Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Get insights from 95 questions on Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoNew answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
Bernoulli's principle states that in a steady flow, the sum of pressure, kinetic energy per unit volume, and potential energy per unit volume remains constant.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
Yes, the Mechanical properties of fluids class 11th physics is important in NEET. On average, 1-2 questions would be asked from this chapter, which you can cover from the Class 11th Mechanical Properties of Fluids notes.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 9
The main mechanical properties of fluids are exerting pressure, resisting flow or viscosity, forming surface tension, following Bernoulli's principle, and moving in a streamline.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Since the water removed from the pond will be equal to the water displacement by the (man + boat) system, the level of water in the pond remains the same.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 9
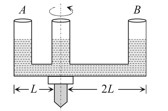
Water level in both section A and B will be goes up due being of centrifugal force water will goes away and it acquire the force from upside so the water will does up so water level in both the section A and B goes up.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers