < 5s < 4d < 5p < 6s < 4f < 5d < 6p…
- Pauli Exclusion Principle
No two electrons in an atom can have all four quantum numbers the same.
- Hund’s Rule (Bus Seat Rule)
Electrons prefer to occupy empty orbitals before pairing up.
Revision Notes for Class 11 Chemistry
Here you can check the Class 11 chemistry notes for other chapters:
| Thermodynamics Class 11 Notes |
|
| Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 Notes |
|
| Hydrogen Class 11 Notes |
|
| States of Matter Class 11 Notes |
The s-Block Element Class 11 Notes |
| Organic Chemistry – Some Basic Principles and Techniques Class 11 Notes |
The p-Block Element Class 11 Notes |
| Environmental Chemistry Class 11 Notes |
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Chemistry
About the Content Reviewer
Structure of Atom FAQs
Commonly asked questions
What is the structure of atom class 11?
The structure of an atom reflects how the atom is made, which includes the nucleus at the centre where protons and neutrons are present, and electrons revolving around the nucleus.
What is the JJ Thomson model of the atom class 11?
JJ Thomson's model of the atom proposed that an atom is like a sphere (pudding) and electrons are spread around it like a plum or chocolate chips. Basically atom is overall neutral.
Who discovered electrons?
JJ Thomson, through the cathode ray tube experiment, discovered electrons. He passes the electricity from the tube and sees rays coming from the negative end. These are tiny negatively charged particles, he named them electrons.
Chemistry Structure of Atom Exam
Student Forum
Other Topics under this Chapter
- Isotope Meaning
- Mole Concept
- What are Electrons
- Isotopes and Isobars
- What is a Saturated solution
- Difference between Atom and Ion
- Discovery of Sub Atomic Particles
- Atomic Models
- Developments Leading to Bohr's Model of Atom
- Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
- Bohr's Model of Hydrogen Atom
- Towards Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
- Structure of Atom
Other Class 11th Chemistry Chapters
- Chemistry Chemical Equilibrium
- Chemistry Structure of Atom
- Chemistry Redox Reactions
- Chemistry Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chemistry Organic Chemistry
- NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
- Chemistry Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chemistry Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chemistry Hydrocarbon
- Chemistry Thermodynamics
Popular Courses After 12th
Exams accepted
CA FoundationExams accepted
ICSI ExamExams accepted
BHU UET | GLAET | GD Goenka TestBachelor of Business Administration & Bachelor of Law
Exams accepted
CLAT | LSAT India | AIBEExams accepted
IPMAT | NMIMS - NPAT | SET
Exams accepted
BHU UET | KUK Entrance Exam | JMI Entrance ExamBachelor of Design in Animation (BDes)
Exams accepted
UCEED | NIFT Entrance Exam | NID Entrance ExamBA LLB (Bachelor of Arts + Bachelor of Laws)
Exams accepted
CLAT | AILET | LSAT IndiaBachelor of Journalism & Mass Communication (BJMC)
Exams accepted
LUACMAT | SRMHCAT | GD Goenka Test