Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Get insights from 90 questions on Mechanical Properties of Fluids, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Soap bubble radius, r = 5.0 mm = 5 m
Surface tension of the soap bubble, S = 2.50 N/m
Relative density of soap solution = 1.20, hence density of soap solution, = 1.2 Kg/
Air bubble formed at a depth, h = 40 cm = 0.4 m
1 atmospheric pressure = 1.01 Pa
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/
We know, the excess pressure inside the soap bubble is given by the relation:
P = = Pa = 20 Pa
Hence, the excess pressure inside the air bubble is given by the relation, P' = = 10 Pa
At a depth of h, the total pressure inside the air bubble = Atmospheric press
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Radius of the mercury droplet, r = 3.00 mm = 3 m
Surface tension, S = 4.65 N/m
Atmospheric pressure, = 1.01 Pa
Total pressure inside the mercury drop = Excess pressure inside mercury + Atmospheric pressure
= + = + 1.01 = 1.01310 Pa
Excess pressure inside mercury = = = 310 Pa
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
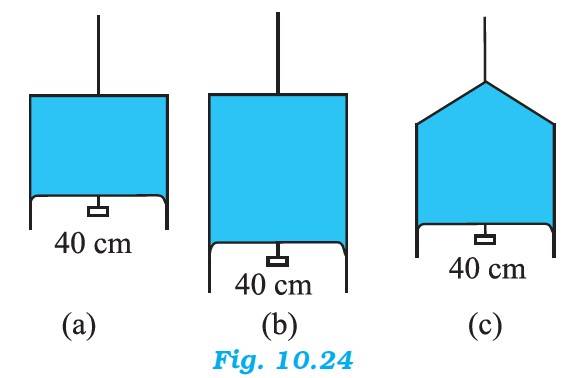
The length of the liquid film supported by the weight, l = 40 cm = 0.4 m
The weight supported by the film, W = 4.5 N
Since a liquid film has two free surfaces,
Surface tension = = = 5.625 N/m
In all 3 figures, the liquid is the same, temperature is also the same. Hence the surface tension in (b) and (c) are also going to be the same, with the value of 5.625 N/m and weight supported in each case is also going to be the same, since length of the film is same.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
The weight that the soap film supports, W = 1.5 N
Length of the slider, l = 30 cm = 0.3 m
A soap film has two free surfaces, hence total length = 2l = 0.6 m
Surface tension, S= = = 2.5 N/m
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Area of cross-section of the spray pump, = 8 = 8
Number of holes, n = 40
Diameter of each hole, d = 1 mm = 1 m
Radius of each hole, r = d/2 = 0.5 m
Area of cross-section of each hole, a = =
Total area of 40 holes, = 40 = 3.14
Speed of liquid inside the tube, = 1.5 m/min = 0.025 m/s
Speed of ejection of liquid =
According to law of continuity, we have = or =
= 0.637 m/s
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
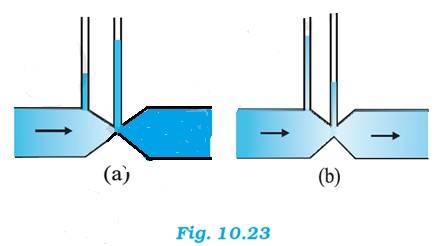
Take the case given in figure (b)
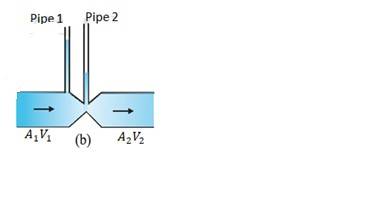
= Area of pipe 1, = Area of pipe 2, = Speed of fluid in pipe 1, = Speed of fluid in pipe 2
From the law of continuity, we have
=
When the area of cross-section in the middle of the venturimeter is small, the speed of the flow of liquid through this part is more. According to Bernoulli's principle, if speed is more, the pressure is less. Pressure is directly proportional to height, hence the level of water in pipe 2 is less. Therefore, figure (a) is not possible.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Speed of the wind on the upper surface of the wing, = 70 m/s
Speed of the wind on the lower surface of the wing, = 63 m/s
Area of the wing, A = 2.5
Density of air, = 1.3 kg/
According to Bernoulli's theorem, we have the relation:
+ = +
( - )= - , where = pressure on the upper surface of the wing and - pressure on the lower surface of the wing
The pressure difference provides lift to the aeroplane
Lift on the wing = ( - )A = - A = - N =
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Length of the horizontal tube, l = 1.5 m
Radius of the tube, r = 1 cm = 0.01 m
Diameter of the tube, d = 2r = 0.02m
Glycerine mass flow rate, M = 4 kg/s
Density of glycerine, = 1.3 kg
Viscosity of glycerine, = 0.83 Pa-s
Now, volume of glycerine flowing per sec V = = /s = 3.08 /s
According to Poiseville's formula, we know the flow rate
V = where p is the pressure difference between two ends of the tube
p = = = 976.47 Pa
Reynolds's number is given by the relation
Re = = = 0.3
Since the Reynolds's number is 0
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
It does not matter if one uses gauge pressure, instead of absolute pressure while applying Bernoulli's equation. There should be significantly different atmospheric pressures, where Bernoulli's equation is applied.
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
No, Bernoulli's equation cannot be used to describe the flow of water through a rapid in a river. In rapid, the flow is turbulent whereas Bernoulli's equation is applicable for laminar flow only.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers