Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Get insights from 90 questions on Mechanical Properties of Fluids, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Consider the diagram.
Let the density of water be and a cubical block of ice of side L be floating in water with x of its height L submerged in water.
Volume of the block V = L3
Mass of the block m = V =L3
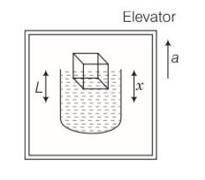
Weight of the block = mg= L3
1st case
Volume of the water displaced by the submerged part of the block= xL2
Weight of the water displaced by the block
In floating condition, x L2
Weight of the block= Weight of the water displaced by the block
L3 = xL2
2nd case
When elevator is accelerating upward with an acceleration a, then effective acceleration
= (g+a)
Then, w
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
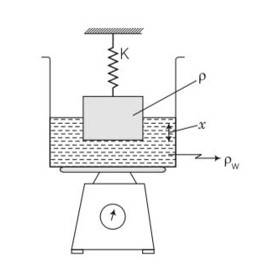
Consider the diagram,
The scale is adjusted to zero, therefore, when the block suspended to a spring is immersed
In water, then the reading of the scale will be equal to the thrust on the block due to water.
Thrust= weight of water displaced
=V wg (where V is volume of the block and w is density of water)
= =
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Given density of ice i = 0.917 g cm-3
Density of water 3
Let V be the total volume of iceberg and V' of its volume be submerged in water.
In floating condition
Weight of the iceberg= weight of the water displaced by the submerged part by ice
V ig = V' g
=
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
No surface tension is a scalar quantity.
Surface tension = work done/ surface area, where work done and surface area both are scalar quantities.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a short answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Viscosity is a property of liquid it does not have any direction hence it is scalar quantity.
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Let the pressure inside the ballon be P1 and the outside pressure be Po, then excess pressure is Pi-Po =2S/r
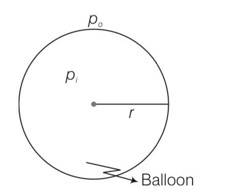
Considering the air to be an ideal gas piV = niRTi = where, V is the volume of the air inside the balloon, ni is the number of moles inside and Ti is the temperature inside, and poV =noRTo where V is the volume of the air displaced and no is the number of moles displaced and To is the temperature outside.
So ni=
Where Mi is the mass of air inside and MA is the molar mass of air
no=
if w Is the load it can raise then w+M1g=Mog
as atmosphere 21% O2 and 79%N2 is pres
New answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) Lv=540 kcal kg-1
= 540 kg-1 = 540 4.2jkg-1
Energy required to evaporate 1kg of water = Lv kcal
And MA kg of water requires MALV kcal
Since there are NA molecules in MA kg of water the energy required for 1 molecule to evaporate
Is
U=
=
=90
= 6.8
(b) Let the water molecules to be points and are separated at a distance d from each other
volume of NA molecule of water =
thus the volume of one molecule is =
the volume around one molecule is d3=
d=
d= 3.1
(c) 1 kg of vapour occupies volume =1601 m3
18 kg of vapour occupies 18 m3
6 molecules occupies 18 m3
1 mo
New question posted
8 months agoNew answer posted
8 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a long answer type question as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a) consider a horizontal parcel of air with cross section A and height dh
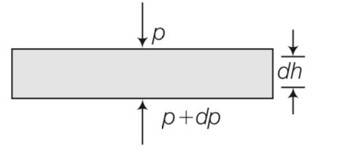
Let the pressure on the top surface and bottom surface be P and p+dp. If the parcel is in equilibrium , then the net upward force must be balanced by the weight
(P+dP)-PA=-
dP= -
negative sign shows that pressure decreases with height.
(b) let o be the density of air on the surface of earth.
As per question , pressure density
dP= -
In
P=Poe(- )
(c) as P =Po
in
p=1/10 Po
in( ) =-
in1/10 =-
h=- in1/10= - -1=
=
=
= 16 103m
(d) we know that
P , temperature remain
New answer posted
9 months agoContributor-Level 10
Volume of the balloon, V = 1425
Mass of the payload, m = 400 kg
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/
= 8000 m
= 0.18 kg m–3
= 1.25 kg m–3
Density of the balloon =
Height to which the balloon will rise = y
Density of air decreases with height and the relationship is given by:
= ……(i)
Differentiating equation (i), we get
, where k is the constant of proportionality
, height changes from 0 to y, while density changes from to . Integrating both sides between the limits, we get:
= -ky
= ….(ii)
From equation (i) and (ii), we get
=&nbs
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers
