Physics Laws of Motion
Get insights from 189 questions on Physics Laws of Motion, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Laws of Motion
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
Initial velocity
Final velocity
Change in velocity
Momentum gain is along
Force experienced is along
Force experienced is in North-East direction.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
Apply conservation of momentum along y-axis, we can write
10v? - 10v? sin 30° = 0
⇒ v? = 20m/s
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
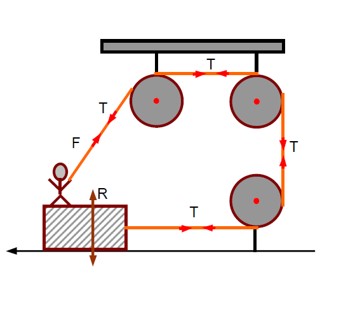
Assuming the rope in the boy's hand is vertical and using a Free Body Diagram (FBD):
f? = T
R + T = 90 ⇒ R = 90 - T
For the piece of wood not to move, f? ≤ µR:
T ≤ 0.5 (90 - T) ⇒ T ≤ 30N
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
The minimum force F? is calculated as:
F? = (μmg) / √* (1 + μ²)* = ( (1/√3) * 1 * 10 ) / √* (1 + (1/√3)²) = 5N
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
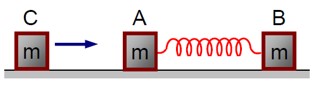
For an elastic collision where C comes to rest, and the compression in the spring is maximum, the velocities of A and B are equal (v). Using the conservation of mechanical energy:
(1/2)mv? ² = 2 * (1/2)mv² + (1/2)kx²
This gives the maximum compression x as:
x = v? * √* (m / 2k)*
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
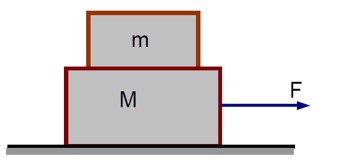
For the combined system of mass M and m, the acceleration under an applied force F is:
a = F / (M + m)
The static friction force (f_s) on the top block (m) provides its acceleration:
f_s = MA = m * [F / (M + m)] = mF / (M + m)
For the top block not to slip, the required static friction must be less than or equal to the maximum possible static friction (μmg):
f_s ≤ μmg
mF / (M + m) ≤ μmg
F ≤ μ (M + m)g
Using the values implied in the solution:
F ≤ 21 N
New answer posted
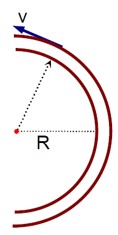
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
N = mg - F_L
f_s = mv²/R ≤ μsN = μs (mg - F_L)
F_L = m (v²/μsR - g)
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Mg + MkV² = MA = -mv (dV/dx)
Vdv = (−) (g + kV²)dx
∫? (Vdv)/ (g + kv²) = ∫? - dx
[ln (g + kV²)/2k]? = -x
ln (g/ (g + ku²) = −2kx
x = (1/2k)ln (1 + ku²/g)
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers