Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a)
Moment of Inertia of the man-platform system = 7.6 kg-m2
Moment of inertia when the man stretches his hands to a distance 90 cm
= 2 x mr2 = 2 x 5 x (0.9)2 = 8.1 kg-m2
Initial moment of inertia of the system, = 7.6 + 8.1 = 15.7 kg-m2
Angular speed = 30 rev/min
Angular momentum, = = 15.7 x 30 …… (i)
Moment of inertia when the man folds his hands to a distance of 20 cm
= 2 x mmr2= 2 x 5 x (0.2)2 = 0.4 kg-m2
Final moment of inertia, = 7.6 + 0.4 = 8 kg-m2
Final angular speed = and final angular of momentum, = = 8 …… (ii)
From the conservation of a
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
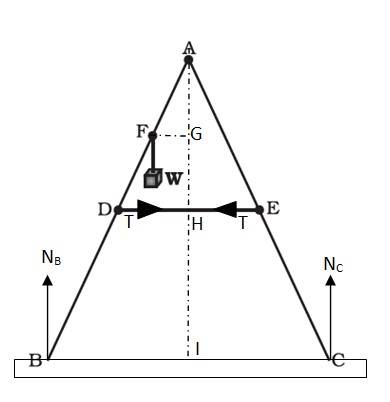
The given situation can be shown as
NB = force exerted on the ladder by the floor point B
NB = force exerted on the ladder by the floor point B
T = Tension in the rope
BA = CA = 1.6 m, DE = 0.5 m and BF = 1.2 m
Mass of the weight, m = 40 kg
The perpendicular drawn from point A on the floor BC, this intersects DE at mid-point H.
Δ ABI and ΔACI are congruent. Therefore BI = IC, I is the mid-point of BC. DE is parallel to BC.
BC = 2 x DE = 1 m and AF = BA – BF = 0.4 m…… (i)
D is the mid-point of AB, hence we can write
AD = (1/2) x BA = 0.8 ……. (ii)
Using equation (i) and (ii), we get FE = 0.4 m
Hence, F is the mid-point of AD.
Hence G will
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
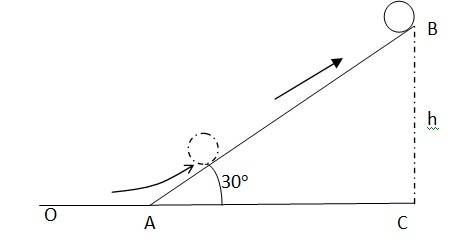
Initial velocity of the cylinder, v = 5 m/s
Angle of inclination, = 30
Height reached by the cylinder = h
Energy of the cylinder at point A:
KE rot + KEtrans
(1/2) I + (1/2) m
Energy of the cylinder at point B = mgh
Using the law of conservation of energy
(1/2) I + (1/2) m = mgh
Moment of inertia of the solid cylinder I = (1/2) mr2
Hence (1/2)(1/2)mr2 + (1/2) m = mgh
We also know v = r
(1/4)m + (1/2) m = mgh
(3/4) = gh
h = (3/4)( = (3/4)(25/9.81) = 1.91 m
In Δ ABC, = , AB = BC / = 3.82 m
Hence the
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5. (i) A = {1, 3, 5, 7, …}
(ii) B = {0,1,2,3,4} (as =4.5 and = –0.5)
(iii) x2 ≤ 4
x2 ≤ 22
x ≤ ± 2
So, C = {–2, –1,0,1,2}
(iv) D = {L, O, Y, A}
(v) E = {February, April, June, September, November}
(vi) F = {b, c, d, f, g, h, j}
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mass of the oxygen molecule, m = 5.30 * 10-26 kg
Moment of inertia, I = 1.94*10-46 kg m2
Velocity of the oxygen molecule, v = 500 m/s
the separation of atoms in oxygen molecule = 2r.
the mass of each oxygen atom = (m/2)
Moment of inertia I can be calculated as I = (m/2)r2 + (m/2)r2
hence r =
r = sqrt (1.94*10-46 / 5.30 * 10-26 = 6.05 x 10-11
It is given that KErotation = KEtranslation
(1/2)I = (2/3) (1/2)mv2
= (v/r)
= 6.8 x 1012 rad/s
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Radius of the hoop, r = 2 m, mass of the hoop, m = 100 kg, velocity of the hoop, v = 20 cm /s = 0.2 m/s
Total energy of the hoop = Translational KE + Rotational KE = m +
Moment of inertia about the centre, I = mr2
So the total energy = m +
Since v = r we get
Total energy = m + =
Required work to be done = 100 x 0.2 x 0.2 J = 4 J
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4. (i) {3,6,9,12}= {3 * 1, 3 * 2, 3 * 3, 3 * 4}
= {x : x = 3n, n is natural number and 1≤ n ≤ 4}
(ii) {2,4,8,16,32}= {21, 22, 23, 24, 25}
= {x : x = 2n, n is natural number and 1 ≤ n ≤ 5}
(iii) {5,25,125,625}= {51, 52, 53, 54}
= {x : x = 5n, n is natural number and 1 ≤ n ≤ 4}
(iv) {2,4,6, }= {2 * 1, 2 * 2, 2 * 3, …}
= {x : x = 2n, n is a natural number}
(v) {1,4,9, …, 100}= {12, 22, 32, …, 102}
= {x : x = n2, x is a natural number and 1 ≤ n ≤ 10}
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(a) Let the mass of the sphere = m
Height of the plane = h
Velocity of the sphere at the bottom of the plane = v
At the top of the plane, the total energy of the sphere = potential energy = mgh
At the bottom of the plane, the sphere has both translational and rotational energies.
Hence, total energy = (1/2)mv2 + (1/2)I
Using the law of conservation of energy, we can write: (1/2)mv2+ (1/2)I = mgh …(1)
For a solid sphere, the moment of inertia, I = (2/5)mr2
The equation (1) becomes (1/2)mv2 + (1/2)( (2/5)mr2 = mgh
(1/2) v2 + (1/5)r2 = gh
From the relation v = , we get
(1/2) v2+ (1/5) v2= gh
v =
Since v depends on
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers