Physics Motion in Straight Line
Get insights from 62 questions on Physics Motion in Straight Line, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics Motion in Straight Line
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
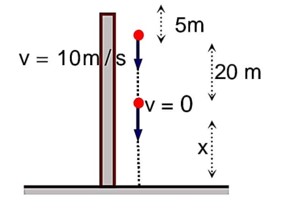
When second stone is released
Equation for first ball:
Equation for second ball :
Using these two equation
20 = 10t t = 2 sec
H = 20 + 20 + 5 = 45 m.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
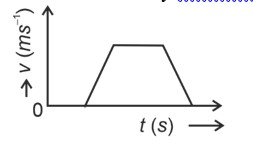
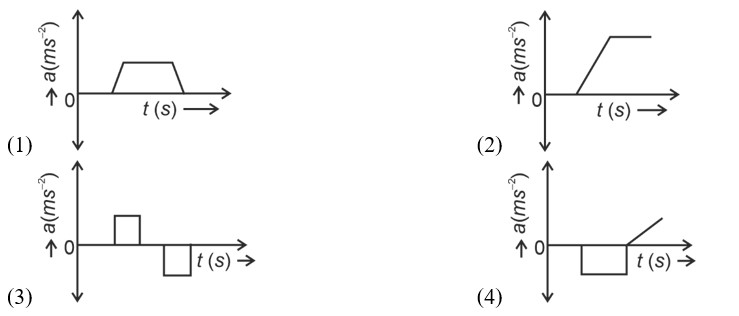
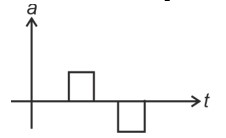
Initially, the body has zero velocity and zero slope. Hence the acceleration would be zero initially.
After that, the slope of v-t curve is constant and positive.
After some time, velocity becomes constant and acceleration is zero.
After that, the slope of v-t curve is constant and negative.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Air resistance resists the motion of an object. In this case, the net acceleration is lesser than 'g' and it shrinks as the speed increases. This makes the object to speed up more slowly. Ultimately, it reaches a constant terminal velocity which is lower for large-area ones and higher for heavy and streamlined ones.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Suppose the position-time graph is a straight line, in this case, the velocity is constant. This means that there is no acceleration.
If the graph is curved, velocity is changing, which means that there is acceleration. If the graph is concave, the slopes will get more positive with time. This means that there is positive acceleration. If the graph is cap-shaped, the slope will become more negative with time. This is known as negative acceleration.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
To graph motion in a straight line, you need to visualise the relationship between different kinematic quantities like position, velocity and time. Suppose an object moves with a constant velocity, the position-time graph will be a straight line with constant slope. If the object accelerates, the slope of position-time graph will change with time and result in a curved line.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Sign conventions are important because all kinematic variables can be positive or negative. You must first choose your coordinate system and positive direction, then consistently apply signs. For example, if you are choosing upward as positive in free-fall problems, gravity becomes negative (a = -g), upward initial velocity is positive, and downward displacement is negative. The equations of motion work for any situation, as long as you substitute values with proper signs. Incorrect conventions lead to wrong answers.
New question posted
6 months agoNew answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
It's not always true. Direction of velocity is the most important consideration here that will tell us whether acceleration increases or decreases speed. You can consider two scenarios. If you're falling, that's negative velocity. That implies negative gravitational acceleration. Here, your speed increases. If you're moving upward, that's positive velocity. Now, with that same negative acceleration, your speed decreases. For choosing the equations of motion, you need to know both the signs of acceleration and velocity to determine if you're speeding up or slowing down.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Zero velocity doesn't mean zero acceleration. When you throw a ball-like object upward, at its peak the velocity is zero. But acceleration remains constant due to gravity. The velocity is still changing from positive to negative at that instant. That means acceleration continues.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
Let the distance travelled is x, so
speed of escalator for ground
speed of boy concerning the escalator
speed of boy concerning ground
The time taken by him to walk up the moving escalator = t =
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 686k Reviews
- 1800k Answers