Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.19 Given, the mass of the trolley, = 300 kg, mass of the sand bag, = 25 kg, uniform velocity of the trolley, v = 27 kmph = 0.75 m/s
Since there is no external force acting on the system, the speed of the trolley will remain unchanged even after entire sand is empty. 27 kmph is the answer.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.18 The length of the pendulum, l = 1.5 m
The potential energy of the bob at horizontal position = mgl
Since it dissipates 5% of its kinetic energy to come to the horizontal position, from the law of conservation of energy we get,
= (0.95)
= 2
v = 5.287 m/s
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
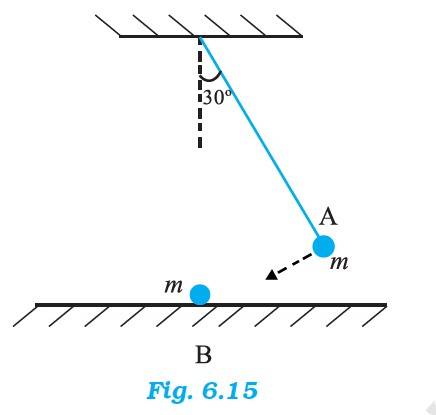
6.17 In an elastic collision, when the ball A will hit the ball B, A comes to rest immediately and the ball B acquires the velocity of ball A. The momentum thus gets transferred from a moving body to a stationary body.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
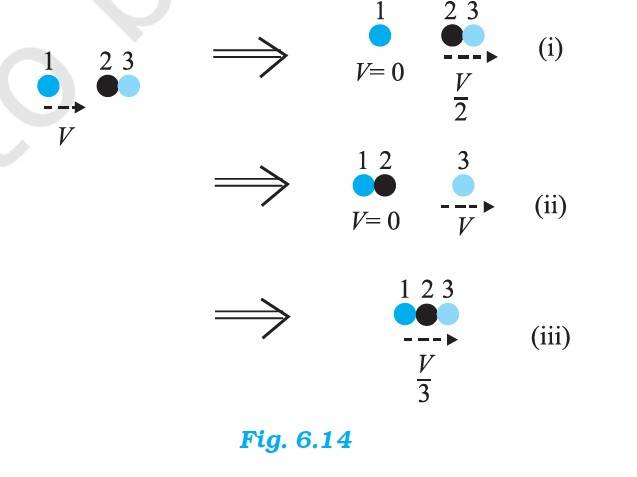
6.16 The mass of the ball bearing = m
Before the collision, the total K.E. of the system = K.E. of the stationary ball bearing + K.E. of the striking ball bearing = 0 +
After the collision, the K.E. of the total system is
(a) Case (i) = 0 + =
(b) Case (ii) = 0 +
(c) Case (iii) = =
Case (ii) is possible since K.E. is conserved in this case.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.15 Given, the volume of the tank, V = 30
Time required to fill the tank, t = 15 min = 900 s
Height of the tank above the ground, h = 40 m
The efficiency of the pump? = 30%
The density of water, = kg/
Now, the mass of the water pumped, m = = 30 kg = 3 kg
Power consumed = W/t = mgh/t = 3 40 / 900 = 13066 W
P input = Power consumed /? = 43.6 kW
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.14 Momentum is always conserved for an elastic or inelastic collision.
The molecule's initial velocity, u = final velocity v = 200 m/s
Initial kinetic energy = (1/2)m
Final kinetic energy = (1/2)m = (1/2)m
Therefore, kinetic energy is also conserved
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.13 The radius of the rain drop = 2 mm = 2 m
The height of drop, s = 500 m
Density of water, = kg/
Mass of the rain drop = volume = (4/3) = 3.35 kg
The gravitational force on the raindrop, F = mg = 3.28 N
Work done by the gravity on the drop is = mgs where s = 250 m
Work done = 0.082 J
The work done during the second half will remain same.
The total energy of the raindrop will be conserved during the motion.
Total energy at the top
E1 = mgh where h = 500 m, E1 = 0.164 J
Due to resistive force, the energy of the drop on reaching the ground
E2 = (1/2)mv2 where
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.12 Electron mass, me = 9.11*10-31 kg
Proton mass, madhya pradesh = 1.67*10–27 kg
Electron's kinetic energy = 10 keV = 10 1.60 *10–19 J = 1.60 *10–15 J
Proton's kinetic energy = 100 keV = 100 1.60 *10–19 J = 1.60 *10–14 J
The electron kinetic energy is given by Eke = (1/2)m where is the velocity of electron
= { (2 Eke )/m} = 5.92 m/s
The velocity of proton = { (2 Pke )/m} = 4.37 m/s
The speed ratio = / = 13.5
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.11: Force exerted on the body, F =? +3 N
Displacement, s = 4 km
Work done, W = F.s
= (? +3
= 0+0-3
= 12 J
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
6.10 Power is given by the relation
P = Fv = mav = mv = constant ( say, k)
vdv =
v =
For displacement x of the body, we have:
v = =
dx = k' dt where k' = = constant
On integrating both sides, we get
x =
Therefore x
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers