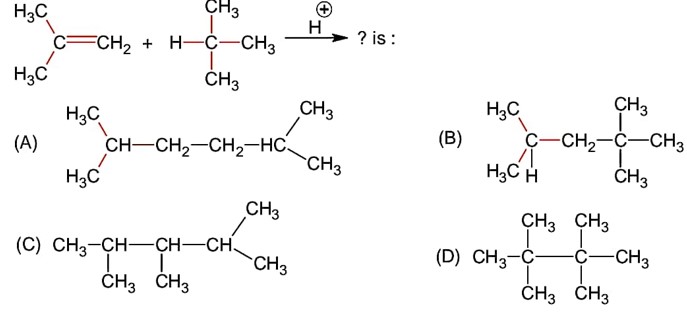
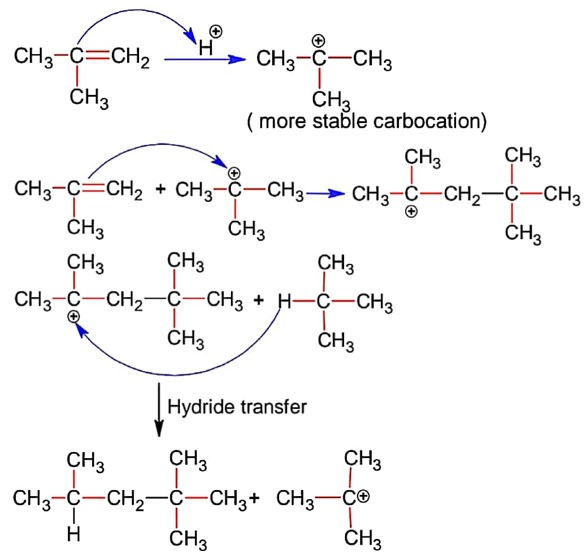
NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
Get insights from 15 questions on NCERT Class 11 Chemistry, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about NCERT Class 11 Chemistry
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
3 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Shiksha provides NCERT Notes for all class 11 and 12 important topics. We have covered all concepts in detail. You can check the key characteristics below;
- We have covered the topic-wise NCERT Notes of all NCERT textbook chapters, including deleted topics and chapters.
- These NCERT Notes are prepared keeping in mind the CBSE Exam pattern and CBSE syllabus 2025-2026.
- We have designed these NCERT Notes as revision notes along with a concise summary.
- You will also get the NCERT-based definition and derivation along with basic problem-solving techniques.
- We have also included solved JEE and NEET questions for holis
New answer posted
4 months agoBeginner-Level 5
The valence bond theory explains the covalent bond formation for two half-filled orbitals. The bond strength depends on several factors, including the extent of overlap of the two atomic orbitals. The bond strength is directly proportional to the extent of overlap.
In simple words, the greater the amount of overlap between two orbitals, the stronger the covalent bond will be.
JEE asks many questions based on the comparison of bond strength for two different pairs of atomic orbitals forming a covalent bond. For example, why H–F bond stronger than the F–F bond?
New answer posted
4 months agoBeginner-Level 5
The concept of delocalization or resonance can be explained for quantum mechanical atomic models in which electrons are considered to be spread over the entire molecular orbital.
The fundamental assumption of the valence bond theory contradicts the delocalization. The valence bond theory assumes that a covalent bond forms from the overlap of atomic orbitals on adjacent atoms, and electron density is localized between two specific nuclei.
That is why VBT cannot explain energy stabilization due to the resonance property.
New answer posted
4 months agoBeginner-Level 5
As you know, electrovalent bonds result very strong electrostatic attraction force. All the factors that help maximize this electrostatic attraction are important for the formation of the ionic bond. Here are the important factors;
- Low ionization energy Metal
- High electron affinity Non Metal
- Large-sized cations
- Small-sized anions
- Electronegativity equal to or greater than 1.7
New answer posted
4 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Covalent and electrovalent bonding are the two major chemical bonding processes. These two bonds are different from each other in multiple aspects. Check the table below to know a concise summary of the differences.
| Particular | Covalent Bond | Ionic Bond |
| Formation | Due to the complete transfer of electrons | Due to the sharing of electron pairs |
| Ion formation | No ions formed | Cations and Anions formed. |
| Nature | Electrostatic attraction between ions | Electrostatic attraction between nuclei and shared electrons |
| Strength | Strong | Less strong |
| Melting/Boiling point | High due to a strong bond | lower due to weaker bond |
| Polarity | Highley Polar | Non-Polar |
New answer posted
5 months agoBeginner-Level 5
You can find complete study material for class 11th at Shiksha.com. We have compiled notes, solutions, and question papers for CBSE exams. We also offer complete JEE and NEET study material based on NCERT books. Access the table below.
New answer posted
5 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Yes! The NCERT Notes are more than enough to get full marks in the board exams. You want to know why these notes are enough?
- NCERT revision notes cover each chapter in clear, easy-to-read summaries along with detailed concepts.
- These notes cover the entire CBSE syllabus in simple language, including important definitions, formulas, and examples for the exams.
- Our subject matter experts have designed information in a genuine and concise way.
- These notes are perfect guides for both quick revision and thorough conceptual understanding.
New answer posted
5 months agoBeginner-Level 5
The reason why bond angle is larger in than are given below.
- In , there is one lone pair on the nitrogen atom increases repulsion, while the lone pair on phosphorus is in a higher energy orbital and causes less repulsion.
- Nitrogen is a small and electronegative atom whereas phosphorus is larger and less electronegative than nitrogen.
- In , the bonding orbitals are nearly pure p-orbitals, which are less directionals–p hybridization, on the other hand, the bond pairs remain fairly directed, leading to a larger bond angle.
Hence, the bond angle in is about 107° ( less than the ideal tetrahedral 109.5°) due to lone pair pres
New answer posted
5 months agoBeginner-Level 5
Molecules usually form chemical bond through either sharing or through rtransfering the electrons. During covalent bonding the electron pairs shared between atoms to form covalent bond are called shared pair or bond pair. At the same time, the electron pair which is not involved in sharing is called lone pair of electrons.
For example: CH4 has 4 bond pairs but H2O has 2 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs.

Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers