Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Nine
Get insights from 28 questions on Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Nine, answered by students, alumni, and experts. You may also ask and answer any question you like about Physics NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 11th Chapter Nine
Follow Ask QuestionQuestions
Discussions
Active Users
Followers
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (d) for steel wire Ysteel= stress/strain=
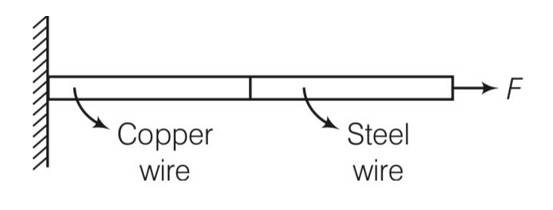
When F and A are same for both the wires . hence stress will be same for both the wire
(Strain)steel= stress/Ysteel and straincopper=stress/Ycopper
Ysteel Ycopper
hence they both have different starin
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (d) An ideal liquid is not compressible
Hence V=0
Bulk modulus B= strss /volumetric strain=
Compressibility K= 1/B=1/
As there is no tangential force exists. So shear strain =0
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
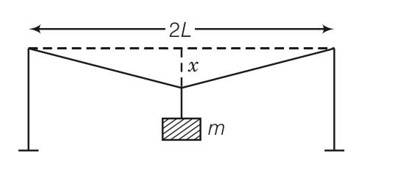
(b), (d) Let mass m is placed at x from the end B respectively.
TA and TB be the tensions in wire A and wire B respectively.
For the rotational equilibrium of the system,
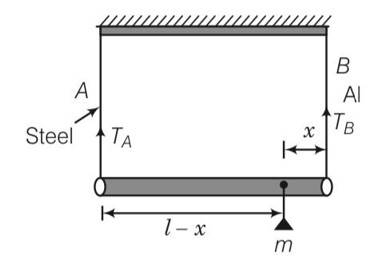
TBx-TA(l-x)=0
=
Stress in wire A = SA=
Stress in wire B = SB= where a are the area of wire
We know that aB=2aA
Now for equal stress
SA=SB
So
So x =l/3 and l-x= 2l/3
Hence mass m should placed to B.
For equal strain
StrainA= StrainB
After solving we get x= x= 10l/17
l-x=l=10l/17=7l/17
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(a), (d) Forces at cross section is F.
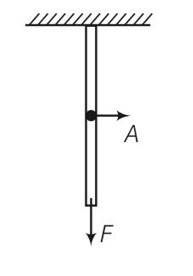
Now applying formula . stress = tension/area=F/A
Tension = applied force =F
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
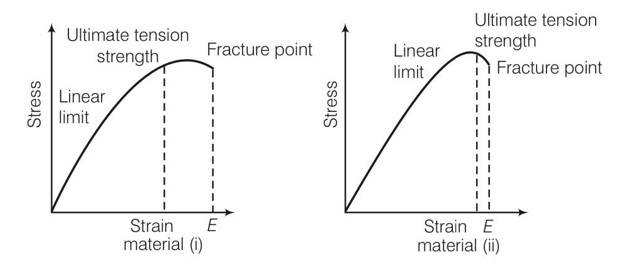
(c), (d) The ultimate tensile strength for material ii is greater hence material ii is elastic over larger region as compared to material (i) for material (ii) fracture point is nearer, hence it is more brittle.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
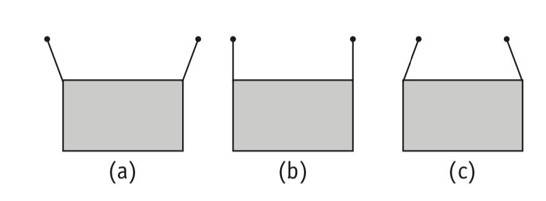
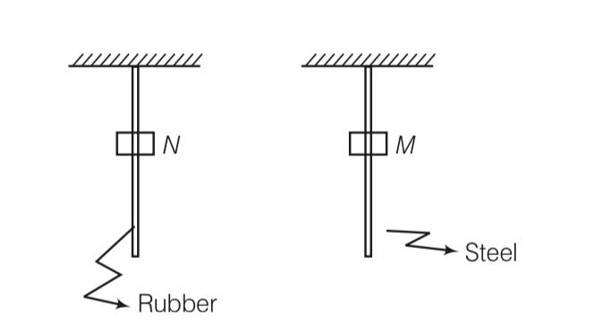
(d) a mass M is attached at the centre. As the mass is attached to both the rods, both rod will be elongated, but due to different elastic properties of material rubber changes shape also.
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
(c) 2Tsin -mg=0
2Tsin =mg
Total horizontal forces = Tcos
T=mg/2sin
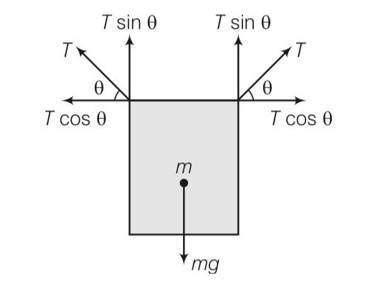
As mg is constant T
Tmax= mg/sin min
Sin min=0, min= 0
Tmin=mg/2sin max
max= 1, =900
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
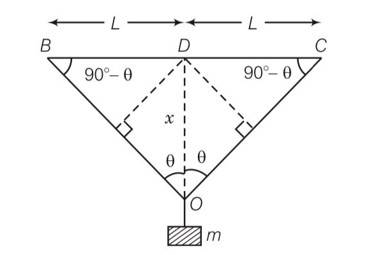
BO+OC- (BD+DC)
= 2BO -2BD
= 2 (BO-BD)
=2 [ (x2+L2)1/2-L]
=2L [ (1+ )1/2-L]
= 2L [ (1+ ]=
Strain =
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
Y=
D2=
D=
New answer posted
6 months agoContributor-Level 10
This is a multiple choice answer as classified in NCERT Exemplar
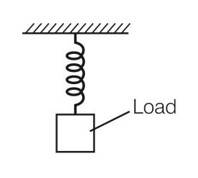
(c) Consider the diagram where a spring is stretched by applying a load to its free end. Clearly the length and shape of the spring changes. The change in length corresponds to longitudinal strain and change in shape corresponds to shearing strain.
Taking an Exam? Selecting a College?
Get authentic answers from experts, students and alumni that you won't find anywhere else
Sign Up on ShikshaOn Shiksha, get access to
- 66k Colleges
- 1.2k Exams
- 681k Reviews
- 1800k Answers