Class 12th
Get insights from 11.8k questions on Class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
Overall charge balance in [Cr (NH3)6]3+ complex:
X + 6 (0) = + 3 X = + 3
Cr is in + 3 oxidation state.
Electronic configuration of Cr in + 2 state: 3d3 . Now ammonia is a weak field ligand so it not causes pairing of the unpaired electron and undergoes hybridisation to form 6 sp3d2 hybrid orbitals filled by the six ammonia ligands. It's geometry is octahedral with unpaired electrons and hence is paramagnetic complex.
In case of [Ni (CN)4]2– ion :
Overall charge balance in [Ni (CN)4]2–complex:
X + 4 (-1) = -2 X = + 2
Ni is in + 2 oxidation state.
Electronic configuration of Ni in + 2 state: 3d8. Now cyanide ion is a strong field ligand so i
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.2
As Physisorption is Exothermic in nature, which means when gas gets adsorbed on the solid surface, Heat is evolved. So, according to Le-Chatelieres when the temperature is an increased reverse process (Desorption) will be favoured. So, Physisorption decreases with the increase of temperature.
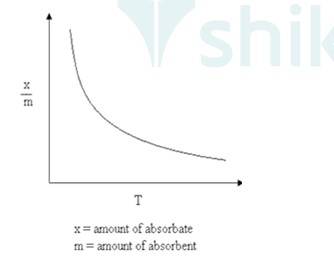
Where x/m: Volume of gas adsorbed
T: Temperature.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The difference between the energies of the two set of the d orbitals is called as crystal field splitting energy (CFSE). The degenerate d orbitals split into two levels i.e t2g and eg level due to the presence of the ligands. This splitting of the degenerate orbitals due to the ligand is called as crystal field splitting and the energy difference between the two levels is called as crystal field splitting energy.
After the splitting of the degenerate orbitals has taken place the filling of the electrons takes place. Now first 3 electrons goes into the lower energy three t2g orbitals. The fourth electron can be filled in two ways:
It can
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
The strong ligands have higher splitting power of d orbitals of the central metal ion, whereas weak ligand has relatively lower splitting power of d orbitals of the central metal ion. The energy difference between t2g and eg sets of d orbitals is CFSE. The strength of the ligands depend on the magnitude of Δ . Strong ligands have larger value of CFSE and in case of weak ligands the CFSE values are smaller. The common ligands can be arranged in a series in the order of their decreasing field strength, as follows.
This series depends on the power of splitting the d orbitals and is called spectrochemical series, The order of field s
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
5.1
The two characteristics of Chemisorption are:
1. In Chemisorption which is highly specific in nature, the adsorb ate and adsorbent get attached by chemical bonds which are either covalent or ionic in
2. High activation energy is required and high temperature is also
3. Chemisorption increases with the increase in surface area which results in more number of active
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
In octahedral complex the splitting of the d orbital will be such a way that the dx2-y2 and dz2 orbitals which face towards the axes along the direction of the ligand will experience more repulsion and will be raised in the energy and the other three orbitals which are directed between the axes are lowered in energy.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.12 2NH3 (g)? N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
Rate of zero order reaction is equal to rate constant. i.e. Rate = 2.5 * 10-4mol L-1sec-1.
According to rate law,
-d [NH3] / 2dt = d [N2] / dt
2.5 * 10-4mol L-1sec-1 = d [N2] / dt
i.e. the rate of production of N2 is 2.5 * 10-4mol L-1 sec-1.
According to rate law,
-d [NH3] / 2dt = d [H2] / 3dt
d [H2] / dt = -3 X d [NH3] / 2dt
i.e. rate of formation of H2 is 3 times rate of reaction = 3 * 2.5 * 10-4mol L-1sec-1
= 7.5 * 10-4mol L-1sec-1
Rate of formation of N2 and H2 is 2.5 * 10-4 mol L-1sec-1 and 7.5 * 10-4 mol L-1sec-1 respectively
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) In the coordination entity iron exists in + 2 oxidation state. Overall charge balance:
X + 6 (-1) = -4 X = + 2.
Its electronic configuration is: 3d6
CN- is strong field ligand so it causes pairing of the unpaired electron and undergoes hybridisation to form 6 d2sp3 hybrid orbitals to be filled by the six cyanide ions. It's geometry is octahedral with no unpaired electrons and hence is diamagnetic complex.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
CuSO4 + KCN? K2 [Cu (CN)4] + K2SO4
[Cu (H2O)4]2+ + 4CN-? [Cu (CN)4]2- + 4H2O
The coordination entity formed is K2 [Cu (CN)4] .
IUPAC name of the coordination entity is potassium tetracyanocuprate (II). It is a very stable complex. The copper atom present inside the coordination sphere does not separate out to form copper ions and cyanide ions due to strong bond between them.It does not ionize to give Cu2+ ions and hence on adding H2S, since there are no copper ions present so no precipitate of copper sulfide is formed.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
4.11 (a) Rate = k [A] [B]2, Rate = 0 * 10-6 [0.1] [0.2]2
Rate = 8 * 10-9 mol L-1sec-1
(b) 2A +B = A2B
=0.06+ 0.18 = 0.02
Situation when A remains 0.06 mol L-1
Now, According to rate law, Rate = k [A] [B]2
Rate = 2 * 10-6 [0.06] [0.18]2
i.e. Rate = 3.888 * 10-9 mol L-1sec-1
Initial rate of reaction is 8 * 10-9 mol L-1sec-1. and rate when concentration of A is 0.06 mol L-1 is 3.888 * 10-9 mol L-1sec-1.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 685k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
