Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Get insights from 170 questions on Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
R = (2μ sinθ) / (1.22λ) . (1)
According to de-Broglie's hypothesis, we can write
λ = h / (mv) . (2)
With the help of equations (1) and (2), we can write
R = (2μmv sinθ) / (1.22h) ⇒ R? /R? = m? /m? = 1837 ⇒ R? = 1837R?
- Concept involved: Resolving Power of Microscope
- Topic: Optics
- Difficulty level: Moderate
- Point of Error: Formula
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
λ? /λ? = (m? v? ) / (m? v? ) ⇒ m? = m? (v? /v? ) (λ? /λ? ) = m? (1/4) (1/2) = (1/8)m?
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
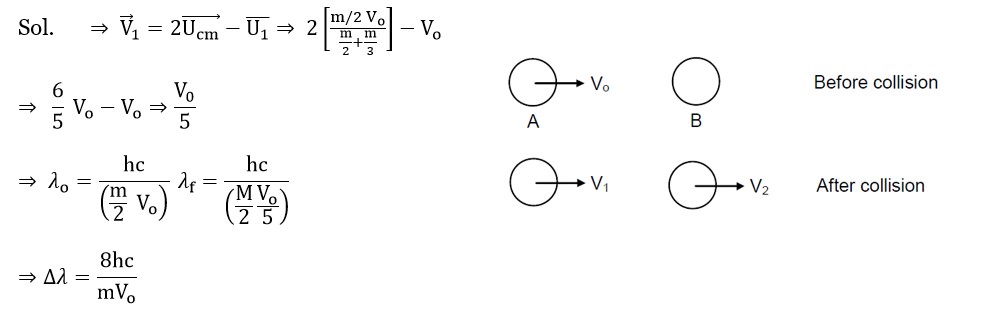
The equation representing the photoelectric effect is given as:
(1/2)mv? ² = hf? - φ . (1)
This continues the solution from number 6 on the previous page.
(1/2)mv? ² = hf? - φ . (2)
With the help of equations (1) and (2), we can write:
v? ² - v? ² = (2h/m) (f? - f? )
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
The relationship between the de Broglie wavelengths of an electron (λe) and a photon (λp) is derived as follows:
For an electron: λe = h / mv = h / √ (2mE)
For a photon: λp = h / p = hc / E
Taking the ratio of the wavelengths squared:
(λe / λp)² = [h / √ (2mE)]² / [hc / E]²
(λe / λp)² = (h² / 2mE) * (E² / h²c²)
(λe / λp)² = E / 2mc²
(λe / λp) = (1/c) * √ (E / 2m)
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
de-Broglie wavelength
λ = h/mv = h / √ (3kT/m * m) = h / √ (3mkT)
λ = (6.63 * 10? ³? ) / √ (3 * 4.64 * 10? ²? * 1.38 * 10? ²³ * 400)
λ = (6.63 / 2.77) * 10? ¹¹ = 2.39 * 10? ¹¹ m ≈ 0.24Å
New answer posted
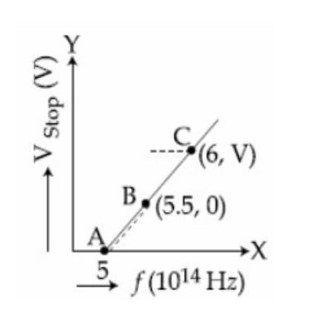
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
eVs = hv – φ
At Vs = 0 ⇒ hv = φ
⇒ φ = [6.62 * 10?³?][10¹?][5.5]
⇒ φ = ([6.62 * 10?³?][10¹?][5.5]eV) / [1.6 * 10?¹?]
= 2.27
New answer posted
4 months agoTaking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers