Class 11th
Get insights from 8k questions on Class 11th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 11th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
2.3
1 Calorie = 4.2 J = 4.2 kgm2s-2
Standard formula for conversion
Given unit / New unit = (M1/M2)x (L1/L2)y (T1/T2)z
Formula for energy = M1L2T-2
Here x = 1, y = 2, z = -2
In this problem
M1 = 1 kg, L1 = 1 m, T1 = 1 s and
M2 =? kg, L2 =? m, T2 =? s
So 1 Calorie = 4.2 (1/? )1 (1/? )2 (1/? )-2
= 4.2? -1? -2? 2
New question posted
8 months agoNew question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ans.2.1
(a) The volume of a cube of side 1 is equal to
The volume of the cube = 1 cm * 1 cm * 1 cm = 1 cm3
1 cm3 = 1 * 10-6 m3
(b) The surface area of a solid cylinder of radius 2.0 cm and height 10.0 cm is equal to1.25 * 104 (mm)2
The surface area of a solid cylinder = 2? r (r+)h, where r = 2.0 cm = 20 mm, h = 10 cm = 100 mmSurface area = 2 * 22/7 * 20 * (100 +20) = 1.51 *
(c) A vehicle moving with a speed of 18 km h–1 covers 5 m in 1 s
Vehicle speed = 18 km/h = 18000/3600 m/s = 5 m/s
(d) The relative density of lead is 11.3. Its density is 11.3 g cm–3 or 11.3 * 103.kg m–3.
Relative density or
New answer posted
8 months ago
Contributor-Level 9
Ans.4.1 A scalar quantity depends only on the magnitude – volume, mass, speeds, density, number of moles, angular frequency are all scalar quantities.
A vector quantity depends on magnitude and direction – velocity, acceleration, displacement and angular velocity are all vector quantities.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
8.12
Mass of the Sun, = kg, Mass of the Earth, = kg
Orbital radius, r = m
Let the mass of the rocket be, m
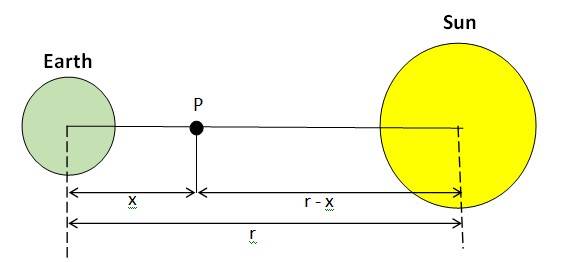
Let x be the distance from the centre of the Earth where the gravitational force acting on satellite P becomes zero.
From Newton's law of gravitation, we can equate gravitational forces acting on the satellite P under the influence of the Sun and the Earth as:
= or(
= ( = ,
= 577.35 , r = 578.35x ,
x = = 2.59 m
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ans.8.1
(a) No. Unlike electrical forces, gravitational force is independent of the status of the objects.
(b) Yes, the size of the space station is large enough and the astronaut will detect the change in Earth's gravity.
(c) Tidal effect depends inversely upon the cube of the distance while gravitational force depends inversely on the square of the distance. Since the distance between the Moon and the Earth is smaller than the distance between the Sun and the Earth, the tidal effect of the Moon's pull is greater than the tidal effect of the Sun's pull.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 8
The differences between old and modern periodic table are as follows:
| Mendeleev's Table (Old Periodic Table) | Modern Periodic Table (Long Form Table) |
| Arrangement of elements are done on atomics weights (mass) | Arrangement of elements are done on atomic number |
| Contains 66 elements | Contains 118 known elements |
| Noble Gases not mentioned in old periodic table because it was not discovered | Noble gases are included in Group 18 |
| Transistion elements were placed with other elements | Transition elements are placed in seperate block |
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 684k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
