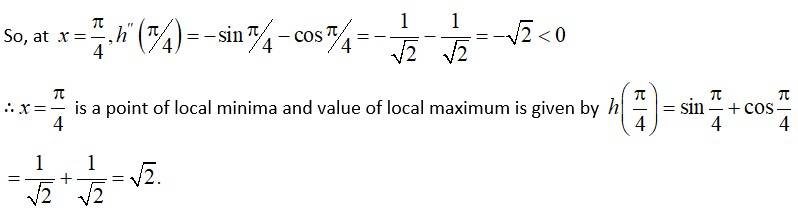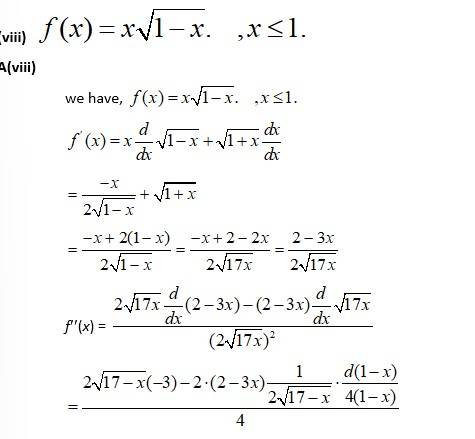Ncert Solutions Maths class 12th
Get insights from 2.5k questions on Ncert Solutions Maths class 12th, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Ncert Solutions Maths class 12th
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have, f (x) =2x3- 24x + 107, x [1,3]
f (x) = 6x2- 24.
At f (x) = 0
6x2- 24= 0
x = ±2. ->x = 2 ∈ [1, 3].
So, f (2) = 2 (2)3- 24 (2) + 107 = 16 - 48 + 107 = 75.
f (1) = 2 (1)3- 24 (1) + 107 = 2 - 24 + 107 = 85.
f (3) = 2 (3)3- 24 (3) + 107 = 54 - 72 + 107 = 89
∴ Maximum value of f (x) in interval [1, 3] is 89 at x = 3.
When x ∈ [ -3, -1]
From f (x) = 0
x = -2 ∈ [ -3, -1]
So, f (- 2) = 2 (- 2)3- 24 (- 2) + 107 = - 16 + 48 + 107 = 139.
f (- 3) = 2 (- 3)3- 24 (- 3) + 107 = - 54 + 72 + 107 = 125.
f (- 1) = 2 (- 1)3- 24 (- 1) + 107 = - 2 + 24 + 107 = 129.
∴ Maximum value of f (x) in interval [ -3, -1] is 139 at x = -2.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have, f (x) = sin x + cos x.
f (x) = cos x - sin x.
At f (x) = 0
cosx - sin x = 0
sinx = cos x
At ,
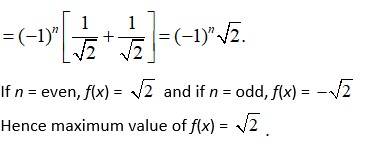
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have, f(x) = sin 2x, x ∈ [0, 2π],
f(x) = 2cos 2x.
At f(x) = 0.
2 cos 2x = 0
cos 2x = 0
.
= 1.
= 1.
f(0) = sin 2(0) = sin 0 = 0
f(2π) = sin 2(2π) = sin 4π = 0
Hence, the points of maximum
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have, f (x) = 3x4- 8x3 + 12x2- 48x + 25, x ∈ [0, 3].
f (x) = 12x3- 24x2 + 24x - 48.
At f (x) = 0.
12x3- 24x2 + 24x - 48 = 0.
x3- 2x2 + 2x - 4 = 0
x2 (x - 2) + 2 (x - 2) = 0
(x - 2) + (x2 + 2) = 0
x = 2 ∈ [0, 3] or x = which is not possible as
∴f (x) = 3 (2)4- 8 (2)3 + 12 (2)2- 4 (2) + 25.
=48 - 64 + 48 - 96 + 25.
= -39.
f (0) =3 (0)4- 8 (0)3 + 12 (0)2- 48 (0) + 25.
= 25.
f (3) = 3 (3)4- 8 (3)3 + 12 (3)2- 48 (3) + 25.
= 243 - 216 + 108 - 144 + 25
= 16.
Maximum value of f (x) = 25 at x = 0.
and minimum value of f (x) = -39 at x = 2.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
We have, p (x) = 41 -f2x - 18x2.
P (x) = - 72 - 36x
P (x) = -36
At extreme point,
- 72 - 36x = 0
.
At x = - 2, p" (x) = - 36 < 0.
∴x = -2 is a point of local maximum and the value of local
Maximum is given by P (2) = 41 - 72 (- 2) - 18 (- 2)2
41 + 144 - 72 = 113 units.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) We have,
f(x) = x3 , x ∈ [– 2, 2].
f(x) = 3x2.
At, f(x) = 0
3x2 = 0
x = 0 <--[-2, 2].
We shall absolute the value of f at x = 0 and points of interval [ -2, 2]. So,
f(0) = 0
f(- 2) = (- 2)3 = 8
f(2) = 23 = 8.
∴ Absolute maximum value of f(x) = 8 at x = 2
and absolute minimum value of f(x) = -8 at x = -2.
(ii) f (x) = sin x + cos x , x ∈ [0, π]
A.(ii)
We have, f(x) = sin x + cos x , x ∈ [0, π]
f(x) = cos x - sin x.
atf(x) = 0
cosx - sin x = 0
sinx = cos x
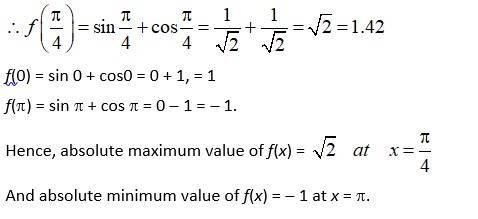
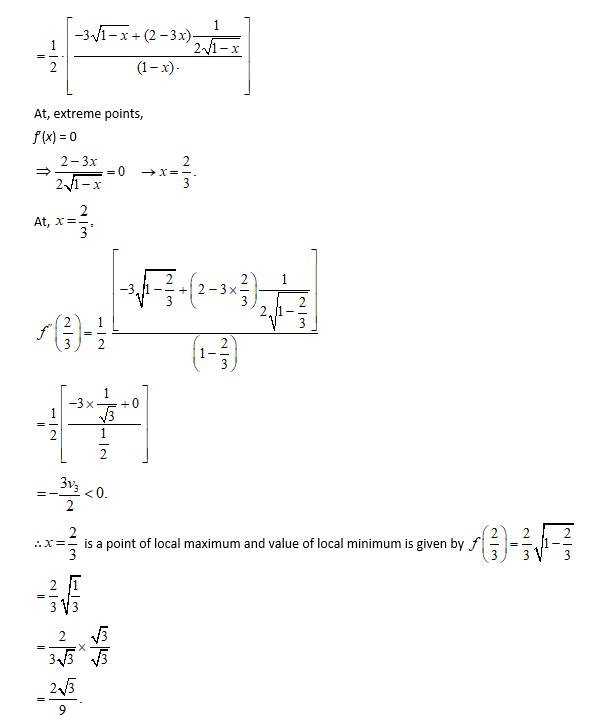
(iii) f(x) = 4x
A.(iii)
We have, f(x) = 4x
f(x) = 4 - x
atf(x) = 0
4- x = 0
x = 4
= 7.87.5
Hence, absolute maximum value of f(x) = 8 at x = 4
and absolute minimum value of f(
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) We have, f (x) = ex
f (x) = ex.
At, extreme points,
f (x) = 0
ex = 0 which has no real 'a' value
∴f (x) has with maximum or minima
(ii) g (x) = log x
A (ii)
We have, g (x) = log x,
g (x) =
At extreme points,
g (x) = 0
1 = 0 which is not true.
∴g (x) was value minima or maxima
(iii) h (x) = x3 + x2 + x + 1.
A (iii)
We have, h (x) = x3 + x2 + x + 1.
h (x) = 3x2 + 2x + 1
At extreme points,
h (x) = 0
3x2 + 2x + 1 = 0
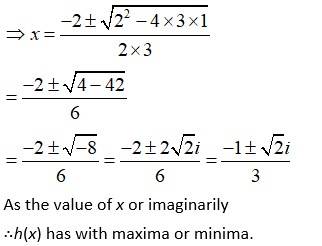
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) we have, f(x) = x2.
f(x) = 2x.
andf(x) = 2.
AR extreme point, f(x) = 0
2x = 0
x = 0.
When x = 0, f(0) = 2 > 0.
∴x = 0 is a point of local minima and value of local minimum is given by f(0) = 02 = 0.
(ii) g(x) = x3 3x
A(ii)
we have, g(x) = x3- 3x
g'(x) = 3x2- 3
g''(x) = 6x.
At extreme point,
g'(x) = 0
3x2- 3 = 0.
3(x2- 1) = 0 ⇒ 3(x - 1)(x + 1) = 0.
x = 1 or x = -1.
At x = 1, g"(1) = 6.1 = 6 > 0.
So, x = 1 is a point of local minima and value of local minimum is given by g(1) = 13- 3.1 = 1 - 3 = - 2.
And at x = -1, g"( -1) = 6 ( -1) = 6 < 0.
So, x = -1 is a point of local minima and value of local minimum is given by
g(- 1) = (- 1)3- 3(- 1) = 1 + 3 = 2.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) we have, f(x) = |x + 2| - 1
We know that, for all
f(x)- 1.
∴ Minimum value of f(x) = -1 when x + 2 = 0 x = - 2.
And maximum value of f(x) does not exist.
(ii)
A(ii)
We have,
For all
g(x) 3.
∴ Maximum value of g(x) = 3 when
And minimum value does not exist.
(iii) h(x) = sin (2x) + 5.
A(iii)
we have, h(x) = sin (2x) + 5.
For all {range of sine function is [-1, 1]}
-1 + 5 sin 2x + 5 1 + 5.
4 h(x) 6.
∴ Maximum value of h(x) = 6.
Minimum value of h(x) = 4.
(iv)
A(iv)
we have,
As for all
-1 + 3 sin 4x + 3 1 + 3
2 f(x) 4.
∴ Maximum value of f(x) = 4.
Minimum value of f(x) = 2.
(
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
(i) We have, f(x) = (2x - 1)2 + 3.
For all
(2x - 1)2 + 3 ≥ 3.
f(x) ≥ 3.
∴The minimum value of f(x) = 3. When 2x - 1 = 0--> x =
Again as as there is vouppa bound to 'x' value hence, f(x) has no maximum values.
(ii)
A(ii)
We have, f(x) = 92 + 12x + 2.
(Taking 9 common from each team).
For all
f(x)≥ - 2.
∴The minimum value of f(x) = -2 when
And as so f(x) has
no maximum values.
(iii) f(x) = (x - 1)2 + 10
A(iii)
we have, f(x) = - (x - 1)2 + 10
For all
(x - 1)2 ≤ 0
-(x- 1)2 + 10 ≤ 10.
f(x) ≤ 10.
∴maximum value of f(x) = 10 when x - 1 = 0 x = 1.
And minimum value of f(x) does n
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 65k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 687k Reviews
- 1800k Answers