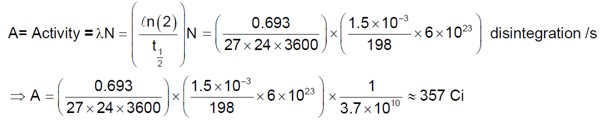Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Get insights from 95 questions on Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Mechanical Properties of Fluids
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
As we know that Reynolds's number R = ρvD/η
In First case: v? = (0.18*10? ³)/ (π (0.5*10? ²)²*60) = 0.03822 m/s
R = (10³ * 0.03822 * 0.01)/10? ³ = 382.2 < 2000 (Laminar/Steady)
In Second case: v? = (0.48*10? ³)/ (π (0.5*10? ²)²*60) = 0.10191 m/s
R? = (10³ * 0.10191 * 0.01)/10? ³ = 1019.1 < 2000 (Laminar/Steady)
The provided solution has a different calculation for R, leading to a different conclusion.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
Range R = v*t = √ (2gh) * √ (2 (H-h)/g) = 2√ (h (H-h).
For R to be max, dR/dh = 0.
h (H-h) must be max. d/dh (Hh-h²)=H-2h=0.
h=H/2 = 12/2=6m.
New answer posted
5 months agoContributor-Level 10
At terminal speed
Mg = Fv = 6πηRv
⇒ V = mg / 6πηR
V = (4/3)πR³ρg / 6πηR
⇒ V = (2/9) * (ρR²g/η)
= (2/9) * (1000 * (0.2 * 10? ³)² * 10) / (1.8 * 10? )
= 4.94 m/s
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
v = √2gh velocity of efflux.
F = v ( dm/dt ) = v (aρv) = aρv² = 2aρgh
fr = µR = µAhρg
For just sliding, for = F
µAhρg = 2aρgh
or µ = 2a/A
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Pressure outside is 0.
Here, Pin = 4T/r
By, P? V? + P? V? = PV (isothermal process, Boyle's law applied to the mass of gas inside)
(4T/r? ) (4/3 πr? ³) + (4T/r? ) (4/3 πr? ³) = (4T/r) (4/3 πr³)
r? ² + r? ² = r²
r = √r? ² + r? ²
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Ratio of masses on two pistons of the hydraulic lift equals to that of their cross- section area.
Now,
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
From volume conservation
Decrease in surface area =
Energy released (W) =
Heat produced (Q) =
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Thermal stress is developed on heating when expansion of rod is hindered.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Thermal strain Longitudinal strain
Longitudinal strain,
Compressive stress Young's Modulus
Compressive force
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers