Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Fifteen
Get insights from 80 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Fifteen, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Fifteen
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Thermal stress is developed on heating when expansion of rod is hindered.
New answer posted
4 months agoContributor-Level 10
Zero error = +0.08 mm.
Diameter = 1 + 72 * 0.01 – 0.08 = 1.64 mm
Radius = 0.82 mm
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, d, e) a) clearly every particle at x will have amplitude =asinkx=fixed
b) for mean position =0
coswt=0
wt= (2n-1)
hence for a fixed of n all particles are having same value of time t= (2n-1)
c) amplitude of all the particles are asinkx which is different for different particles at different values of x
d) the energy is a stationary wave is confined between two nodes.
e) particles at different nodes are always at rest.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b) vo=400Hz, v=340m/s
Vm=10m/s
(a) as both source and observer are stationary, hence frequency observed will be same as natural frequency vo=400Hz
(b) the speed of sound v=v+vw= 340+10=350m/s
(c) there will be on effect on frequency because there is no relative motion between source and observer hence c, d are incorrect.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a, b, d) As we know by y (x, t) = 0.06 sin (2πx/3) cos (120πt)
By comparing the equation with general equation N denotes nodes and A denotes antinodes.
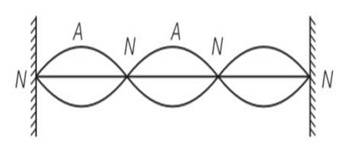
(a) Clearly frequency is common for all the points
(b) Consider all the particles between two nodes they are having same phase at given time
(c) But are having different amplitude of 0.06sin (2 ) and because of different amplitudes they are having different energies.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
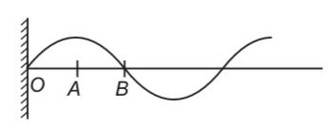
during propagation of a plane progressive mechanical wave
(i) clearly the particles O, A and B are having different phase.
(ii) Particles of the wave are having up and SHM.
(iii) For a progressive wave propagating in a fluid
V= , V=
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c, d) Speed of sound waves in a fluid is given by
V=
V= V so when we increase velocity bulk modulus also increases.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(b, c) y (x, t) = 0.06 sin (2πx/3) cos (120πt)
(a) y (x, t)=asinkxcoswt
(b) w=120 , f=60hz
(c) k=2 , v =60 (3)=180m/s
(d) since in stationary wave all particles of the medium executes SHM with varying amplitude nodes.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers